(→Overview) |
|||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| type = Microprocessors | | type = Microprocessors | ||
| first announced = April 27, 2000 | | first announced = April 27, 2000 | ||
| − | | first launched = | + | | first launched = June 19, 2000 |
| production start = 2000 | | production start = 2000 | ||
| production end = 2005 | | production end = 2005 | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
| predecessor link = amd/k6-iii | | predecessor link = amd/k6-iii | ||
| successor = Sempron | | successor = Sempron | ||
| − | | successor link = amd/ | + | | successor link = amd/sempron |
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Duron''' was a family of {{arch|32}} [[x86]] microprocessors developed by [[AMD]] and introduced in early 2000. Duron, a low-budget derivative of {{amd|Athlon}} ({{amd|microarchitectures/k7|K7-based}}), was introduced as a way for AMD to aggressively compete against [[Intel]]'s {{intel|Celeron}} in the ultra-cheap PC segment. | + | '''Duron''' was a family of budget {{arch|32}} [[x86]] microprocessors developed by [[AMD]] and introduced in early 2000. Duron, a low-budget derivative of {{amd|Athlon}} ({{amd|microarchitectures/k7|K7-based}}), was introduced as a way for AMD to aggressively compete against [[Intel]]'s {{intel|Celeron}} in the ultra-cheap PC segment. Announced in April of [[2000]], Duron processors offered the best price-performance ratio providing {{intel|Celeron}} with stiff competition. |
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| + | [[File:KL AMD Duron Morgan.jpg|left|250px|link=amd/duron/dhd1300amt1b]] | ||
In April of [[1998]] Intel introduced their {{intel|Celeron}} family of processors - a family specifically designed to target the ultra-cheaper computer segment. Duron (still nameless at the time) was marked on [[AMD]]'s roadmap during the Microprocessor Forum in [[1998]]. Almost a year after the introduction of {{amd|Athlon}}, AMD introduced the Duron family. With Celeron, Intel opted to using a single socket ([[Socket 370]]) for both the {{intel|Pentium III}} and {{intel|Celeron}} families. This allowed simplification for OEMs and opens the door for the end user to future upgrades. AMD moved in the same direction, using [[Socket A]] for {{amd|Athlon}} and the new Duron family. | In April of [[1998]] Intel introduced their {{intel|Celeron}} family of processors - a family specifically designed to target the ultra-cheaper computer segment. Duron (still nameless at the time) was marked on [[AMD]]'s roadmap during the Microprocessor Forum in [[1998]]. Almost a year after the introduction of {{amd|Athlon}}, AMD introduced the Duron family. With Celeron, Intel opted to using a single socket ([[Socket 370]]) for both the {{intel|Pentium III}} and {{intel|Celeron}} families. This allowed simplification for OEMs and opens the door for the end user to future upgrades. AMD moved in the same direction, using [[Socket A]] for {{amd|Athlon}} and the new Duron family. | ||
Unlike original Celeron processor models which were artificially slowed down by Intel (e.g. slower bus speed), Duron processors shared the same specs as Athlon - including a higher speed of 100 MHz bus DDR (200 MT/s). Additionally, Intel used the same production for both Celeron and Pentium III, disabling various features as needed during the manufacturing process. Unlike Intel, AMD gave Duron a design of its own, the reduced cache for example directly resulted in smaller die size and thus cheaper manufacturing. These differences played fairly well in AMD's advantage - Duron models were cheaper and had superior performance over their Celeron counterparts. | Unlike original Celeron processor models which were artificially slowed down by Intel (e.g. slower bus speed), Duron processors shared the same specs as Athlon - including a higher speed of 100 MHz bus DDR (200 MT/s). Additionally, Intel used the same production for both Celeron and Pentium III, disabling various features as needed during the manufacturing process. Unlike Intel, AMD gave Duron a design of its own, the reduced cache for example directly resulted in smaller die size and thus cheaper manufacturing. These differences played fairly well in AMD's advantage - Duron models were cheaper and had superior performance over their Celeron counterparts. | ||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| − | {{main|amd/ | + | {{main|amd/microarchitectures/k7|l1=K7 Microarchitecture}}[[File:AMD Duron processor 3.jpg|right|350px]] |
{{empty section}} | {{empty section}} | ||
== Die Shot == | == Die Shot == | ||
| − | {{ | + | |
| + | === {{\\|D800AUT1B}} ({{amd|Spitfire|l=core}}) === | ||
| + | [[File:AMD D800AUT1B die shot.jpg|550px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === {{\\|DHD1200AMT1B}} ({{amd|Morgan|l=core}}) === | ||
| + | [[File:AMD DHD1200AMT1B die shot.jpg|550px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Model Identification == | ||
| + | Duron processors follow AMD's Ordering Part Number (OPN): | ||
| + | {{chip identification | ||
| + | | parts = 8 | ||
| + | | ex 1 = D | ||
| + | | ex 2 = | ||
| + | | ex 3 = 950 | ||
| + | | ex 4 = A | ||
| + | | ex 5 = U | ||
| + | | ex 6 = T | ||
| + | | ex 7 = 1 | ||
| + | | ex 8 = B | ||
| + | | ex 2 1 = D | ||
| + | | ex 2 2 = HD | ||
| + | | ex 2 3 = 600 | ||
| + | | ex 2 4 = D | ||
| + | | ex 2 5 = L | ||
| + | | ex 2 6 = V | ||
| + | | ex 2 7 = 1 | ||
| + | | ex 2 8 = C | ||
