| Edit Values | |
| Socket TR4 | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | AMD |
| Introduction | May 16, 2017 (announced) August 10, 2017 (launched) |
| Market | Desktop, Workstation |
| Microarchitecture | Zen, Zen+ |
| TDP | 180 W 180,000 mW , 250 W0.241 hp 0.18 kW 250,000 mW 0.335 hp 0.25 kW |
| Package | |
| Name | TR4, FCLGA-4094 |
| Type | FC-OLGA |
| Contacts | 4094 |
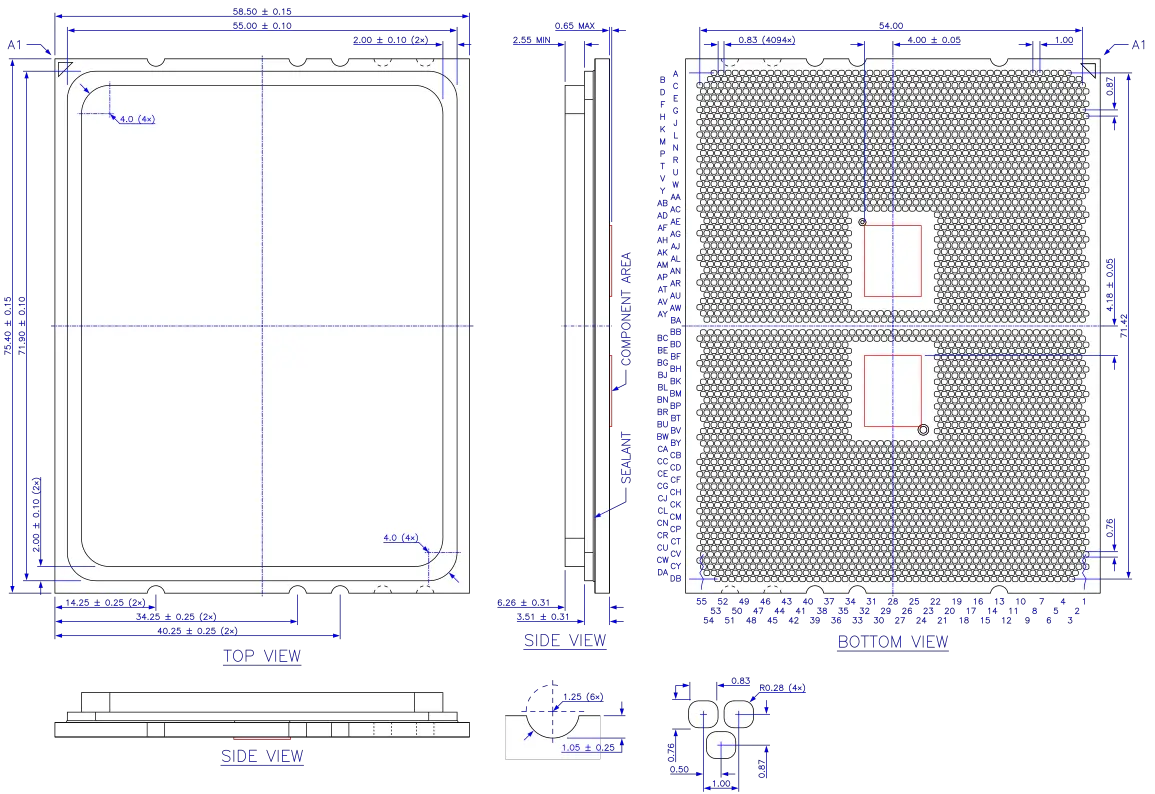
| Dimension | 75.40 mm 7.54 cm × 58.50 mm2.969 in 5.85 cm × 6.26 mm2.303 in 0.246 in |
| Pitch | 0.87 mm 0.0343 in × 1.00 mm0.0394 in |
| Socket | |
| Name | TR4, SP3r2, sTR4 |
| Type | SM-LGA |
| Succession | |
Socket TR4 a.k.a. Socket SP3r2 and sTR4 is a microprocessor socket designed by AMD for their first and second generation Ryzen Threadripper high-end desktop processors. It was superseeded by Socket sTRX4. Contemporary mainstream desktop processors use Socket AM4, server processors Socket SP3.
Socket TR4 is mechanically identical and almost pin-compatible to Socket SP3 and the sockets sTRX4 and sWRX8 also derived from it, but differs by the number of memory channels and I/O interfaces available: SP3 processors use DDR4 RDIMMs on up to eight memory channels, sWRX8 processors UDIMMs or RDIMMs, while TR4 and sTRX4 processors support only UDIMMs on up to four memory channels. TR4 and sTRX4 omit four of eight PCIe interfaces present on Socket SP3 and sWRX8, but TR4 processors also pin out four additional USB ports, a HDA interface, and other client-oriented features which are not supported by the other infrastructures.
Contents
Overview[edit]
Socket TR4 is a zero insertion force, screw actuated, surface-mount land grid array socket for use with a 4094-contact, 1.00 mm × 0.87 mm interstitial pitch, organic land grid array CPU package.
It supports four channels of 72-bit DDR4 memory with up to two DIMMs per channel, four 16-lane PCIe Gen 3 I/O interfaces, eight USB 3.1 Gen 1 ports, and up to 16 SATA Gen 3 ports. 8-layer motherboards are required to route these signals.
The following AMD processor families use Socket TR4:
| CPU Family | Microarch. | Process | Products | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 0 | Family 17h Models 00h–0Fh | Zen | GlobalFoundries 14 nm (14LPP) | Threadripper 1900 "Whitehaven" (Model 01h) |
| Zen+ | GlobalFoundries 12 nm (12LP) | Threadripper 2900 "Colfax" (Model 08h) |
Codenames of AMD TR4 reference platforms (CRBs) are "Whitehaven", "Whitehaven OPS", and "Whitehaven DAP".
Package Description[edit]
The TR4 CPU package is lidded, has a 58.50 mm × 75.40 mm organic substrate with flip chip die attachment, and 4094 nickel and gold plated land pads. It ships with a carrier frame pre-installed. The carrier frame, made from an orange colored polycarbonate material, is a part of the package loading mechanism and remains on the package in the socket.
