(→Industry) |
(→Industry) |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{lithography processes}} | {{lithography processes}} | ||
| − | The '''22 nm lithography process''' is a [[technology node|full node]] semiconductor manufacturing process following the [[28 nm lithography process|28 nm process]] stopgap. Commercial [[integrated circuit]] manufacturing using 22 nm process began in 2008 for memory and 2012 for [[MPU]]s. This technology was replaced by with [[20 nm lithography process|20 nm process]] (HN) in 2014 and [[16 nm lithography process|16 nm process]] (FN) in late 2015. | + | The '''22 nanometer (22 nm) lithography process''' is a [[technology node|full node]] semiconductor manufacturing process following the [[28 nm lithography process|28 nm process]] stopgap. The term "22 nm" is simply a commercial name for a generation of a certain size and its technology, as opposed to gate length or half pitch. Commercial [[integrated circuit]] manufacturing using 22 nm process began in 2008 for memory and 2012 for [[MPU]]s. This technology was replaced by with [[20 nm lithography process|20 nm process]] (HN) in 2014 and [[16 nm lithography process|16 nm process]] (FN) in late 2015. |
== Industry == | == Industry == | ||
| − | The 22 nm became Intel's first generation of Tri-gate [[FinFET]] transistors and the first such transistor on the market. This process became 3rd generation high-k + metal gate transistors for Intel. | + | The 22 nm became Intel's first generation of Tri-gate [[FinFET]] transistors and the first such transistor on the market. This process became 3rd generation high-k + metal gate transistors for Intel. In 2017 Intel announce the introduction of a new process "22FFL" specifically for low power IOT and mobile products for their custom foundry. |
| − | {{ | + | |
| − | | | + | {{finfet nodes comp |
| − | | | + | <!-- Intel --> |
| − | | | + | | process 1 fab = [[Intel]] |
| − | | | + | | process 1 name = P1270 (CPU) / P1271 (SoC) |
| − | | | + | | process 1 date = 2011 |
| − | | | + | | process 1 lith = 193 nm |
| − | | | + | | process 1 immersion = Yes |
| − | | | + | | process 1 exposure = [[SADP]] |
| + | | process 1 wafer type = Bulk | ||
| + | | process 1 wafer size = 300 mm | ||
| + | | process 1 transistor = FinFET | ||
| + | | process 1 volt = 0.75 V | ||
| + | | process 1 delta from = [[32 nm]] Δ | ||
| + | | process 1 fin pitch = 60 nm | ||
| + | | process 1 fin pitch Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 1 fin width = 8 nm | ||
| + | | process 1 fin width Δ = | ||
| + | | process 1 fin height = 34 nm | ||
| + | | process 1 fin height Δ = | ||
| + | | process 1 gate len = 26 nm | ||
| + | | process 1 gate len Δ = | ||
| + | | process 1 cpp = 90 nm | ||
| + | | process 1 cpp Δ = 0.80x | ||
| + | | process 1 mmp = 80 nm | ||
| + | | process 1 mmp Δ = 0.71x | ||
| + | | process 1 sram hp = 0.130 µm² | ||
| + | | process 1 sram hp Δ = 0.65x | ||
| + | | process 1 sram hd = 0.092 µm² | ||
| + | | process 1 sram hd Δ = 0.62x | ||
| + | | process 1 sram lv = 0.108 µm² | ||
| + | | process 1 sram lv Δ = 0.63x | ||
| + | | process 1 dram = 0.029 µm² | ||
| + | | process 1 dram Δ = | ||
| + | <!-- Intel 22FFL --> | ||
| + | | process 2 fab = [[Intel]] | ||
| + | | process 2 name = 22FFL (P1222) | ||
| + | | process 2 date = 2017 | ||
| + | | process 2 lith = 193 nm | ||
| + | | process 2 immersion = Yes | ||
| + | | process 2 exposure = [[SADP]] | ||
| + | | process 2 wafer type = Bulk | ||
| + | | process 2 wafer size = 300 mm | ||
| + | | process 2 transistor = FinFET | ||
| + | | process 2 volt = 0.7 V | ||
| + | | process 2 delta from = [[32 nm]] Δ | ||
| + | | process 2 fin pitch = 45 nm | ||
| + | | process 2 fin pitch Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 2 fin width = | ||