| + | | desc 1 = '''Family Designation'''<br><table><tr><td style="width: 55px;">'''D'''</td><td>Duron Processor</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | | desc 2 = '''Model Variation'''<br><table><tr><td style="width: 55px;">'''''(none)'''''</td><td>Original Desktop Processor</td></tr><tr><td style="width: 55px;">'''M'''</td><td>Original Mobile Desktop Processor</td></tr><tr><td style="width: 55px;">'''HD'''</td><td>High-Performance Desktop Processor</td></tr><tr><td>'''HM'''</td><td>High-Performance Mobile Processor</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | | desc 3 = '''Frequency (MHz)''' | ||
| + | | desc 4 = '''Package Designation'''<br><table><tr><td style="width: 50px;">'''A'''</td><td>CPGA-453</td></tr><tr><td>'''D'''</td><td>OPGA</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | | desc 5 = '''Core Voltage'''<br><table><tr><td style="width: 50px;">'''V'''</td><td>1.4 V ± 0.1 V</td></tr><tr><td>'''Q'''</td><td>1.45 V ± 0.1 V</td></tr><tr><td>'''S'''</td><td>1.5 V ± 0.1 V</td></tr><tr><td>'''L'''</td><td>1.5 V ± 0.1 V</td></tr><tr><td>'''U'''</td><td>1.6 V ± 0.1 V</td></tr><tr><td>'''M'''</td><td>1.75 V ± 0.1 V</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | | desc 6 = '''T<sub>CASE</sub> Range'''<br><table><tr><td style="width: 50px;">'''V'''</td><td>0 °C – 85 °C</td><td> </td><td>'''S'''</td><td>0 °C – 95 °C</td></tr><tr><td>'''T'''</td><td>0 °C – 90 °C</td><td> </td><td>'''Q'''</td><td>0 °C – 100 °C</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | | desc 7 = '''[[L2$]] Size'''<br><table><tr><td style="width: 55px;">'''1'''</td><td>64 KB</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | | desc 8 = '''Max [[front size bus|FSB]]'''<br><table><tr><td style="width: 55px;">'''B'''</td><td>200 MT/s</td></tr><tr><td>'''C'''</td><td>266 MT/s</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Members == | == Members == | ||
| − | {{ | + | === Desktop Processors === |
| + | ==== Spitfire Core ==== | ||
| + | {{amd|Spitfire|l=core}}-based processors incorporated {{x86|MMX}}, {{x86|Extended MMX}}, {{x86|3DNow!}}, and {{x86|Extended 3DNow!}}. | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: http://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <table class="wikitable sortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="11" style="background:#D6D6FF;">Spitfire-based Desktop Models</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th>Model</th><th>Launched</th><th>Process</th><th>Freq</th><th>Mult.</th><th>Bus</th><th>Max Mem</th><th>V<sub>CORE</sub></th><th>Package</th><th>Min T<sub>case</sub></th><th>Max T<sub>case</sub></th></tr> | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Desktop]][[core name::Spitfire]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?process | ||
| + | |?base frequency#MHz | ||
| + | |?clock multiplier | ||
| + | |?bus speed#MHz | ||
| + | |?max memory#GB | ||
| + | |?core voltage | ||
| + | |?package | ||
| + | |?min case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |?max case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 2 | ||
| + | |userparam=12 | ||
| + | |sep=, | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{table count|col=11|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Desktop]][[core name::Spitfire]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | ==== Morgan Core ==== | ||
| + | {{amd|Morgan|l=core}}-based processors incorporated {{x86|MMX}}, {{x86|Extended MMX}}, {{x86|3DNow!}}, {{x86|Extended 3DNow!}}, and {{x86|SSE}}. | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: http://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <table class="wikitable sortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="11" style="background:#D6D6FF;">Morgan-based Desktop Models</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th>Model</th><th>Launched</th><th>Process</th><th>Freq</th><th>Mult.</th><th>Bus</th><th>Max Mem</th><th>V<sub>CORE</sub></th><th>Package</th><th>Min T<sub>case</sub></th><th>Max T<sub>case</sub></th></tr> | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Desktop]][[core name::Morgan]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?process | ||
| + | |?base frequency#MHz | ||
| + | |?clock multiplier | ||
| + | |?bus speed#MHz | ||
| + | |?max memory#GB | ||
| + | |?core voltage | ||
| + | |?package | ||
| + | |?min case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |?max case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 2 | ||
| + | |userparam=12 | ||
| + | |sep=, | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{table count|col=11|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Desktop]][[core name::Morgan]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | ==== Applebred Core ==== | ||
| + | {{amd|Applebred|l=core}}-based processors incorporated {{x86|MMX}}, {{x86|Extended MMX}}, {{x86|3DNow!}}, {{x86|Extended 3DNow!}}, and {{x86|SSE}}. Applebred was based on the {{amd|Appaloosa|l=core}} which was announced but never officially released. | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: http://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <table class="wikitable sortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="11" style="background:#D6D6FF;">Applebred-based Desktop Models</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th>Model</th><th>Launched</th><th>Process</th><th>Freq</th><th>Mult.</th><th>Bus</th><th>Max Mem</th><th>V<sub>CORE</sub></th><th>Package</th><th>Min T<sub>case</sub></th><th>Max T<sub>case</sub></th></tr> | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Desktop]][[core name::Applebred]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?process | ||