The package substrate has six keying notches along the short edges preventing it from being inserted 180 degrees rotated into the carrier frame or socket, or in an incompatible socket with mismatching keying features. Four additional positions are reserved for future models. However all sockets SP3, TR4, sTRX4, and sWRX8, and all processors for these sockets have the same keying. TR4 packages are electrically keyed by pin SP3R2 and Socket TR4 motherboards are not supposed to power up the socket if a SP3 or sWRX8 processor is installed. To boot the processor they must also provide compatible firmware.
The lid a.k.a. integrated heat spreader has an internal support bar bisecting the dies in the package. Decoupling capacitors are placed under the lid around the chiplet periphery on the top side, and in two windows in the pad grid on the bottom side. TR4 packages use solder as TIM between the dies and the lid with ≈ 62 W/(m⋅K). A triangular symbol on both sides of the substrate marks the location of pin A1, with corresponding markings on the socket.
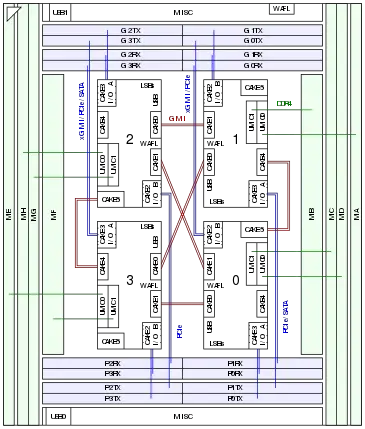
TR4 is a multi-chip package integrating two identical dies and two dummies for mechanical stability. Each die contains eight CPU cores and implements one half of the processor's memory and I/O interfaces. Model 01h uses "Zeppelin" ZP-B1 dies, Model 08h "Pinnacle Ridge" PiR-B2 dies. AMD used the same dies in various revisions for first generation EPYC server and embedded processors, and the first two generations of Ryzen desktop processors without iGPU; see CPU Family 17h. The dummies were shown to be patterned dies and are probably rejects. TR4 processors utilize customized, single-ended, 4:1 Serializer–Deserializer (SerDes) links on several package routing layers, 32 lanes wide in each direction, to connect the dies. The SerDes run at FCLK so for instance a 1.33 GHz FCLK coupled to the bus clock of DDR4-2666 SDRAM gives a raw data rate of 5.33 GT/s per lane or 21.33 GB/s in each direction.
Socket TR4 was derived from Socket SP3, avoiding the expenses of designing and producing another socket for a small market segment. AMD actually designed a more compact dual-die BGA package SP4 for EPYC 3000 embedded processors. TR4 packages are not merely EPYC processors with two disabled dies, the signal routing is different. Only the four memory channels pinned out closest to the package edge, and only four of the eight PCIe interfaces are connected to the two active dies. The interfaces were renumbered to reflect this. Two, rather than just one, Data Fabric on-package links connect the dies. Since each die actually implements four USB ports and an audio controller some unused lands were repurposed to pin out these signals in addition to the four USB ports supported by Socket SP3.
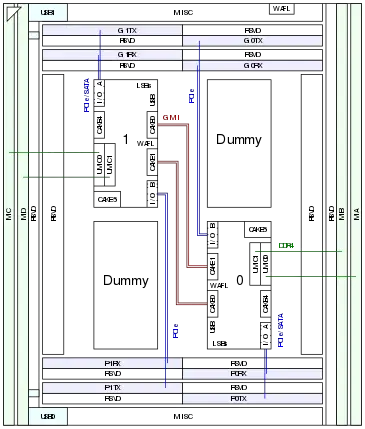 |
| |
| TR4 package top view, not to scale | SP3 Type-0 package for comparison |
Socket TR4 has four 16-lane multi-function I/O interfaces P0, P1, G0, and G1. All of these interfaces can be configured as PCIe link, some lanes alternatively as SATA link. The xGMI, S-Link, and XGBE protocols are not supported on this socket, nor is the WAFL interface. (xGMI and WAFL connect the Data and Control Fabrics of each processor on dual-socket server platforms. S-Link is a cache coherent link to CCIX memory expanders. XGBE is a backplane Ethernet link with data rates up to 10 Gbit/s.)
Socket Description[edit]
Socket TR4 (SP3r2) is mechanically identical to Socket SP3.
Feature Summary[edit]
- Lidded land grid array package, 75.40 mm × 58.50 mm
- 4094 contacts in a 82 × 55 grid with 0.87 mm × 1.00 mm interstitial pitch
- Organic substrate, flip chip die attachment
- 4 × 64/72 bit DDR4 SDRAM interface
- Up to 1467 MHz, PC4-23466 (DDR4-2933), 93.87 GB/s total raw bandwidth, not overclocked
- Up to 2 DIMMs/channel; SR/DR UDIMMs only
- ECC support
- Memory addressing up to ? GiB/channel
- Max. total memory capacity 256 GiB using eight 32 GiB DIMMs
- Four multi-function I/O interfaces P0, P1, G0, G1
Lane 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 PCIe x16 x8 x8 x4 x4 x4 x4 x2 x2 x2 x2 x2 x2 x2 x2 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 x1 SATA 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 PHY 4 PHY 3 PHY 2 PHY 1 PHY 0
- PCIe Gen 1, 2, 3 (8 GT/s) protocol supported on all interfaces
- 16 lanes, up to 8 ports per interface configurable x16, x8, x4, x2, x1 with power-of-two alignment (e.g. 1x4 + 4x1 + 1x8)
- Max. 7 PCIe ports in each 8-lane subset (e.g. 0x8 + 8x1 is not possible)
- Max. 7 PCIe ports per interface if any lane is configured as SATA port
- Different PCIe generations supported on the ports in the same interface
- Lane polarity inversion, per port lane reversal
- Up to 60 PCIe lanes total (one x4 link reserved for chipset attachment)
- PCIe Gen 1, 2, 3 (8 GT/s) protocol supported on all interfaces
- SATA Gen 1, 2, 3 (6 Gb/s) protocol supported on the lower 8 lanes of P0 and G1
- P0: SATA00-07, G1: SATA10-17
- Up to 16 SATA ports total
- SATA Gen 1, 2, 3 (6 Gb/s) protocol supported on the lower 8 lanes of P0 and G1
- Five PHY groups on each interface
- Lanes sharing a PHY group must use the same protocol (PCIe, SATA)
- Five PHY groups on each interface
- 8 × USB 1.1, 2.0, 3.1 Gen 1 (5 Gb/s)
- Low speed interfaces (some sharing pins):
Chipset[edit]
TR4 processors are SoCs with an integrated controller hub so they do not require a chipset, but are paired with the AMD X399 chipset (AMD 300-Series) serving as I/O expander.