| + | | process 2 fin width Δ = | ||
| + | | process 2 fin height = | ||
| + | | process 2 fin height Δ = | ||
| + | | process 2 gate len = 30 nm | ||
| + | | process 2 gate len Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 2 cpp = 108 nm | ||
| + | | process 2 cpp Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 2 mmp = 90 nm | ||
| + | | process 2 mmp Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 2 sram hp = | ||
| + | | process 2 sram hp Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 2 sram hd = 0.088 µm² | ||
| + | | process 2 sram hd Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 2 sram lv = | ||
| + | | process 2 sram lv Δ = - | ||
| + | | process 2 dram = | ||
| + | | process 2 dram Δ = - | ||
| + | <!-- Samsung --> | ||
| + | | process 3 fab = [[IBM]] | ||
| + | | process 3 name = 22HP | ||
| + | | process 3 date = 2013 | ||
| + | | process 3 lith = 193 | ||
| + | | process 3 immersion = Yes | ||
| + | | process 3 exposure = | ||
| + | | process 3 wafer type = SOI | ||
| + | | process 3 wafer size = 300 mm | ||
| + | | process 3 transistor = Planar | ||
| + | | process 3 volt = 0.75 V | ||
| + | | process 3 delta from = [[32 nm]] Δ | ||
| + | | process 3 fin pitch = - | ||
| + | | process 3 fin pitch Δ = | ||
| + | | process 3 fin width = | ||
| + | | process 3 fin width Δ = | ||
| + | | process 3 fin height = | ||
| + | | process 3 fin height Δ = | ||
| + | | process 3 gate len = 25-33 nm | ||
| + | | process 3 gate len Δ = 0.83-1.1x | ||
| + | | process 3 cpp = 100 nm | ||
| + | | process 3 cpp Δ = 0.79x | ||
| + | | process 3 mmp = 80 nm | ||
| + | | process 3 mmp Δ = 0.80x | ||
| + | | process 3 sram hp = 0.144 µm² | ||
| + | | process 3 sram hp Δ = | ||
| + | | process 3 sram hd = 0.128 µm² | ||
| + | | process 3 sram hd Δ = 0.86x | ||
| + | | process 3 sram lv = | ||
| + | | process 3 sram lv Δ = | ||
| + | | process 3 dram = 0.026 µm² | ||
| + | | process 3 dram Δ = 0.67x | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | === Intel === | |
| − | + | [[File:intel 22nm tri-gate transistors.png|650px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! colspan=" | + | ! colspan="7" | Intel 22nm SoC Interconnect Design Rules |
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! Layer !! Pitch !! Process !! Dielectric Materials !! [[CPU]] !! [[SoC]] | + | ! Layer !! Pitch !! Process !! Dielectric Materials !! [[CPU]] !! [[SoC]] || Image |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Fin || 60 nm || - || - || Fin || Fin | + | | Fin || 60 nm || - || - || Fin || Fin || rowspan="9" | [[File:intel 22nm rules.png]] |
|- | |- | ||
| Contact || 90 nm || SAC || - || Contact || Contact | | Contact || 90 nm || SAC || - || Contact || Contact | ||
| Line 60: | Line 131: | ||
| MT - TOP || 14 µm || Plate Up || Polymer || M9 || Top Metal | | MT - TOP || 14 µm || Plate Up || Polymer || M9 || Top Metal | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! colspan="7" | Intel 22nm SoC Transistor Characteristics | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Transistor Type !! colspan="2" | High Speed Logic !! colspan="2" | Low Power Logic !! colspan="2" | High Voltage Logic | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Options || High Performance (HP) || Standard Perf/Power (SP) || Low Power (LP) || Ultra-Low Power (ULP) || 1.8 V || 3.3 V | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | V<sub>dd</sub> (V) || 0.7 V / 1 V || 0.75 V / 1 V || 0.75 V / 1 V || 0.75 V / 1.2 V || 1.5 V / 1.8 V / 3.3 V || 3.3 V / >5V | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gate Pitch (nm) || 90 || 90 || 90 || 108 || min. 180 || min 450 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | L<sub>gate</sub> (nm) || 30 || 34 || 34 || 40 || min. 80 || in 280 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | N/PMOS Idsat/Ioff (mA/µm) || 1.08/0.91 @ 0.75 V, 100 nA/µm || 0.71/0.59 @0.75 V, 1 nA/µm || 0.41/0.37 @ 0.75 V, 30 pA/µm || 0.35/0.33 @ 0.75 V, 15 pA/µm || 0.92/0.8 @ 1.8 V, 10 pA/µm || 1/0.8 @ 3.3 V, 10 pA/µm | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Find models == | ||