| + | |?base frequency#MHz | ||
| + | |?clock multiplier | ||
| + | |?bus speed#MHz | ||
| + | |?max memory#GB | ||
| + | |?core voltage | ||
| + | |?package | ||
| + | |?min case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |?max case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 2 | ||
| + | |userparam=12 | ||
| + | |sep=, | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{table count|col=11|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Desktop]][[core name::Applebred]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Mobile Processors === | ||
| + | ==== Spitfire Core ==== | ||
| + | {{amd|Spitfire|l=core}}-based processors incorporated {{x86|MMX}}, {{x86|Extended MMX}}, {{x86|3DNow!}}, and {{x86|Extended 3DNow!}}. | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: http://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <table class="wikitable sortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="11" style="background:#D6D6FF;">Spitfire-based Mobile Models</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th>Model</th><th>Launched</th><th>Process</th><th>Freq</th><th>Mult.</th><th>Bus</th><th>Max Mem</th><th>V<sub>CORE</sub></th><th>Package</th><th>Min T<sub>case</sub></th><th>Max T<sub>case</sub></th></tr> | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Mobile]][[core name::Spitfire]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?process | ||
| + | |?base frequency#MHz | ||
| + | |?clock multiplier | ||
| + | |?bus speed#MHz | ||
| + | |?max memory#GB | ||
| + | |?core voltage | ||
| + | |?package | ||
| + | |?min case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |?max case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 2 | ||
| + | |userparam=12 | ||
| + | |sep=, | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{table count|col=11|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Mobile]][[core name::Spitfire]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | ==== Morgan Core ==== | ||
| + | {{amd|Morgan|l=core}}-based (formerly Camaro) processors incorporated {{x86|MMX}}, {{x86|Extended MMX}}, {{x86|3DNow!}}, {{x86|Extended 3DNow!}}, and {{x86|SSE}}. | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: http://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <table class="wikitable sortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="11" style="background:#D6D6FF;">Camaro-based Mobile Models</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th>Model</th><th>Launched</th><th>Process</th><th>Freq</th><th>Mult.</th><th>Bus</th><th>Max Mem</th><th>V<sub>CORE</sub></th><th>Package</th><th>Min T<sub>case</sub></th><th>Max T<sub>case</sub></th></tr> | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Mobile]][[core name::Morgan]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?process | ||
| + | |?base frequency#MHz | ||
| + | |?clock multiplier | ||
| + | |?bus speed#MHz | ||
| + | |?max memory#GB | ||
| + | |?core voltage | ||
| + | |?package | ||
| + | |?min case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |?max case temperature#°C | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 2 | ||
| + | |userparam=12 | ||
| + | |sep=, | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{table count|col=11|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by amd]][[instance of::microprocessor]][[microprocessor family::Duron]][[market segment::Mobile]][[core name::Morgan]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Motherboards == | ||
| + | [[File:Mainboard Elitegroup K7S5A.jpg|right|350px|thumb|Elitegroup K7S5A with SIS 735 Chipset.]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Vendor !! Model !! Form !! Chipset | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Abit || KD7 || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Abit || KR7A || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Acorp || 7KT266A || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Albatron || KX400+ || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Albatron || KX400+ Pro || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Albatron || KX400-8X || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AOpen || AK77-333 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AOpen || AK77-8X Max || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AOpen || AK77-8XN || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7N266-VM || µATX || NVIDIA nForce 220D | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7N266-VM || µATX || NVIDIA nForce 220D | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7N266-VM/AA || µATX || NVIDIA nForce 220D | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7N8X || ATX || NVIDIA nForce2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7V266-E || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7V333 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7V333 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Asus || A7V8X || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | AZZA || KT33F-ANB || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Biostar || M7VIF || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Biostar || M7VIG || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Biostar || M7VIK || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Biostar || M7VIP || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Chaintech || 7AIV5 || µATX || VIA KM133A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Chaintech || 7SIF || µATX || SiS 740 