The chipset is attached with an x4 PCIe Gen 3 link and can provide the following additional interfaces:
- 8 lanes PCIe Gen 1, 2 (5 GT/s)
- 2 × SATA Express (two PCIe lanes or two SATA ports each)
- 4 × SATA Gen 1, 2, 3 (6 Gb/s)
- 2 × USB 1.1, 2.0, 3.1 Gen 2 (10 Gb/s)
- 6 × USB 1.1, 2.0, 3.1 Gen 1 (5 Gb/s)
- 6 × USB 1.1, 2.0
Processors using Socket TR4[edit]
| Model | Cores | Threads | L2$ | L3$ | Base | Turbo | Memory | TDP | Launched | Price | OPN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1900X | 8 | 16 | 4 MiB 4,096 KiB 4,194,304 B 0.00391 GiB | 16 MiB 16,384 KiB 16,777,216 B 0.0156 GiB | 3.8 GHz 3,800 MHz 3,800,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 180 W 180,000 mW 0.241 hp 0.18 kW | 31 August 2017 | $ 549.00 € 494.10 £ 444.69 ¥ 56,728.17 | YD190XA8AEWOF | |
| 1920X | 12 | 24 | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB 6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB | 32 MiB 32,768 KiB 33,554,432 B 0.0313 GiB | 3.5 GHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 180 W 180,000 mW 0.241 hp 0.18 kW | 10 August 2017 | $ 799.00 € 719.10 £ 647.19 ¥ 82,560.67 | YD192XA8AEWOF | |
| 1950X | 16 | 32 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 32 MiB 32,768 KiB 33,554,432 B 0.0313 GiB | 3.4 GHz 3,400 MHz 3,400,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 180 W 180,000 mW 0.241 hp 0.18 kW | 10 August 2017 | $ 999.00 € 899.10 £ 809.19 ¥ 103,226.67 | YD195XA8AEWOF | |
| 2920X | 12 | 24 | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB 6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB | 32 MiB 32,768 KiB 33,554,432 B 0.0313 GiB | 3.5 GHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | 4.3 GHz 4,300 MHz 4,300,000 kHz | DDR4-3600 | 180 W 180,000 mW 0.241 hp 0.18 kW | 29 October 2018 | $ 649.00 € 584.10 £ 525.69 ¥ 67,061.17 | YD292XA8UC9AF |
| 2950X | 16 | 32 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 32 MiB 32,768 KiB 33,554,432 B 0.0313 GiB | 3.5 GHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 180 W 180,000 mW 0.241 hp 0.18 kW | 31 August 2018 | $ 899.00 € 809.10 £ 728.19 ¥ 92,893.67 | YD295XA8UGAAF |
| 2970WX | 24 | 48 | 12 MiB 12,288 KiB 12,582,912 B 0.0117 GiB | 64 MiB 65,536 KiB 67,108,864 B 0.0625 GiB | 3 GHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 4.2 GHz 4,200 MHz 4,200,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 250 W 250,000 mW 0.335 hp 0.25 kW | 29 October 2018 | $ 1,299.00 € 1,169.10 £ 1,052.19 ¥ 134,225.67 | YD297XAZUHCAF |
| 2990WX | 32 | 64 | 16 MiB 16,384 KiB 16,777,216 B 0.0156 GiB | 64 MiB 65,536 KiB 67,108,864 B 0.0625 GiB | 3 GHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 4.2 GHz 4,200 MHz 4,200,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 250 W 250,000 mW 0.335 hp 0.25 kW | 13 August 2018 | $ 1,799.00 € 1,619.10 £ 1,457.19 ¥ 185,890.67 | YD299XAZUIHAF, YD299XAZAFWOF |
| Count: 7 |
Photos[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Package Diagrams[edit]
TR4 package. All dimensions in millimeters.
Socket Diagrams[edit]
Pin Map[edit]
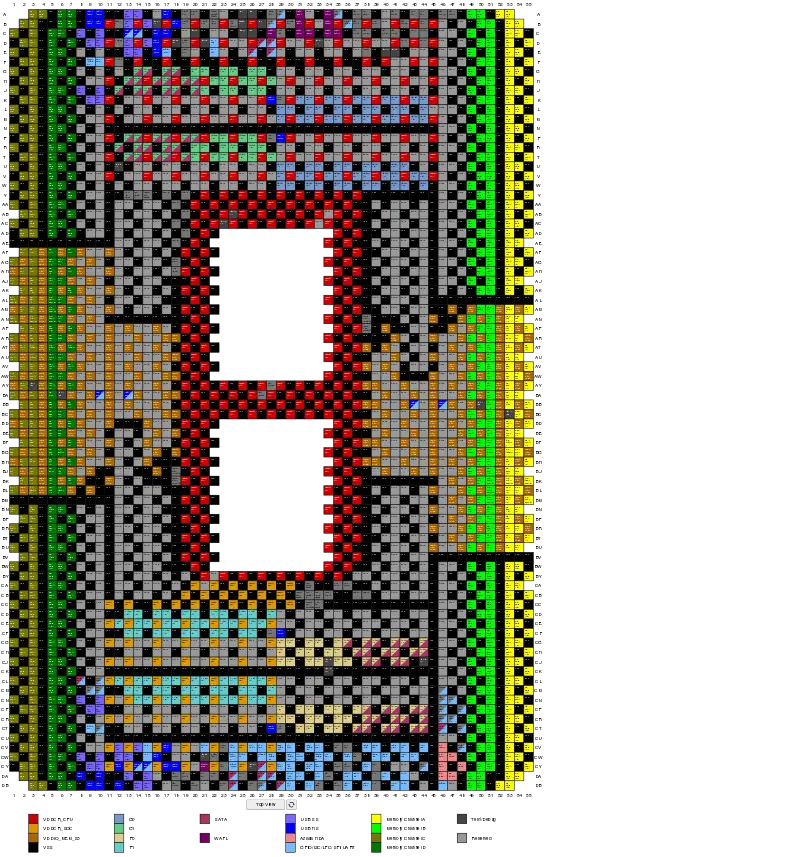
Socket TR4 (SP3r2) pinout, top view. This is a preview, click for a larger image and other views.
