(→Industry) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| 42 nm || 1.24x || ~38 nm || ~38 nm || ? nm || 25 nm | | 42 nm || 1.24x || ~38 nm || ~38 nm || ? nm || 25 nm | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 20 nm || 0.77x || || || || || || || || | + | | 20 nm || 0.77x || 30 nm || || 30 nm || || || || || |
|- | |- | ||
| 70 nm || 0.78x || 78 nm || 1.22x || 78 nm || 1.22x || ? nm || ?x || 80 nm || 0.80x | | 70 nm || 0.78x || 78 nm || 1.22x || 78 nm || 1.22x || ? nm || ?x || 80 nm || 0.80x | ||
Revision as of 08:48, 4 April 2017
The 14 nanometer (14 nm) lithography process is a half-node semiconductor manufacturing process used as a stopgap between the 16 nm and 10 nm processes. The term "14 nm" is simply a commercial name for a generation of a certain size and its technology, as opposed to gate length or half pitch. Commercial integrated circuit manufacturing using 14 nm process began in 2014. This technology is set to be replaced with 10 nm process in 2017.
Contents
Industry
14 nm became Intel's 2nd generation finFET transistors. This process became Samsungs' and GlobalFoundries first generation of finFet-based transistors. Intel uses TiN pMOS / TiAlN nMOS while Samsung uses TiN pMOS / TiAIC nMOS as work function metals. Intel makes use of Self-Aligned Double Patterning (SADP) with 193 nm immersion lithography at critical patterning layers.
| Fab |
|---|
| Process Name |
| 1st Production |
| Transistor |
| Type |
| Wafer |
| |
| Fin Pitch |
| Fin Width |
| Fin Height |
| Gate Length |
| Contacted Gate Pitch |
| Interconnect Pitch (M1P) |
| SRAM bit cell (HP) |
| SRAM bit cell (HD) |
| DRAM bit cell |
| Intel | Samsung | GlobalFoundries | UMC | IBM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1272 (CPU) / P1273 (SoC) | 14LPE 1st generation; 14 nm Low Power Early , 14LPP2nd generation; 14 nm Low Power Performance , 14LPC3rd generation; 14 nm Low Power Cost [reduced] , 14LPU4th generation; 14 nm Low Power Ultimate |
14LPP 2nd generation; 14 nm Low Power Performance |
|||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | 2015 | 2017 | 2015 | |||||
| FinFET | |||||||||
| Bulk | SOI | ||||||||
| 300mm | |||||||||
| Value | 22 nm Δ | Value | 20 nm Δ | Value | 20 nm Δ | Value | 28 nm Δ | Value | 22 nm Δ |
| 42 nm | 0.70x | 48 nm | N/A | 48 nm | N/A | ? nm | N/A | 42 nm | N/A |
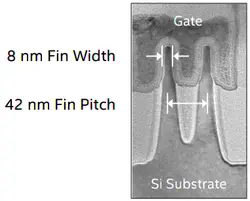
| 8 nm | 1.00x | 8 nm | 8 nm | ? nm | 10 nm | ||||
| 42 nm | 1.24x | ~38 nm | ~38 nm | ? nm | 25 nm | ||||
| 20 nm | 0.77x | 30 nm | 30 nm | ||||||
| 70 nm | 0.78x | 78 nm | 1.22x | 78 nm | 1.22x | ? nm | ?x | 80 nm | 0.80x |
| 52 nm | 0.65x | 64 nm | 1.00x | 64 nm | 1.00x | ? nm | ?x | 64 nm | 0.80x |
| 0.0588 µm² | 0.54x | 0.0806 µm² | ?x | 0.0806 µm² | ?x | ? µm² | ?x | 0.900 µm² | |
| 0.064 µm² | ?x | 0.064 µm² | ?x | ? µm² | ?x | 0.081 µm² | 0.81x | ||
| ? µm² | ?x | 0.0174 µm² | 0.67x | ||||||
Intel
| Intel 14nm Design Rules | ||
|---|---|---|
| Layer | Pitch | Scale Factor |
| Fin | 42 nm | 0.70 |
| Contacted Gate Pitch | 70 nm | 0.78 |
| Metal 0 | 56 | - |
| Metal 1 | 70 | 0.78 |
| Metal 2 | 52 | 0.65 |
Find models
Click to browse all 14 nm MPU models
14 nm Microprocessors
- Intel
- AMD
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
14 nm Microarchitectures
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Documents
References
- Natarajan, S., et al. "A 14nm logic technology featuring 2 nd-generation FinFET, air-gapped interconnects, self-aligned double patterning and a 0.0588 µm 2 SRAM cell size." Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 2014 IEEE International. IEEE, 2014.
- Lin, C. H., et al. "High performance 14nm SOI FinFET CMOS technology with 0.0174 µm 2 embedded DRAM and 15 levels of Cu metallization." Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 2014 IEEE International. IEEE, 2014.
 Semiconductor lithography processes technology
Semiconductor lithography processes technology