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Chaintech || 7VIA || µATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Chaintech || 7VJDA || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Chaintech || 7VJS || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | DFI || AD73PRO || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || K7S5A || ATX || SiS 735 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || K7S6A || ATX || SiS 745 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || K7SOM/M841LR || ATX || SiS 740 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || K7VTA3 || ATX || VIA KT266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || K7VTA3 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || L7VMM || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || L7VTA || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | ECS || M825ULR || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EPoX || 8KHA+ || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EPoX || 8KMM+ || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EPoX || EP-8K3A || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EPoX || EP-8K9A2 || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | EPoX || EP-8KMM+ || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FIC || AM-35 || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FIC || AM37 || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FIC || AN-17 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FIC || AN11 || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FIC || AN19C || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | FIC || AN19E || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7DX || ATX || AMD-761 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7DX+ || ATX || AMD-761 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7DXE || ATX || AMD-761 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7DXR+ || ATX || AMD-761 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VA || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VAX || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VAXP || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VAXP Ultra || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VKML || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VR || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VRX || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VRX || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VRXP || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VTXE+ || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gigabyte || GA-7VTXH+ || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Jetway || 866AS-Ultra || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Jetway || V333DA || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Leadtek || 7350KDA || ATX || SiS 735 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Leadtek || K7N415DA || ATX || NVIDIA nForce 415D | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mach Speed Technologies || MZ333DA || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mach Speed Technologies || MZ866AS || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || K7N2 || ATX || NVIDIA nForce2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || K7T Turbo2 || ATX || VIA KT133A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || K7T266 Pro2 || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || KT3 Ultra || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || KT3 Ultra2 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || KT4 Ultra || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || KT4M || µATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || KT4V || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || MS-6340M || µATX || VIA KM133A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || MS-6367 || µATX || nVidia nForce 420D | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || MS-6382E || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || MS-6390 || µATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || MS-6568 || µATX || SiS 740 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | MSI || MS-6593 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | QDI || KD7X || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | QDI || KuDoZ 7E/333 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | QDI || KuDoz 7 || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shuttle || AK35GTR || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shuttle || AK35GTR || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shuttle || AK37GTR || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shuttle || AK38 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shuttle || AK39N || ATX || VIA KT400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shuttle || FS40 || FlexATX || SiS 740 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Shuttle || FX41 || FlexATX || VIA KM266 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Soltek || SL-75DRV5 || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Soyo || K7V Dragon Plus || ATX || VIA KT266A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Soyo || SY-KT333 Dragon Lite || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Soyo || SY-KT333 Dragon Ultra || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | XFX || KT33F-ANB || ATX || VIA KT333 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Documents == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === DataSheet === | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Duron Processor Model 3 Data Sheet (June, 2001).pdf|AMD Duron Processor Model 3 Data Sheet]]; Publication # 23802; Rev: I; Issue Date: June 2001. | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Data Sheet (January, 2002).pdf|AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Data Sheet]]; Publication # 24310; Rev: G; Issue Date: January 2002. | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Duron Processor Model 8 Data Sheet (August, 2003).pdf|AMD Duron Processor Model 8 Data Sheet]]; Publication # 25848; Rev: B; Issue Date: August 2003. | ||