Pin Description[edit]
| Signal | Type | Description | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA-MD_ACT_L | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Channel A-D Activation Command | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_ADD[13:0] | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Column/Row Address | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_ADD_17 | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Column/Row Address 17 | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_ALERT_L | I-IOMEM-S | DRAM Alert (CRC error and Command/Address parity error) | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_BANK[1:0] | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Bank Address | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_BG[1:0] | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Bank Group | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_CAS_L_ADD[15] | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Column Address Strobe or Column/Row Address 15 | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_CHECK[7:0] | B-IOMEM-S | DRAM ECC Check Bits | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_C[2:0] | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Chip ID Signals | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_DATA[63:0] | B-IOMEM-S | DRAM Data Bus | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_DQS_H/L[8:0] | B-IOMEM-S | DRAM Differential Data Strobe | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_DQS_H[17:9] | B-IOMEM-S | DRAM Differential Data Strobe for RDIMMs, DM[8:0] Data Mask output for UDIMMs; RDIMMs not supported on Socket TR4 | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_DQS_L[17:9] | B-IOMEM-S | DRAM Differential Data Strobe for RDIMMs, not connected for UDIMMs | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_EVENT_L | I-IOMEM-S | DRAM Thermal Event | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_PAROUT | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Command and Address Parity | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_RAS_L_ADD[16] | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Row Address Strobe or Column/Row Address 16 | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_RESET_L | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Reset | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_WE_L_ADD[14] | O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Write Enable or Column/Row Address 14 | |||||||||||||||
| MA-MD_ZVSS | A | DRAM Interface Drive-Strength Auto-Compensation Resistor to VSS | |||||||||||||||
| MA0-MD0_CKE[1:0] MA1-MD1_CKE[1:0] |
O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Channel A-D DIMM 0-1 Clock Enable | |||||||||||||||
| MA0-MD0_CLK_H/L[1:0] MA1-MD1_CLK_H/L[1:0] |
O-IOMEM-D | DRAM Channel A-D DIMM 0-1 Differential Clock | |||||||||||||||
| MA0-MD0_CS_L[1:0] MA1-MD1_CS_L[1:0] |
O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Channel A-D DIMM 0-1 Chip Select | |||||||||||||||
| MA0-MD0_ODT[1:0] MA1-MD1_ODT[1:0] |
O-IOMEM-S | DRAM Channel A-D DIMM 0-1 Enable Pin for On Die Termination | |||||||||||||||
| FORCE_SELFREFRESH | I-IO33-S | NVDIMM Force Self-Refresh; NVDIMMs not supported on Socket TR4 | |||||||||||||||
| NV_SAVE_L | O-IO18-S | NVDIMM SAVE Signal | |||||||||||||||
| P0/P1_RXP/RXN[15:0] | I-PCIE-D | PCIe Interface P0/P1 Receive Data Differential Pairs | |||||||||||||||
| P0/P1_TXP/TXN[15:0] | O-PCIE-D | PCIe Transmit Data Differential Pairs | |||||||||||||||
| P0A/P1B_ZVSS | A | PCIe Drive-Strength Auto-Compensation Resistor to VSS for P0/P1 | |||||||||||||||
| G0/G1_RXP/RXN[15:0] | I-PCIE-D | PCIe Interface G0/G1 Receive Data Differential Pairs | |||||||||||||||
| G0/G1_TXP/TXN[15:0] | O-PCIE-D | PCIe Transmit Data Differential Pairs | |||||||||||||||
| G0B/G1A_ZVSS | A | PCIe Drive-Strength Auto-Compensation Resistor to VSS for G0/G1 | |||||||||||||||
| PCIE_RST(0-1)_L | Reset signal for PCIe devices, die 0/1 | ||||||||||||||||
| WAFL_RXP/RXN[1:0] | I-WAFL-D | WAFL Receive Data Differential Pairs; WAFL not supported on Socket TR4 | |||||||||||||||
| WAFL_TXP/TXN[1:0] | O-WAFL-D | WAFL Transmit Data Differential Pairs | |||||||||||||||
| WAFL(0-1)_ZVSS | A | WAFL Drive-Strength Auto-Compensation Resistor to VSS, die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| SATA(0-1)(0-7)_RXP/RXN | I-SATA-D | SATA Receive Data Differential Pairs (alt. func. of P0, G1 lane 0-7) | |||||||||||||||