| + | {{#ask: | ||
| + | [[instance of::microprocessor]] | ||
| + | [[process::22 nm]] | ||
| + | | ?full page name | ||
| + | | ?name | ||
| + | | ?microprocessor family | ||
| + | | ?microarchitecture | ||
| + | | ?process | ||
| + | | ?designer | ||
| + | | ?manufacturer | ||
| + | | ?first launched | ||
| + | | ?base frequency | ||
| + | | format=template|link=all|sort=name|order=asc|headers=hide|mainlabel=-|intro=<table class="wikitable"><tr><th colspan="8">[[22 nm]] Microprocessors</th></tr><tr><th colspan="3">Model</th><th colspan="5">Specs</th></tr><tr><th>Model</th><th>Family</th><th>µarch</th><th>Process</th><th>Designer</th><th>Manufacturer</th><th>Intro</th><th>Freq</th></tr>|outro=</table>|limit=0|searchlabel=Click to browse all 22 nm MPU models|sep=,|template=proc table 1|userparam=9 | ||
| + | }} | ||
== 22 nm Microprocessors== | == 22 nm Microprocessors== | ||
* Intel | * Intel | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Core i3}} | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Core i5}} | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Core i7}} | ||
** {{intel|Core i7EE}} | ** {{intel|Core i7EE}} | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Xeon}} | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Xeon E3}} | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Xeon E5}} | ||
| + | ** {{intel|Xeon E7}} | ||
| + | {{expand list}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | == 22 nm | + | {{#ask: |
| − | + | [[instance of::microprocessor]] | |
| + | [[process::22 nm]] | ||
| + | | ?name | ||
| + | | ?process | ||
| + | | ?manufacturer | ||
| + | | ?microprocessor family | ||
| + | | format=broadtable | ||
| + | | limit=0 | ||
| + | | sep=, | ||
| + | | searchlabel=Click to browse all 22 nm MPU models | ||
| + | }} | ||
== 22 nm Microarchitectures== | == 22 nm Microarchitectures== | ||
| − | * Intel | + | * Intel |
| − | ** {{intel|Haswell}} | + | ** {{intel|Haswell|l=arch}} |
| − | ** {{intel|Ivy Bridge}} | + | ** {{intel|Ivy Bridge|l=arch}} |
| − | ** {{intel|Silvermont}} | + | ** {{intel|Silvermont|l=arch}} |
| + | * IBM | ||
| + | ** {{ibm|POWER8|l=arch}} | ||
| + | ** {{ibm|z13|l=arch}} | ||
| + | {{expand list}} | ||
| − | + | == Documents == | |
| + | * [[:File:22FFL-2017.pdf|Intel's 22FFL technology]] | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | * IEDM 2012 | ||
| + | * IEDM 2014 | ||
| + | * ISSCC 2015 | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[category:lithography]] |
Latest revision as of 09:52, 25 November 2020
The 22 nanometer (22 nm) lithography process is a full node semiconductor manufacturing process following the 28 nm process stopgap. The term "22 nm" is simply a commercial name for a generation of a certain size and its technology, as opposed to gate length or half pitch. Commercial integrated circuit manufacturing using 22 nm process began in 2008 for memory and 2012 for MPUs. This technology was replaced by with 20 nm process (HN) in 2014 and 16 nm process (FN) in late 2015.
Contents
Industry[edit]
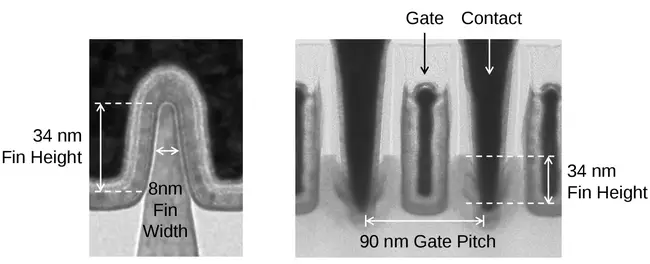
The 22 nm became Intel's first generation of Tri-gate FinFET transistors and the first such transistor on the market. This process became 3rd generation high-k + metal gate transistors for Intel. In 2017 Intel announce the introduction of a new process "22FFL" specifically for low power IOT and mobile products for their custom foundry.