| + | * [[:File:Mobile AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Data Sheet (December, 2001).pdf|Mobile AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Data Sheet]]; Publication # 24068; Rev: F; Issue Date: December 2001. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Software Manual === | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Duron Processor Rev. A0- CPUID Reporting of L2 Cache Size (July, 2000).pdf|AMD Duron Processor Rev. A0: CPUID Reporting of L2 Cache Size]]. | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Processor Recognition (June, 2000).pdf|AMD Processor Recognition Application Note]]; Publication # 20734; Rev: R; Issue Date: June 2000. | ||
| + | * [[:File:Methodologies for Measuring Temperature on AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processors.pdf|Methodologies for Measuring Temperature on AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processors Application Note]]; Publication # 24228; Revision: E; Issue Date: January 2003. | ||
| + | * [[:File:Microsoft Windows 2000 Patch for AGP Applications on AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processors.pdf|Microsoft Windows 2000 Patch for AGP Applications on AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processors]]; September 21, 2000. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Other === | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Duron Processor Model 3 Revision Guide (October, 2003).pdf|AMD Duron Processor Model 3 Revision Guide]]; Publication # 23865; Rev: K; Issue Date: October 2003. | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Revision Guid (October, 2003).pdf|AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Revision Guide]]; Publication # 24806; Rev: E; Issue Date: October 2003. | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Duron Processor Revision Guide (August, 200).pdf|AMD Duron Processor Revision Guide; Publication # 23865]]; Rev: C; Issue Date: August 2000. | ||
| + | * [[:File:AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processor-Based System Build Checklist.pdf|AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processor-Based System Build Checklist]]; Publication # 24387; Rev A; October 2000. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Artwork == | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:AMD Duron processor 1.gif | ||
| + | File:AMD Duron processor 2.jpg | ||
| + | File:AMD Duron processor 3.jpg | ||
| + | File:AMD Duron processor earth.jpg | ||
| + | File:AMD Duron processor global.gif | ||
| + | File:AMD Duron processor laptop.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
Latest revision as of 16:30, 3 December 2016
| AMD Duron | |

| |
| Duron Logo | |
| Developer | AMD |
| Manufacturer | AMD |
| Type | Microprocessors |
| Introduction | April 27, 2000 (announced) June 19, 2000 (launch) |
| Production | 2000-2005 |
| Architecture | K7-derived processor for budget computers |
| ISA | IA-32 |
| µarch | K7 |
| Word size | 32 bit 4 octets
8 nibbles |
| Process | 180 nm 0.18 μm , 130 nm1.8e-4 mm 0.13 μm
1.3e-4 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 600 MHz-1,800 MHz |
| Package | CPGA-453 |
| Socket | Socket A |
| Succession | |
| ← | → |
| K6-III | Sempron |
Duron was a family of budget 32-bit x86 microprocessors developed by AMD and introduced in early 2000. Duron, a low-budget derivative of Athlon (K7-based), was introduced as a way for AMD to aggressively compete against Intel's Celeron in the ultra-cheap PC segment. Announced in April of 2000, Duron processors offered the best price-performance ratio providing Celeron with stiff competition.
Contents
Overview[edit]
In April of 1998 Intel introduced their Celeron family of processors - a family specifically designed to target the ultra-cheaper computer segment. Duron (still nameless at the time) was marked on AMD's roadmap during the Microprocessor Forum in 1998. Almost a year after the introduction of Athlon, AMD introduced the Duron family. With Celeron, Intel opted to using a single socket (Socket 370) for both the Pentium III and Celeron families. This allowed simplification for OEMs and opens the door for the end user to future upgrades. AMD moved in the same direction, using Socket A for Athlon and the new Duron family.
Unlike original Celeron processor models which were artificially slowed down by Intel (e.g. slower bus speed), Duron processors shared the same specs as Athlon - including a higher speed of 100 MHz bus DDR (200 MT/s). Additionally, Intel used the same production for both Celeron and Pentium III, disabling various features as needed during the manufacturing process. Unlike Intel, AMD gave Duron a design of its own, the reduced cache for example directly resulted in smaller die size and thus cheaper manufacturing. These differences played fairly well in AMD's advantage - Duron models were cheaper and had superior performance over their Celeron counterparts.