| SATA(0-1)(0-7)_TXP/TXN | O-SATA-D | SATA Transmit Data Differential Pairs | |||||||||||||||
| DEVSLP(0-1) | SATA DEVSLP | ||||||||||||||||
| SATA_ACT_0/1_L | SATA Channel Active (HD LED), die 0/1 | ||||||||||||||||
| SGPIO(0-1)_CLK | O-IO33S5-S | SGPIO Interface CLK Output; SGPIO not supported on Socket TR4 | |||||||||||||||
| SGPIO(0-1)_DATAIN | I-IO33S5-S | SGPIO DATA Input | |||||||||||||||
| SGPIO(0-1)_DATAOUT | O-IO33S5-S | SGPIO DATA Output | |||||||||||||||
| SGPIO(0-1)_LOAD | O-IO33S5-S | SGPIO LOAD Output | |||||||||||||||
| XGBE(0-1)(0-3)_RXP/RXN | I-XGBE-D | XGBE Receive Data Differential Pairs (alt. func. of P0, G1 lane 4-7); XGBE not supported on Socket TR4 | |||||||||||||||
| XGBE(0-1)(0-3)_TXP/TXN | O-XGBE-D | XGBE Transmit Data Differential Pairs | |||||||||||||||
| MDIO(0-3)_SCL | MDIO Port 0-3 Clock (alt. func. of SGPIO interface); MDIO not supported on Socket TR4 | ||||||||||||||||
| MDIO(0-3)_SDA | MDIO Data | ||||||||||||||||
| USB_0/1_HSD(0-3)P/N | B-IO33S5-D | USB Port 0-3 High Speed I/O Differential Pairs; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| USB_0/1_SS_(0-3)RXP/RXN | I-USBS5-D | USB Port 0-3 Super Speed Receive Differential Pairs; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| USB_0/1_SS_(0-3)TXP/TXN | O-USBS5-D | USB Port 0-3 Super Speed Transmit Differential Pairs; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| USB_0/1_OC(0-3)_L | I-IO33S5-S | USB Port 0-3 Over Current signal from USB connector; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| USB_0/1_(0-3)_ZVSS | A | USB Port 0-3 Drive-Strength Auto-Compensation Resistor to VSS; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| AZ_BITCLK | B-AUD_S5-S | Azalia HD Audio Interface Bit Clock; all audio signals routed to die 0 | |||||||||||||||
| AZ_RST_L | B-AUD_S5-S | HDA Reset | |||||||||||||||
| AZ_SDIN(0-2) | B-AUD_S5-S | HDA Serial Data Input from Codec 0-2 | |||||||||||||||
| AZ_SDOUT | B-AUD_S5-S | HDA Serial Data Output to Codec | |||||||||||||||
| AZ_SYNC | B-AUD_S5-S | HDA Sync Signal to Codec | |||||||||||||||
| SPKR | O-IO33-S | PC speaker/beeper PWM output | |||||||||||||||
| UART(0-1)_CTS_L | I-IO33-S | UART Clear To Send Input (alt. func. of UART(2-3)_RXD) | |||||||||||||||
| UART(0-1)_INTR | B-IO33-S | UART Interrupt Request | |||||||||||||||
| UART(0-1)_RTS_L | B-IO33-S | UART Request To Send Output (alt. func. of UART(2-3)_TXD) | |||||||||||||||
| UART(0-3)_RXD | I-IO33-S | UART Receive Data | |||||||||||||||
| UART(0-3)_TXD | O-IO33-S | UART Transmit Data | |||||||||||||||
| SPI_CLK | O-IO18-S | SPI Clock; all SPI signals routed to die 0 | |||||||||||||||
| SPI_DO | B-IO18-S | SPI Data Out or Data 0 for multi-I/O ESPI device | |||||||||||||||
| SPI_DI | B-IO18-S | SPI Data In or Data 1 | |||||||||||||||
| SPI_WP_L | B-IO18-S | SPI Write Protect or Data 2 | |||||||||||||||
| SPI_HOLD_L | B-IO18-S | SPI Hold Signal (asserted low to hold the SPI transaction) or Data 3 | |||||||||||||||
| PSP_ROM_CS_L SPI_TPM_CS_L |
O-IO18-S | SPI Chip Select for PSP ROM or TPM | |||||||||||||||
| SPI_CS1/CS2_L | O-IO18-OD | SPI Chip Select | |||||||||||||||
| ESPI_CLK | O-IO18-S | ESPI Clock (alt. func. of SPI_CLK) | |||||||||||||||
| ESPI_DAT(0-3) | B-IO33-S | ESPI Data[0], Data[1:0], Data[3:0] (alt. func. of SPI_DO/DI/WP_L/HOLD_L) | |||||||||||||||
| ESPI_CS_L | O-IO18-S | ESPI Chip Select (SPI_CS2_L) | |||||||||||||||
| ESPI_ALERT_L | I-DUAL-S | ESPI Alert Input (LDRQ0_L) | |||||||||||||||
| ESPI_RESET_L | B-IO33-S | ESPI Reset (KBRST_L) | |||||||||||||||
| LAD(0-3) | B-IO33-S | LPC Command/Address/Data; all LPC signals routed to die 0 | |||||||||||||||
| LDRQ0_L | I-IO33-S | Encoded DMA/Bus Master Request 0 | |||||||||||||||
| LFRAME_L | O-IO33-S | LPC Bus Frame | |||||||||||||||
| LPCCLK(0-1) | O-IO33-S | LPC 33 MHz Clock | |||||||||||||||
| LPC_CLKRUN_L | B-IO33-OD | LPC CLKRUN Signal | |||||||||||||||
| LPC_PD_L | O-DUAL_S5-S | LPC Power Down | |||||||||||||||
| LPC_PME_L | I-IO33S5-S | LPC Power Management Event | |||||||||||||||
| LPC_RST_L | O-IO33S5-S | LPC Reset | |||||||||||||||
| LPC_SMI_L | I-IO33-S | LPC System Management Interrupt | |||||||||||||||
| SERIRQ | B-IO33-S | Serial IRQ for DMA | |||||||||||||||
| I2C(0-5)_SCL | B-DUAL-OD | I2C Port 0-5 Clock | |||||||||||||||
| I2C(0-5)_SDA | B-DUAL-OD | I2C Data | |||||||||||||||
| SCL0 | B-IO33-OD | SMBus Port 0 Clock (alt. func. of I2C2) | |||||||||||||||