| Process Name | |
|---|---|
| 1st Production | |
| Litho- graphy |
Lithography |
| Immersion | |
| Exposure | |
| Wafer | Type |
| Size | |
| Tran- sistor |
Type |
| Voltage | |
| Fin | Pitch |
| Width | |
| Height | |
| Gate Length (Lg) | |
| Contacted Gate Pitch (CPP) | |
| Minimum Metal Pitch (MMP) | |
| SRAM bitcell |
High-Perf (HP) |
| High-Density (HD) | |
| Low-Voltage (LV) | |
| DRAM bitcell |
eDRAM |
| Intel | Intel | IBM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1270 (CPU) / P1271 (SoC) | 22FFL (P1222) | 22HP | |||
| 2011 | 2017 | 2013 | |||
| 193 nm | 193 nm | 193 | |||
| Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| SADP | SADP | ||||
| Bulk | Bulk | SOI | |||
| 300 mm | 300 mm | 300 mm | |||
| FinFET | FinFET | Planar | |||
| 0.75 V | 0.7 V | 0.75 V | |||
| Value | 32 nm Δ | Value | 32 nm Δ | Value | 32 nm Δ |
| 60 nm | N/A | 45 nm | N/A | N/A | |
| 8 nm | |||||
| 34 nm | |||||
| 26 nm | 30 nm | 25-33 nm | 0.83-1.1x | ||
| 90 nm | 0.80x | 108 nm | 100 nm | 0.79x | |
| 80 nm | 0.71x | 90 nm | 80 nm | 0.80x | |
| 0.130 µm² | 0.65x | 0.144 µm² | |||
| 0.092 µm² | 0.62x | 0.088 µm² | 0.128 µm² | 0.86x | |
| 0.108 µm² | 0.63x | ||||
| 0.029 µm² | 0.026 µm² | 0.67x | |||
Intel[edit]
| Intel 22nm SoC Interconnect Design Rules | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | Pitch | Process | Dielectric Materials | CPU | SoC | Image |
| Fin | 60 nm | - | - | Fin | Fin | 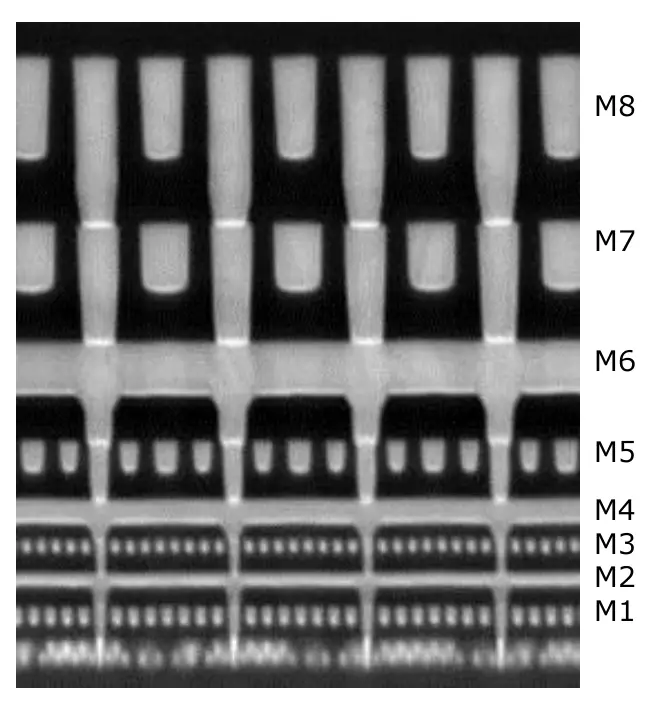
|
| Contact | 90 nm | SAC | - | Contact | Contact | |
| M1 | 90 nm | SAV | ULK CDO | M1 | M1 | |
| MT - 1x | 80 nm | SAV | ULK CDO | M2/M3 | 2-6 layers | |
| MT - 1.4x | 112 nm | SAV | ULK CDO | M4 | Semi-global | |
| MT - 2x | 160 nm | SAV | ULK CDO | M5 | Semi-global | |
| MT - 3x | 240 nm | SAV | ULK CDO | M6 | Global Routing | |
| MT - 4x | 320 nm 360 nm |
Via First | LK CDO | M7/M8 | Global Routing | |
| MT - TOP | 14 µm | Plate Up | Polymer | M9 | Top Metal | |
| Intel 22nm SoC Transistor Characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transistor Type | High Speed Logic | Low Power Logic | High Voltage Logic | |||
| Options | High Performance (HP) | Standard Perf/Power (SP) | Low Power (LP) | Ultra-Low Power (ULP) | 1.8 V | 3.3 V |
| Vdd (V) | 0.7 V / 1 V | 0.75 V / 1 V | 0.75 V / 1 V | 0.75 V / 1.2 V | 1.5 V / 1.8 V / 3.3 V | 3.3 V / >5V |
| Gate Pitch (nm) | 90 | 90 | 90 | 108 | min. 180 | min 450 |
| Lgate (nm) | 30 | 34 | 34 | 40 | min. 80 | in 280 |
| N/PMOS Idsat/Ioff (mA/µm) | 1.08/0.91 @ 0.75 V, 100 nA/µm | 0.71/0.59 @0.75 V, 1 nA/µm | 0.41/0.37 @ 0.75 V, 30 pA/µm | 0.35/0.33 @ 0.75 V, 15 pA/µm | 0.92/0.8 @ 1.8 V, 10 pA/µm | 1/0.8 @ 3.3 V, 10 pA/µm |
Find models[edit]
Click to browse all 22 nm MPU models
22 nm Microprocessors[edit]
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Click to browse all 22 nm MPU models
22 nm Microarchitectures[edit]
- Intel
- IBM
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Documents[edit]
References[edit]
- IEDM 2012
- IEDM 2014
- ISSCC 2015
 Semiconductor lithography processes technology
Semiconductor lithography processes technology