Architecture[edit]
- Main article: K7 Microarchitecture
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
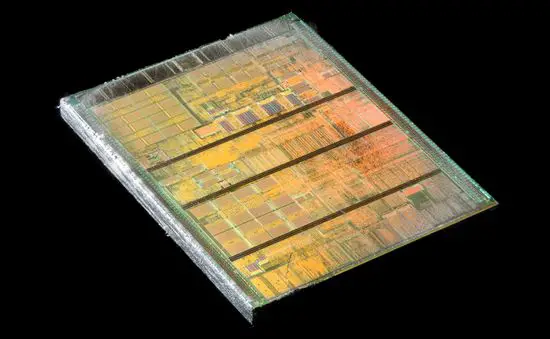
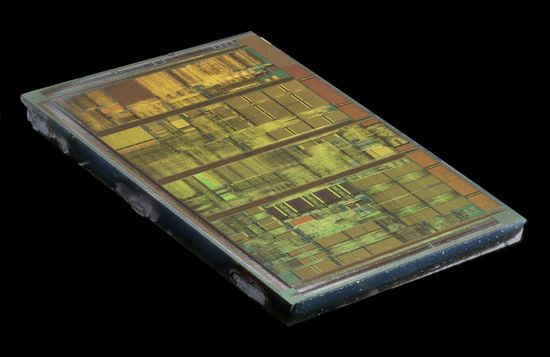
Die Shot[edit]
D800AUT1B (Spitfire)[edit]
DHD1200AMT1B (Morgan)[edit]
Model Identification[edit]
Duron processors follow AMD's Ordering Part Number (OPN):
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||
| D | 950 | A | U | T | 1 | B | ||||||||||||||
| D | HD | 600 | D | L | V | 1 | C | |||||||||||||
Max FSB
| ||||||||||||||||||||
L2$ Size
| ||||||||||||||||||||
TCASE Range
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Core Voltage
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Package Designation
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Frequency (MHz) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Model Variation
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Family Designation
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Members[edit]
Desktop Processors[edit]
Spitfire Core[edit]
Spitfire-based processors incorporated MMX, Extended MMX, 3DNow!, and Extended 3DNow!.
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,| Spitfire-based Desktop Models | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Process | Freq | Mult. | Bus | Max Mem | VCORE | Package | Min Tcase | Max Tcase |
| Duron 550 | 19 June 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 550 MHz 0.55 GHz 550,000 kHz | 5.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 600 | 19 June 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 600 MHz 0.6 GHz 600,000 kHz | 6 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 600 | 19 June 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 600 MHz 0.6 GHz 600,000 kHz | 6 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 650 | 19 June 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 550 MHz 0.55 GHz 550,000 kHz | 6.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 650 | 19 June 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 kHz | 6.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 700 | 17 October 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 700 MHz 0.7 GHz 700,000 kHz | 7 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 700 | 19 June 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 700 MHz 0.7 GHz 700,000 kHz | 7 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 700 | 19 June 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 700 MHz 0.7 GHz 700,000 kHz | 7 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 750 | 5 September 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 750 MHz 0.75 GHz 750,000 kHz | 7.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 750 | 5 September 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 750 MHz 0.75 GHz 750,000 kHz | 7.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 800 | 17 October 2000 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 800 MHz 0.8 GHz 800,000 kHz | 8 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 800 | 2 April 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 800 MHz 0.8 GHz 800,000 kHz | 8 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 850 | 8 January 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 850 MHz 0.85 GHz 850,000 kHz | 8.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 900 | 2 April 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 kHz | 9 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 950 | 6 June 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 kHz | 9.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.6 V 16 dV 160 cV 1,600 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Count: 15 | ||||||||||
Morgan Core[edit]
Morgan-based processors incorporated MMX, Extended MMX, 3DNow!, Extended 3DNow!, and SSE.
,,,,,| Morgan-based Desktop Models | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Process | Freq | Mult. | Bus | Max Mem | VCORE | Package | Min Tcase | Max Tcase |
| Duron 1000 | 20 August 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 kHz | 10 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.75 V 17.5 dV 175 cV 1,750 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 1100 | 1 October 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz 1,100,000 kHz | 11 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.75 V 17.5 dV 175 cV 1,750 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 1200 | 15 November 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,200 MHz 1.2 GHz 1,200,000 kHz | 12 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.75 V 17.5 dV 175 cV 1,750 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 1300 | 21 January 2002 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,300 MHz 1.3 GHz 1,300,000 kHz | 13 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.75 V 17.5 dV 175 cV 1,750 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 900 | 2 April 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 kHz | 9 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.75 V 17.5 dV 175 cV 1,750 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Duron 950 | 12 July 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 kHz | 9.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.75 V 17.5 dV 175 cV 1,750 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 90 °C 363.15 K 194 °F 653.67 °R | |
| Count: 6 | ||||||||||
Applebred Core[edit]
Applebred-based processors incorporated MMX, Extended MMX, 3DNow!, Extended 3DNow!, and SSE. Applebred was based on the Appaloosa which was announced but never officially released.
,,| Applebred-based Desktop Models | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Process | Freq | Mult. | Bus | Max Mem | VCORE | Package | Min Tcase | Max Tcase |
| Duron 1400 | 15 August 2003 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 1,400 MHz 1.4 GHz 1,400,000 kHz | 10.5 | 133.33 MHz 0.133 GHz 133,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 85 °C 358.15 K 185 °F 644.67 °R | |
| Duron 1600 | 15 August 2003 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 1,600 MHz 1.6 GHz 1,600,000 kHz | 12 | 133.33 MHz 0.133 GHz 133,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 85 °C 358.15 K 185 °F 644.67 °R | |
| Duron 1800 | 15 August 2003 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 1,800 MHz 1.8 GHz 1,800,000 kHz | 13.5 | 133.33 MHz 0.133 GHz 133,330 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 85 °C 358.15 K 185 °F 644.67 °R | |
| Count: 3 | ||||||||||
Mobile Processors[edit]
Spitfire Core[edit]
Spitfire-based processors incorporated MMX, Extended MMX, 3DNow!, and Extended 3DNow!.