| SDA0 | B-IO33-OD | SMBus Port 0 Data | |||||||||||||||
| SCL1 | B-DUAL_S5-OD | SMBus Port 1 Clock (alt. func. of I2C3) | |||||||||||||||
| SDA1 | B-DUAL_S5-OD | SMBus Port 1 Data | |||||||||||||||
| HP_SCL, HP_SDA | Hotplug SMBus (I2C0) | ||||||||||||||||
| SFP_SCL, SFP_SDA | SFP Bus (I2C1) | ||||||||||||||||
| SPD_SCL, SPD_SDA | SPD Bus (I2C2) | ||||||||||||||||
| BMC_SCL, BMC_SDA | BMC SMBus (I2C3) | ||||||||||||||||
| AGPIO*_0/1 | Advanced GPIO pin for interrupt, wake, or I/O; die 0/1 | ||||||||||||||||
| EGPIO*_0/1 | Enhanced GPIO for I/O only; die 0/1 | ||||||||||||||||
| EGPIO* | Enhanced GPIO for I/O only; die 0 | ||||||||||||||||
| GENINT(1-2)_L | I-IO33-S | Generic Interrupt Request | |||||||||||||||
| GFX_CLK00P/N | B-PCIe_S5-D | PCIe Expansion 100 MHz Differential PCIe Reference Clock; die 0 | |||||||||||||||
| GFX_CLK1(0-1)P/N | B-PCIe_S5-D | PCIe Expansion 100 MHz Differential PCIe Reference Clock; die 1 | |||||||||||||||
| GPP_CLK0(0-3)P/N | O-PCIe_S5-D | GPP Expansion 100 MHz Differential Reference Clock; die 0 | |||||||||||||||
| GPP_CLK1(1-3)P/N | O-PCIe_S5-D | GPP Expansion 100 MHz Differential Reference Clock; die 1 | |||||||||||||||
| CLK_REQ(0-3)_0_L | B-IO33-S | PCIe 0 Clock Request 0-3; die 0 | |||||||||||||||
| CLK_REQ(1-3)_1_L | B-IO33-S | PCIe 0 Clock Request 1-3; die 1 | |||||||||||||||
| CLK_REQG_0/1_L | B-IO33-S | PCIe Graphic Slot Clock Request / 14 MHz Clock Input; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| X156M_H/L[1:0] | Differential 156.25 MHz Reference CLK Input; XGBE not supported on Socket TR4 | ||||||||||||||||
| X32K_X1/X2 | I-IO18S5-S | 32 kHz Clock XTAL or (X32K_X1 only) Clock Input, for the integrated RTC | |||||||||||||||
| X48M_X1/X2 | I-IO18S5-S | 48 MHz Clock XTAL or (X48M_X1 only) Clock Input, for the integrated clock generator | |||||||||||||||
| RTCCLK | O-IO18S5-S | 32 kHz Real Time Clock Output, for a device requiring an RTC clock | |||||||||||||||
| KBRST_L | I-IO33-S | Keyboard Controller Reset Input (warm reset) | |||||||||||||||
| PWR_BTN_L | I-IO33S5 | Power Button; Requests sleep state or causes wake event | |||||||||||||||
| PWR_GOOD | I-IO33S5 | Power Good Input; Asserted when all voltages and clock inputs are within specification | |||||||||||||||
| PWROK | B-IO18-OD | Power OK; Asserted by the processor after all power planes are active, the system clock generators are powered up and run stably | |||||||||||||||
| RESET_L | B-IO18-S | Bidirectional signal that resets the processor when asserted; Normally controlled by an internal state machine but can also be asserted by a second external source | |||||||||||||||
| RSMRST_L | I-IO18S5-S | Resume Reset from motherboard, resets all in-processor S5 and S0 logic. Asserted on power up, deasserted when S5 power supplies are within specification. | |||||||||||||||
| S0A3_GPIO_0/1 | B-IO33S5-S | S0A3 Indicator | |||||||||||||||
| SLP_S3/S5_L | O-IO33S5-S | S3/S5 Sleep State Power Plane Control Signal | |||||||||||||||
| SYS_RESET_L | I-IO33S5-S | System Reset Input (reset button) | |||||||||||||||
| WAKE_L | I-IO33S5-S | PCIe WAKE_L signal, wake system out of sleep state | |||||||||||||||
| BLINK | B-IO33S5-S | Blink LED S-state Indicator | |||||||||||||||
| FANIN(0-1) | I-IO33-S | Fan tachometer input; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| FANOUT(0-1) | O-IO33-S | Fan PWM output; die 0/1 | |||||||||||||||
| ALERT_L | O-IO33-OD | Programmable pin that can indicate different events, including a SB-TSI interrupt | |||||||||||||||
| PROCHOT_L | I-IO33-OD | Asserted to force the processor into HTC-active state | |||||||||||||||
| SIC | B-DUAL-OD | Sideband Interface Clock [1] | |||||||||||||||
| SID | B-DUAL-OD | Sideband Interface Data | |||||||||||||||
| THERMTRIP_L | B-IO33-OD | Temperature Trip Input/Output | |||||||||||||||
| DBREQ_L | I-IO18S5-S | Debug Request input to JTAG controller | |||||||||||||||
| TCK | I-IO18S5-S | JTAG Clock | |||||||||||||||
| TDI | I-IO18S5-S | JTAG Data Input | |||||||||||||||
| TDO | O-IO18S5-S | JTAG Data Output | |||||||||||||||
| TMS | I-IO18S5-S | JTAG Mode Select | |||||||||||||||
| TRST_L | I-IO18S5-S | JTAG Reset | |||||||||||||||
| TEST* | Test Pins | ||||||||||||||||
| XTRIG_L[7:4] | B-IO18-OD | XTRIG Debug Signals | |||||||||||||||
| SVC_CPU, SVC_SOC | O-IO18-S | Serial VID Interface Clock for VDDCR_CPU, VDDCR_SOC regulator | |||||||||||||||
| SVD_CPU, SVD_SOC | B-IO18-S | Serial VID Interface Data | |||||||||||||||
