From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "16 nm lithography process"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|Transistor | |Transistor | ||
|Wafer | |Wafer | ||
| + | |Voltage | ||
| | | | ||
|Fin Pitch | |Fin Pitch | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
|- style="text-align: center;" | |- style="text-align: center;" | ||
| colspan="2" | 300 mm | | colspan="2" | 300 mm | ||
| + | |- style="text-align: center;" | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | 0.75 V | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Value !! [[20 nm]] Δ | ! Value !! [[20 nm]] Δ | ||
Revision as of 07:55, 5 April 2017
The 16 nanometer (16 nm) lithography process is a full node semiconductor manufacturing process following the 20 nm process stopgap. Commercial integrated circuit manufacturing using 16 nm process began in 2014. The term "16 nm" is simply a commercial name for a generation of a certain size and its technology, as opposed to gate length or half pitch. This technology is set to be replaced with 10 nm process in 2017.
Industry
| Fab |
|---|
| 1st Production |
| Transistor |
| Wafer |
| Voltage |
| |
| Fin Pitch |
| Fin Width |
| Fin Height |
| Gate Length |
| Contacted Gate Pitch |
| Interconnect Pitch (M1P) |
| SRAM bit cell |
| TSMC | |
|---|---|
| 2015 | |
| FinFET | |
| 300 mm | |
| 0.75 V | |
| Value | 20 nm Δ |
| 48 nm | N/A |
| ? nm | |
| 37 nm | |
| 34 nm | |
| 90 nm | 1x |
| 64 nm | 1x |
| 0.074 µm² | 0.86x |
TSMC
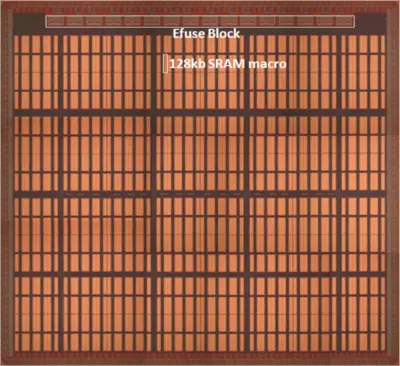
TSMC demonstrated their 128 Mebibit SRAM wafer from their 16 nm HKMG FinFET process at the 2014 IEEE ISSCC.
16 nm Microprocessors
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
16 nm Microarchitectures
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
References
- Chen, Yen-Huei, et al. "A 16 nm 128 Mb SRAM in High-κ Metal-Gate FinFET Technology With Write-Assist Circuitry for Low-VMIN Applications." IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 50.1 (2015): 170-177.
- Wu, Shien-Yang, et al. "A 16nm FinFET CMOS technology for mobile SoC and computing applications." Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 2013 IEEE International. IEEE, 2013.
- TechInsights/Chipworks, Kevin Gibb, The ConFab 2016
 Semiconductor lithography processes technology
Semiconductor lithography processes technology