,,| Spitfire-based Mobile Models | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Process | Freq | Mult. | Bus | Max Mem | VCORE | Package | Min Tcase | Max Tcase |
| Duron 600 | 15 January 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 600 MHz 0.6 GHz 600,000 kHz | 6 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 650 | 15 January 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 650 MHz 0.65 GHz 650,000 kHz | 6.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 700 | 15 January 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 700 MHz 0.7 GHz 700,000 kHz | 7 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Count: 3 | ||||||||||
Morgan Core[edit]
Morgan-based (formerly Camaro) processors incorporated MMX, Extended MMX, 3DNow!, Extended 3DNow!, and SSE.
,,,,,,,,,,,| Camaro-based Mobile Models | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Process | Freq | Mult. | Bus | Max Mem | VCORE | Package | Min Tcase | Max Tcase |
| Duron 1000 | 17 December 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 kHz | 10 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 1100 | 30 January 2002 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,100 MHz 1.1 GHz 1,100,000 kHz | 11 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.55 V 15.5 dV 155 cV 1,550 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 1200 | 30 January 2002 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,200 MHz 1.2 GHz 1,200,000 kHz | 12 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.45 V 14.5 dV 145 cV 1,450 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 1300 | 30 January 2002 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 1,300 MHz 1.3 GHz 1,300,000 kHz | 13 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 800 | 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 800 MHz 0.8 GHz 800,000 kHz | 8 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 800 | 14 May 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 800 MHz 0.8 GHz 800,000 kHz | 8 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 800 | 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 800 MHz 0.8 GHz 800,000 kHz | 8 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 850 | 14 May 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 850 MHz 0.85 GHz 850,000 kHz | 8.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 850 | 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 850 MHz 0.85 GHz 850,000 kHz | 8.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.4 V 14 dV 140 cV 1,400 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 850 | 14 May 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 850 MHz 0.85 GHz 850,000 kHz | 8.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.5 V 15 dV 150 cV 1,500 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 900 | 20 August 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 900 MHz 0.9 GHz 900,000 kHz | 9 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.45 V 14.5 dV 145 cV 1,450 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Duron 950 | 12 November 2001 | 180 nm 0.18 μm 1.8e-4 mm | 950 MHz 0.95 GHz 950,000 kHz | 9.5 | 100 MHz 0.1 GHz 100,000 kHz | 4,096 MiB 4,194,304 KiB 4,294,967,296 B 4 GiB 0.00391 TiB | 1.45 V 14.5 dV 145 cV 1,450 mV | 0 °C 273.15 K 32 °F 491.67 °R | 95 °C 368.15 K 203 °F 662.67 °R | |
| Count: 12 | ||||||||||
Motherboards[edit]
| Vendor | Model | Form | Chipset |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abit | KD7 | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Abit | KR7A | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Acorp | 7KT266A | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Albatron | KX400+ | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Albatron | KX400+ Pro | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Albatron | KX400-8X | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| AOpen | AK77-333 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| AOpen | AK77-8X Max | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| AOpen | AK77-8XN | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Asus | A7N266-VM | µATX | NVIDIA nForce 220D |
| Asus | A7N266-VM | µATX | NVIDIA nForce 220D |
| Asus | A7N266-VM/AA | µATX | NVIDIA nForce 220D |
| Asus | A7N8X | ATX | NVIDIA nForce2 |
| Asus | A7V266-E | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Asus | A7V333 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Asus | A7V333 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Asus | A7V8X | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| AZZA | KT33F-ANB | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Biostar | M7VIF | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Biostar | M7VIG | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| Biostar | M7VIK | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Biostar | M7VIP | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Chaintech | 7AIV5 | µATX | VIA KM133A |
| Chaintech | 7SIF | µATX | SiS 740 |
| Chaintech | 7VIA | µATX | VIA KT333 |
| Chaintech | 7VJDA | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Chaintech | 7VJS | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| DFI | AD73PRO | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| ECS | K7S5A | ATX | SiS 735 |
| ECS | K7S6A | ATX | SiS 745 |
| ECS | K7SOM/M841LR | ATX | SiS 740 |
| ECS | K7VTA3 | ATX | VIA KT266 |