| SVT_CPU, SVT_SOC | I-IO18-S | Serial VID Interface Telemetry | |||||||||||||||
| VDDIO_AUDIO | S | Azalia HD Audio power supply, 1.5 V or 1.8 V ±5% | |||||||||||||||
| VDDBT_RTC_G | S | Integrated Real Time Clock battery power supply, 1.5 V ±5% or 1.8 V ±5% [2] | |||||||||||||||
| VDDCR_CPU | S | Supply voltage for the CPU core | |||||||||||||||
| VDDCR_CPU_SENSE | A | VDDCR_CPU voltage sense output, differential feedback with VSS_SENSE_A | |||||||||||||||
| VDDCR_SOC | S | Supply voltage for the Northbridge (integrated FCH, SATA, NBIO, SMU, DDR PHY logic) | |||||||||||||||
| VDDCR_SOC_SENSE | A | VDDCR_SOC voltage sense output, differential feedback with VSS_SENSE_B | |||||||||||||||
| VDDCR_SOC_S5 | S | Always on 0.9 V ± 20 mV supply voltage for the FCH and USB PHYs | |||||||||||||||
| VDDCR_SOC_S5_SENSE | A | VDDCR_SOC_S5 voltage sense output, differential feedback with VSS_SENSE_B | |||||||||||||||
| VDDIO_MEM_S3_AB/CD | S | 1.2 V ±5% supply voltage for DIMMs, PCIe PHYs, SATA PHYs, and an auxiliary supply for the DDR section of the processor | |||||||||||||||
| VDDIO_MEM_S3_AB_FB_H/L | A | VDDIO_MEM_S3_AB voltage differential feedback to VDDIO_MEM_S3_AB regulator | |||||||||||||||
| VDDIO_MEM_S3_CD_FB_H/L | A | VDDIO_MEM_S3_CD voltage differential feedback | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_18 | S | 1.8 V ±2% supply voltage | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_18_SENSE | A | VDD_18 voltage monitor pin, differential feedback with VSS_SENSE_A | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_18_S5 | S | Always on 1.8 V ±5% supply voltage | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_18_S5_SENSE | A | VDD_18_S5 voltage monitor pin, differential feedback with VSS_SENSE_A | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_33 | S | 3.3 V ±5% supply voltage | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_33_SENSE | A | VDD_33 voltage monitor pin, differential feedback with VSS_SENSE_B | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_33_S5 | S | Always on 3.3 V ±5% supply voltage | |||||||||||||||
| VDD_33_S5_SENSE | A | VDD_33_S5 voltage monitor pin, differential feedback with VSS_SENSE_B | |||||||||||||||
| VSS | S | Ground | |||||||||||||||
| VSS_SENSE_A | A | VSS sense pin for VDDCR_CPU, VDD_18, VDD_18_S5 regulator | |||||||||||||||
| VSS_SENSE_B | A | VSS sense pin for VDDCR_SOC, VDDCR_SOC_S5, VDD_33, VDD_33_S5 regulator | |||||||||||||||
| CORETYPE | Processor Core Type Indicator; NC = Not connected, VSS = connected to VSS on the package
| ||||||||||||||||
| SP3R1, SP3R2 | Processor Family Revision Identifier (electrical keying); NC = Not connected, VSS = connected to VSS on the package
| ||||||||||||||||
| CPU_PRESENT_L | CPU Presence Indicator; connected to VSS on the package | ||||||||||||||||
| SA[2:0] | I-IO18S5-S | Socket Identifier | |||||||||||||||
| RSVD | Reserved |
- ↑ The Sideband Interface (SBI) a.k.a. APML is a SMBus interconnect to the processor's SB-RMI and SB-TSI interfaces.
- ↑ From 1.5 V or 1.8 V always on supply, or 3 V coin cell battery using an LDO, or jumpered to VSS to "Clear CMOS".
Pin Types[edit]
| I/O/B-PCIe/SATA/XGBE/WAFL-D | Input / Output / Bidirectional, PCIe / SATA / XGBE / WAFL Voltage Domain, Differential |
| I/O/B-USBS5-S/OD | Input / Output / Bidirectional, USB (VDDCR_SOC_S5) Voltage Domain, Single-Ended / Open Drain |
| I/O/B-IOMEM-D/S | Input / Output / Bidirectional, VDDIO_MEM_S3, Differential / Single-Ended |
| I/O/B-IO18-D/S/OD | Input / Output / Bidirectional, VDD_18, Differential / Single-Ended / Open Drain |
| I/O/B-IO18S5-D/S/OD | Input / Output / Bidirectional, VDD_18_S5, Differential / Single-Ended / Open Drain |
| I/O/B-IO33-D/S/OD | Input / Output / Bidirectional, VDD_33, Differential / Single-Ended / Open Drain |
| I/O/B-IO33S5-D/S/OD | Input / Output / Bidirectional, VDD_33_S5, Differential / Single-Ended / Open Drain |
| I/O/B-DUAL-S/OD | Input / Output / Bidirectional, VDD_18 or VDD_33, Single-Ended / Open Drain |
| I/O/B-DUAL_S5-S/OD | Input / Output / Bidirectional, VDD_18_S5 or VDD_33_S5, Single-Ended / Open Drain |
| O/B-AUD_S5-S | Output / Bidirectional, VDDIO_AUDIO (VDD_18_S5), Single-Ended |
| O/B-PCIe_S5-D | Output / Bidirectional, PCIe Clock, Differential |
| A | Analog |
| S | Supply Voltage |
Socket SP3/TR4 Differences[edit]
| Pin | Socket SP3 | Socket TR4 a.k.a. SP3r2 |
|---|---|---|
| E25 | AGPIO23_1/SGPIO1_LOAD/MDIO3_SDA | RSVD |
| E28 | AGPIO23_2/SGPIO2_LOAD/MDIO5_SDA | EGPIO23_1/SGPIO1_LOAD/MDIO3_SDA |
