(→All ARM2 Chips) |
|||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
== All ARM2 Chips == | == All ARM2 Chips == | ||
| − | {{ | + | <!-- NOTE: |
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: http://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc11 tc12 tc13"> | ||
| + | <tr class="comptable-header"><th> </th><th colspan="12">List of ARM2-based Processors</th></tr> | ||
| + | {{comp table header 1|cols=Process, Launched, Frequency, Power Dissipation, Max Memory}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by acorn computers]] [[instance of::microprocessor]] [[microprocessor family::ARM]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?microarchitecture | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?base frequency#MHz | ||
| + | |?power dissipation | ||
| + | |?max memory#MiB | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=7 | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | |valuesep=, | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by acorn computer]] [[instance of::microprocessor]] [[microprocessor family::arm]] [[microarchitecture::Zen]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* Furber, S. B., and A. R. Wilson. "The Acorn RISC Machine ߞ an architectural view." Electronics and Power 33.6 (1987): 402-405. | * Furber, S. B., and A. R. Wilson. "The Acorn RISC Machine ߞ an architectural view." Electronics and Power 33.6 (1987): 402-405. | ||
Revision as of 18:02, 30 June 2017
| Edit Values | |
| ARM2 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Acorn Computers |
| Manufacturer | VLSI Technology, Sanyo |
| Introduction | 1986 |
| Process | 2 µm |
| Core Configs | 1 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Scalar, Pipelined |
| Stages | 3 |
| Decode | 1-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv2 |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 0 KiB/Core |
| L1D Cache | 0 KiB/Core |
| Succession | |
ARM2 is the second ARM implementation designed by Acorn Computers as a successor to the ARM1. Introduced in 1986, the ARM2 brings a number of major improvements over its predecessor.
Contents
[hide]Overview
- See also: ARM's History
Introduced in 1986, the ARM2 is a reimplementation of the ARM1 on a smaller process along with the addition of a number of additional enhancements. The ARM2 was capable of exceeding 10 MIPS when not bottlenecked by memory with an average of around 6 MIPS. Unlike the ARM1 which was predominantly a research project, the ARM2 became the first commercially successful ARM microprocessor.
The ARM2 was designed to work as an embedded controller or a coprocessor or as a stand-alone microprocessor system. The Acorn Archimedes family of personal computers was built using the ARM2 along with a number of fully custom support chips that were also designed by Acorn Computer.
Process Technology
- See also: 2 µm process
ARM2 chips were manufactured by VLSI Technology and Sanyo on a 2 µm double-level metal CMOS process.
Architecture
Key changes from ARM1
- 2 µm process (from 3 µm)
- > 2x MIPS when not bottlenecked by memory
- 27-entry register file (from 25)
- 2 new program status registers
- Aid Fast Interrupts
- New support for coprocessors
- New support for hardware multiply and accumulate
New instructions
ARM2 introduces a number of new instructions to deal with the new features:
Coprocessor:
-
CDP- Coprocessor data process -
LDC- Load to coprocessor -
STC- Store from coprocessor -
MCR- Move to coprocessor -
MRC- Move from coprocessor
Arithmetics:
-
MUL- Multiplication -
MLA- Multiplication and accumulate
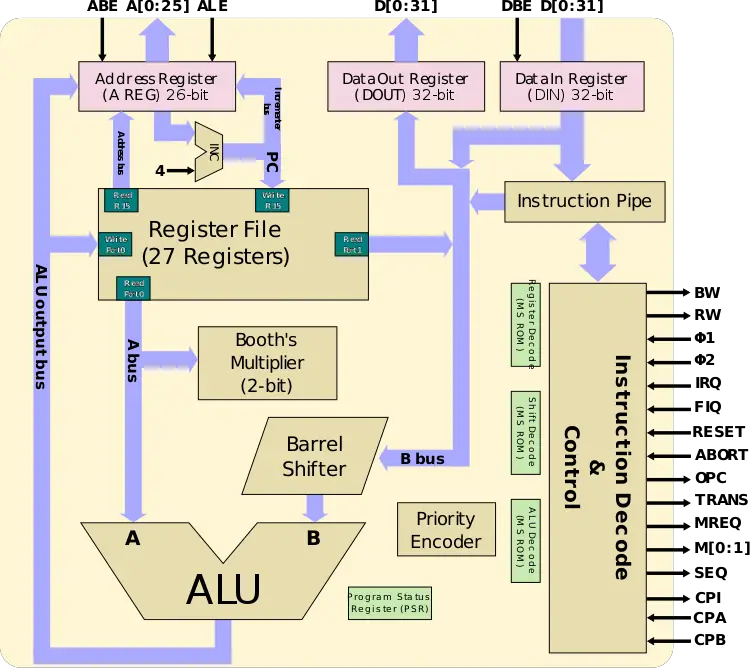
Block Diagram
Core
Core
Pipeline
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Die
- 2 µm process
- 27,000 transistors
- ~5.5 mm x 5.5 mm
- 30.25 mm² die size
All ARM2 Chips
| List of ARM2-based Processors | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Process | Launched | Frequency | Power Dissipation | Max Memory | |||||||
| Count: 0 | ||||||||||||
References
- Furber, S. B., and A. R. Wilson. "The Acorn RISC Machine ߞ an architectural view." Electronics and Power 33.6 (1987): 402-405.
| codename | ARM2 + |
| core count | 1 + |
| designer | Acorn Computers + |
| first launched | 1986 + |
| full page name | acorn/microarchitectures/arm2 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv2 + |
| manufacturer | VLSI Technology + and Sanyo + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | ARM2 + |
| pipeline stages | 3 + |
| process | 2,000 nm (2 μm, 0.002 mm) + |