(→14 nm Microprocessors) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{lithography processes}} | {{lithography processes}} | ||
| − | The '''14 nm lithography process''' is a [[technology node#half node|half-node]] semiconductor manufacturing process used as a stopgap between the [[16 nm lithography process|16 nm]] and [[10 nm lithography process|10 nm]] processes. Commercial [[integrated circuit]] manufacturing using 14 nm process began in 2014. This technology is set to be replaced with [[10 nm lithography process|10 nm process]] in | + | The '''14 nm lithography process''' is a [[technology node#half node|half-node]] semiconductor manufacturing process used as a stopgap between the [[16 nm lithography process|16 nm]] and [[10 nm lithography process|10 nm]] processes. As is the case with all recent process nodes, while the term "14 nm" is used by a number of companies, the exact feature sizes various wildly from one manufacturer to another. Commercial [[integrated circuit]] manufacturing using 14 nm process began in 2014. This technology is set to be replaced with [[10 nm lithography process|10 nm process]] in 2017. |
| + | |||
| + | == Industry == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Intel === | ||
| + | Intel continues with its 2nd generation trigate transistors. A change from [[22 nm]] in Intel's process is that the fins have been significantly modified. They are now much more vertical and slimmer, down to 8 nm width. Low-k dielectrics is used in the first eight levels. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || Measurement || Scaling from [[22 nm]] || rowspan="5" | [[File:intel 14nm gate.png|215px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fin Pitch || 42 nm || 0.70x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Contacted Gate Pitch || 70 nm || 0.78x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Interconnect Pitch (M1P) || 52 nm || 0.65x | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[SRAM]] bit cell || 0.0588 µm<sup>2</sup> || 0.54x | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Global Foundries / Samsung === | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || Measurement || Notes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Fin Pitch || 48 nm || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Contacted Gate Pitch || 78 nm || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Interconnect Pitch (M1P) || 64 nm || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[SRAM]] bit cell || 0.08 µm<sup>2</sup> || High Performance | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[SRAM]] bit cell || 0.064 µm<sup>2</sup> || High Density | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{clear|left}} | ||
== 14 nm Microprocessors== | == 14 nm Microprocessors== | ||
* Intel | * Intel | ||
| Line 20: | Line 55: | ||
** {{intel|Goldmont}} | ** {{intel|Goldmont}} | ||
** {{intel|Broadwell}} | ** {{intel|Broadwell}} | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Skylake}} | ||
{{expand list}} | {{expand list}} | ||
[[Category:Lithography]] | [[Category:Lithography]] | ||
Revision as of 18:34, 23 April 2016
The 14 nm lithography process is a half-node semiconductor manufacturing process used as a stopgap between the 16 nm and 10 nm processes. As is the case with all recent process nodes, while the term "14 nm" is used by a number of companies, the exact feature sizes various wildly from one manufacturer to another. Commercial integrated circuit manufacturing using 14 nm process began in 2014. This technology is set to be replaced with 10 nm process in 2017.
Contents
Industry
Intel
Intel continues with its 2nd generation trigate transistors. A change from 22 nm in Intel's process is that the fins have been significantly modified. They are now much more vertical and slimmer, down to 8 nm width. Low-k dielectrics is used in the first eight levels.
| Measurement | Scaling from 22 nm | 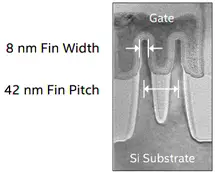
| |
| Fin Pitch | 42 nm | 0.70x | |
| Contacted Gate Pitch | 70 nm | 0.78x | |
| Interconnect Pitch (M1P) | 52 nm | 0.65x | |
| SRAM bit cell | 0.0588 µm2 | 0.54x |
Global Foundries / Samsung
| Measurement | Notes | |
| Fin Pitch | 48 nm | |
| Contacted Gate Pitch | 78 nm | |
| Interconnect Pitch (M1P) | 64 nm | |
| SRAM bit cell | 0.08 µm2 | High Performance |
| SRAM bit cell | 0.064 µm2 | High Density |
14 nm Microprocessors
- Intel
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
14 nm System on Chips
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
14 nm Microarchitectures
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
 Semiconductor lithography processes technology
Semiconductor lithography processes technology