| ECS | K7VTA3 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| ECS | L7VMM | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| ECS | L7VTA | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| ECS | M825ULR | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| EPoX | 8KHA+ | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| EPoX | 8KMM+ | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| EPoX | EP-8K3A | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| EPoX | EP-8K9A2 | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| EPoX | EP-8KMM+ | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| FIC | AM-35 | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| FIC | AM37 | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| FIC | AN-17 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| FIC | AN11 | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| FIC | AN19C | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| FIC | AN19E | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7DX | ATX | AMD-761 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7DX+ | ATX | AMD-761 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7DXE | ATX | AMD-761 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7DXR+ | ATX | AMD-761 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VA | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VAX | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VAXP | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VAXP Ultra | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VKML | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VR | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VRX | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VRX | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VRXP | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VTXE+ | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Gigabyte | GA-7VTXH+ | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Jetway | 866AS-Ultra | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Jetway | V333DA | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Leadtek | 7350KDA | ATX | SiS 735 |
| Leadtek | K7N415DA | ATX | NVIDIA nForce 415D |
| Mach Speed Technologies | MZ333DA | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Mach Speed Technologies | MZ866AS | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| MSI | K7N2 | ATX | NVIDIA nForce2 |
| MSI | K7T Turbo2 | ATX | VIA KT133A |
| MSI | K7T266 Pro2 | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| MSI | KT3 Ultra | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| MSI | KT3 Ultra2 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| MSI | KT4 Ultra | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| MSI | KT4M | µATX | VIA KT400 |
| MSI | KT4V | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| MSI | MS-6340M | µATX | VIA KM133A |
| MSI | MS-6367 | µATX | nVidia nForce 420D |
| MSI | MS-6382E | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| MSI | MS-6390 | µATX | VIA KM266 |
| MSI | MS-6568 | µATX | SiS 740 |
| MSI | MS-6593 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| QDI | KD7X | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| QDI | KuDoZ 7E/333 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| QDI | KuDoz 7 | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Shuttle | AK35GTR | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Shuttle | AK35GTR | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Shuttle | AK37GTR | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Shuttle | AK38 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Shuttle | AK39N | ATX | VIA KT400 |
| Shuttle | FS40 | FlexATX | SiS 740 |
| Shuttle | FX41 | FlexATX | VIA KM266 |
| Soltek | SL-75DRV5 | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Soyo | K7V Dragon Plus | ATX | VIA KT266A |
| Soyo | SY-KT333 Dragon Lite | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| Soyo | SY-KT333 Dragon Ultra | ATX | VIA KT333 |
| XFX | KT33F-ANB | ATX | VIA KT333 |
Documents[edit]
DataSheet[edit]
- AMD Duron Processor Model 3 Data Sheet; Publication # 23802; Rev: I; Issue Date: June 2001.
- AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Data Sheet; Publication # 24310; Rev: G; Issue Date: January 2002.
- AMD Duron Processor Model 8 Data Sheet; Publication # 25848; Rev: B; Issue Date: August 2003.
- Mobile AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Data Sheet; Publication # 24068; Rev: F; Issue Date: December 2001.
Software Manual[edit]
- AMD Duron Processor Rev. A0: CPUID Reporting of L2 Cache Size.
- AMD Processor Recognition Application Note; Publication # 20734; Rev: R; Issue Date: June 2000.
- Methodologies for Measuring Temperature on AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processors Application Note; Publication # 24228; Revision: E; Issue Date: January 2003.
- Microsoft Windows 2000 Patch for AGP Applications on AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processors; September 21, 2000.
Other[edit]
- AMD Duron Processor Model 3 Revision Guide; Publication # 23865; Rev: K; Issue Date: October 2003.
- AMD Duron Processor Model 7 Revision Guide; Publication # 24806; Rev: E; Issue Date: October 2003.
- AMD Duron Processor Revision Guide; Publication # 23865; Rev: C; Issue Date: August 2000.
- AMD Athlon and AMD Duron Processor-Based System Build Checklist; Publication # 24387; Rev A; October 2000.
Artwork[edit]
See Also[edit]
| designer | AMD + |
| first announced | April 27, 2000 + |
| first launched | June 19, 2000 + |
| full page name | amd/duron + |
| instance of | microprocessor family + |
| instruction set architecture | IA-32 + |
| main designer | AMD + |
| manufacturer | AMD + |
| microarchitecture | K7 + |
| name | AMD Duron + |
| package | CPGA-453 + |
| process | 180 nm (0.18 μm, 1.8e-4 mm) + and 130 nm (0.13 μm, 1.3e-4 mm) + |
| socket | Socket A + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 32 bit (4 octets, 8 nibbles) + |