From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "qualcomm/msm"
(→Timeline) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
| successor link = | | successor link = | ||
}} | }} | ||
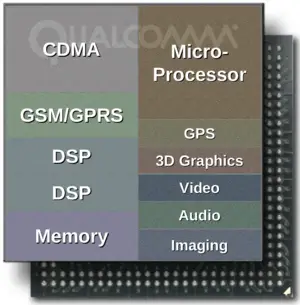
| − | '''MSM''' ('''Mobile Station Modem''') is a series of [[2G]]/[[3G]]-capable [[system on chips]] designed by [[Qualcomm]] since the early 1990s to date. | + | '''MSM''' ('''Mobile Station Modem''') is a series of [[2G]]/[[3G]]/[[4G]]-capable [[system on chips]] designed by [[Qualcomm]] since the early 1990s to date. |
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
<tr><td>{{\\|Snapdragon 800}}</td><td>[[2013]]</td><td>[[28 nm]]-[[10 nm]]</td><td></td></tr> | <tr><td>{{\\|Snapdragon 800}}</td><td>[[2013]]</td><td>[[28 nm]]-[[10 nm]]</td><td></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:52, 2 January 2017
| Qualcomm MSM | |

| |
| Developer | Qualcomm, Intel, ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | IBM, TSMC, Samsung |
| Type | System on chips |
| Introduction | 1993 (announced) 1993 (launch) |
| Production | 1994 |
| Architecture | System on a chip with wireless capabilities |
| ISA | x86-16, ARMv4, ARMv5 |
| µarch | 80186, ARM7TDMI, ARM926EJ-S |
| Word size | 16 bit 2 octets , 32 bit4 nibbles 4 octets ,
8 nibbles |
| Process | 800 nm 0.8 μm , 500 nm8.0e-4 mm 0.5 μm , 350 nm5.0e-4 mm 0.35 μm , 250 nm3.5e-4 mm 0.25 μm , 180 nm2.5e-4 mm 0.18 μm , 130 nm1.8e-4 mm 0.13 μm , 90 nm1.3e-4 mm 0.09 μm , 65 nm9.0e-5 mm 0.065 μm , 45 nm6.5e-5 mm 0.045 μm , 32 nm4.5e-5 mm 0.032 μm , 20 nm3.2e-5 mm 0.02 μm , 14 nm2.0e-5 mm 0.014 μm , 10 nm1.4e-5 mm 0.01 μm
1.0e-5 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 2.1 MHz-3,000 MHz |
MSM (Mobile Station Modem) is a series of 2G/3G/4G-capable system on chips designed by Qualcomm since the early 1990s to date.
Overview[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Timeline[edit]
| 1990 | 1.2 µm | 80186 | First generation (R&D only) | |
| MSM1 | 1993 | 800 nm | 80186 | Second generation |
| MSM2 | 1995 | 500 nm | 80186 | Third generation |
| MSM2300 | 1995 | 80186 | Fourth generation | |
| MSM3000 | 1995 | ARM7TDMI | Fifth generation | |
| MSM3100 | 1998 | ARM7TDMI | Sixth generation | |
| MSM3300 | 2000 | ARM7TDMI | ||
| MSM4500 | N/A | ARM7TDMI | Announced but not released | |
| MSM5000 | 2001 | ARM7TDMI | ||
| MSM5105 | 2002 | ARM7TDMI | ||
| MSM5100 | 2001 | ARM7TDMI | ||
| MSM5200 | 2001 | ARM7TDMI | ||
| MSM5500 | 2001 | ARM7TDMI | ||
| MSM6xxx | 2002 | 250 nm-65 nm | ARM7TDMI / ARM926EJ-S | |
| MSM7xxx | 2004 | 90 nm-65 nm | ||
| Snapdragon S1 | 2007 | 65 nm-45 nm | ||
| Snapdragon S2 | 2010 | 45 nm | ||
| Snapdragon S3 | 2010 | 45 nm | ||
| Snapdragon S4 | 2012 | 45 nm-28 nm | ||
| Snapdragon 200 | 2014 | 45 nm-28 nm | ||
| Snapdragon 400 | 2013 | 28 nm | ||
| Snapdragon 600 | 2013 | 28 nm-14 nm | ||
| Snapdragon 800 | 2013 | 28 nm-10 nm |
| This article is still a stub and needs your attention. You can help improve this article by editing this page and adding the missing information. |
Facts about "MSM (Mobile Station Modem) - Qualcomm"
| designer | Qualcomm +, Intel + and ARM Holdings + |
| first announced | 1993 + |
| first launched | 1993 + |
| full page name | qualcomm/msm + |
| instance of | system on a chip extended family + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-16 +, ARMv4 + and ARMv5 + |
| main designer | Qualcomm + |
| manufacturer | IBM +, TSMC + and Samsung + |
| microarchitecture | 80186 +, ARM7TDMI + and ARM926EJ-S + |
| name | Qualcomm MSM + |
| process | 800 nm (0.8 μm, 8.0e-4 mm) +, 500 nm (0.5 μm, 5.0e-4 mm) +, 350 nm (0.35 μm, 3.5e-4 mm) +, 250 nm (0.25 μm, 2.5e-4 mm) +, 180 nm (0.18 μm, 1.8e-4 mm) +, 130 nm (0.13 μm, 1.3e-4 mm) +, 90 nm (0.09 μm, 9.0e-5 mm) +, 65 nm (0.065 μm, 6.5e-5 mm) +, 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) +, 32 nm (0.032 μm, 3.2e-5 mm) +, 20 nm (0.02 μm, 2.0e-5 mm) +, 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) + and 10 nm (0.01 μm, 1.0e-5 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 16 bit (2 octets, 4 nibbles) + and 32 bit (4 octets, 8 nibbles) + |