From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "zhaoxin/microarchitectures/lujiazui"
(→Key changes from {{\\|WuDaoKou}}) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
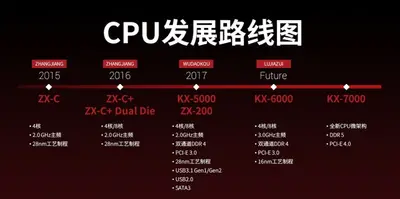
'''LuJiaZui''' is the successor to {{\\|WuDaoKou}}, a [[16 nm]] [[x86]] microarchitecture designed by [[Zhaoxin]] for mainstream laptops, desktops, and servers. | '''LuJiaZui''' is the successor to {{\\|WuDaoKou}}, a [[16 nm]] [[x86]] microarchitecture designed by [[Zhaoxin]] for mainstream laptops, desktops, and servers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Etymology == | ||
| + | As with prior microarchitectures, LuJiaZui is named after the [[wikipedia:Lujiazui station|Lujiazui station]] of the Shanghai Metro. The station is located in the highly prosperous Pudong district of Shanghai. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Brands == | ||
| + | [[File:zhaoxin roadmap (2017).png|right|400px]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Family !! Series !! Description | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{zhaoxin|KaiXian}} || KX (6000) || Desktop, Laptops | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{zhaoxin|Kaisheng}} || KH (30000) || Storage, Servers | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Process Technology == | ||
| + | Lujiazui is manufactured on [[TSMC]]'s [[16 nm|16 nm FinFET process]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Architecture == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Key changes from {{\\|WuDaoKou}} === | ||
| + | * [[16 nm|16 nm FinFET]] (from [[28 nm]]) | ||
| + | * 1.5x performance ([[SPEC CPU2006]] Int) | ||
| + | * Higher clock speed (3 GHz, up from 2 GHz) | ||
| + | * Improved memory controller | ||
| + | ** Support for up to 3200 MT/s (from 2400 MT/s) | ||
| + | ** Higher memory capacity (128 GiB, up from 64 GiB) | ||
| + | * Improved integrated GPU | ||
| + | ** DirectX 11.1 | ||
| + | ** HDMI 2.0 | ||
| + | {{expand list}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == All LuJiaZui Processors == | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc4 tc8"> | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|7:List of LuJiaZui-based Processors}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|7:Main processor}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Family|Launched|Cores|L2|%Frequency|Max Memory|ECC}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by zhaoxin]] [[microarchitecture::LuJiaZui]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?family | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?l2$ size | ||
| + | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?max memory#GiB | ||
| + | |?has ecc memory support | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=9:9 | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by zhaoxin]] [[microarchitecture::LuJiaZui]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:10, 12 December 2019
| Edit Values | |
| LuJiaZui µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Zhaoxin |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | 2019 |
| Process | 16 nm |
| Core Configs | 2, 4, 8 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Succession | |
LuJiaZui is the successor to WuDaoKou, a 16 nm x86 microarchitecture designed by Zhaoxin for mainstream laptops, desktops, and servers.
Contents
Etymology[edit]
As with prior microarchitectures, LuJiaZui is named after the Lujiazui station of the Shanghai Metro. The station is located in the highly prosperous Pudong district of Shanghai.
Brands[edit]
| Family | Series | Description |
|---|---|---|
| KaiXian | KX (6000) | Desktop, Laptops |
| Kaisheng | KH (30000) | Storage, Servers |
Process Technology[edit]
Lujiazui is manufactured on TSMC's 16 nm FinFET process.
Architecture[edit]
Key changes from WuDaoKou[edit]
- 16 nm FinFET (from 28 nm)
- 1.5x performance (SPEC CPU2006 Int)
- Higher clock speed (3 GHz, up from 2 GHz)
- Improved memory controller
- Support for up to 3200 MT/s (from 2400 MT/s)
- Higher memory capacity (128 GiB, up from 64 GiB)
- Improved integrated GPU
- DirectX 11.1
- HDMI 2.0
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
All LuJiaZui Processors[edit]
| List of LuJiaZui-based Processors | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | |||||||
| Model | Family | Launched | Cores | L2 | Frequency | Max Memory | ECC |
| KX-U6880 | KaiXian | 8 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 3 GHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 64 GiB 65,536 MiB 67,108,864 KiB 68,719,476,736 B 0.0625 TiB | ✘ | |
| Count: 1 | |||||||
Facts about "LuJiaZui - Microarchitectures - Zhaoxin"
| codename | LuJiaZui + |
| core count | 2 +, 4 + and 8 + |
| designer | Zhaoxin + |
| first launched | 2019 + |
| full page name | zhaoxin/microarchitectures/lujiazui + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | LuJiaZui + |
| process | 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) + |