| CY42 | AGPIO23_3/SGPIO3_LOAD/MDIO7_SDA | RSVD |
| D24 | AGPIO40_1/SGPIO1_DATAIN/MDIO2_SDA | RSVD |
| D27 | AGPIO40_2/SGPIO2_DATAIN/MDIO4_SDA | EGPIO40_1/SGPIO1_DATAIN/MDIO2_SDA |
| DB44 | AGPIO40_3/SGPIO3_DATAIN/MDIO6_SDA | RSVD |
| D25 | AGPIO9_1/SGPIO1_DATAOUT/MDIO3_SCL | RSVD |
| D28 | AGPIO9_2/SGPIO2_DATAOUT/MDIO5_SCL | EGPIO9_1/SGPIO1_DATAOUT/MDIO3_SCL |
| CY41 | AGPIO9_3/SGPIO3_DATAOUT/MDIO7_SCL | RSVD |
| E40 | BP0 (Break Point Indicator, test/debug) | TEST14 |
| E41 | BP1 | TEST15 |
| D21 | BP2 | TEST16 |
| C20 | BP3 | TEST17 |
| C22 | BP4 | RSVD |
| C23 | BP5 | RSVD |
| misc. | G1 interface | All pins RSVD |
| P29 | G1B_ZVSS | USB_1_3_ZVSS |
| misc. | G2 interface | G1 interface |
| misc. | G3 interface | All pins RSVD |
| K28 | G3A_ZVSS | USB_1_2_ZVSS |
| DB20 | GPP_CLK0BN | GPP_CLK01N |
| DA19 | GPP_CLK0BP | GPP_CLK01P |
| DB18 | GPP_CLK0TN | GFX_CLK00N |
| DA18 | GPP_CLK0TP | GFX_CLK00P |
| B42 | GPP_CLK1BN | GPP_CLK13N |
| A41 | GPP_CLK1BP | GPP_CLK13P |
| C41 | GPP_CLK1TN | GPP_CLK12N |
| C40 | GPP_CLK1TP | GPP_CLK12P |
| A37 | GPP_CLK2BN | GFX_CLK11N |
| B37 | GPP_CLK2BP | GFX_CLK11P |
| C38 | GPP_CLK2TN | GFX_CLK10N |
| C37 | GPP_CLK2TP | GFX_CLK10P |
| DB35 | GPP_CLK3BN | GPP_CLK03N |
| DA34 | GPP_CLK3BP | GPP_CLK03P |
| CY36 | GPP_CLK3TN | GPP_CLK02N |
| CY35 | GPP_CLK3TP | GPP_CLK02P |
| misc. | Memory channel B | All pins RSVD with the following exceptions |
| AR40 | MB0_CKE[0] (DRAM Clock Enable) | VSS |
| AP41 | MB0_CKE[1] | VSS |
| AT39 | MB1_CKE[0] | VSS |
| AR39 | MB1_CKE[1] | VSS |
| BB43 | MB_ANALOGOUT (Test pin) | USB_0_OC3_L/AGPIO24_0 |
| AP39 | MB_RESET_L | VSS |
| misc. | Memory channel C | All pins RSVD with the following exceptions |
| AN47 | MC0_CKE[0] | VSS |
| AM48 | MC0_CKE[1] | VSS |
| AP46 | MC1_CKE[0] | VSS |
| AN46 | MC1_CKE[1] | VSS |
| BB46 | MC_ANALOGOUT | USB_0_OC2_L/AGPIO18_0 |
| A47 | MC_DATA[0] | GPP_CLK11P |
| CM46 | MC_DATA[49] | FANIN0/AGPIO84_0/NMI |
| CT48 | MC_DATA[50] | CLK_REQ0_0_L/AGPIO92_0 |
| CT46 | MC_DATA[51] | SATA_ACT_0_L/AGPIO130_0 |
| CR47 | MC_DATA[54] | CLK_REQ2_0_L/AGPIO116_0 |
| CR46 | MC_DATA[55] | CLK_REQG_0_L/OSCIN/EGPIO132_0 |
| CV48 | MC_DATA[56] | SPKR/AGPIO91 |
| CV46 | MC_DATA[57] | AZ_SDOUT |
| DA46 | MC_DATA[58] | AZ_SYNC |
| DB46 | MC_DATA[59] | AGPIO8 |
| A46 | MC_DATA[5] | GPP_CLK11N |
| DA47 | MC_DATA[62] | AZ_BITCLK |
| CN47 | MC_DQS_H[15] | FANOUT0/AGPIO85_0 |
| CW47 | MC_DQS_H[16] | AZ_SDIN2 |
| CP46 | MC_DQS_H[6] | CLK_REQ3_0_L/EGPIO131_0 |
| CY46 | MC_DQS_H[7] | AZ_RST_L |
| CP48 | MC_DQS_L[15] | CLK_REQ1_0_L/AGPIO115_0 |
| CY48 | MC_DQS_L[16] | AZ_SDIN0 |
| CN46 | MC_DQS_L[6] | GENINT2_L/AGPIO90 |
| CW46 | MC_DQS_L[7] | AZ_SDIN1 |
| AM46 | MC_RESET_L | VSS |
| misc. | Memory channel D | Memory channel B |
| misc. | Memory channel E | Memory channel C |
| misc. | Memory channel F | All pins RSVD with the following exceptions |
| BH16 | MF0_CKE[0] | VSS |
| BJ15 | MF0_CKE[1] | VSS |
| BG17 | MF1_CKE[0] | VSS |
| BH17 | MF1_CKE[1] | VSS |
| BA13 | MF_ANALOGOUT | USB_1_OC3_L/EGPIO24_1 |
| BJ17 | MF_RESET_L | VSS |
| misc. | Memory channel G | All pins RSVD with the following exceptions |
| BK9 | MG0_CKE[0] | VSS |
| BL8 | MG0_CKE[1] | VSS |
| BJ10 | MG1_CKE[0] | VSS |
| BK10 | MG1_CKE[1] | VSS |
| BA10 | MG_ANALOGOUT | USB_1_OC2_L/EGPIO18_1 |
| DB9 | MG_DATA[0] | USB_0_HSD3N |
| CL10 | MG_DATA[10] | CLK_REQG_1_L/EGPIO132_1 |
| CL8 | MG_DATA[11] | SATA_ACT_1_L/EGPIO130_1 |
| CT10 | MG_DATA[12] | CLK_REQ3_1_L/EGPIO131_1 |
| CT9 | MG_DATA[13] | EGPIO92_1 |
| CM10 | MG_DATA[14] | CLK_REQ2_1_L/EGPIO116_1 |
| CM9 | MG_DATA[15] | CLK_REQ1_1_L/EGPIO115_1 |
| DA8 | MG_DATA[1] | USB_0_HSD3P |
| DA10 | MG_DATA[4] | USB_0_HSD2P |
| B10 | MG_DATA[58] | USB_1_HSD2P |
| A10 | MG_DATA[59] | USB_1_HSD2N |
| DB10 | MG_DATA[5] | USB_0_HSD2N |
| F9 | MG_DATA[60] | FANIN1/EGPIO84_1 |
| F10 | MG_DATA[61] | FANOUT1/EGPIO85_1 |
| B9 | MG_DATA[62] | USB_1_HSD3P |
| A9 | MG_DATA[63] | USB_1_HSD3N |
| CW8 | MG_DQS_H[0] | USB_0_SS_3TXP |
| CP10 | MG_DQS_H[10] | USB_0_SS_2RXP |
| K9 | MG_DQS_H[15] | USB_1_SS_2RXN |
| D9 | MG_DQS_H[16] | USB_1_SS_2TXP |
| CN8 | MG_DQS_H[1] | USB_0_SS_3RXN |
| J10 | MG_DQS_H[6] | USB_1_SS_3RXP |
| C10 | MG_DQS_H[7] | USB_1_SS_3TXN |
| CY10 | MG_DQS_H[9] | USB_0_SS_2TXN |
| CY9 | MG_DQS_L[0] | USB_0_SS_3TXN |
| CN10 | MG_DQS_L[10] | USB_0_SS_2RXN |
| J8 | MG_DQS_L[15] | USB_1_SS_2RXP |
| C8 | MG_DQS_L[16] | USB_1_SS_2TXN |
| CP9 | MG_DQS_L[1] | USB_0_SS_3RXP |
| K10 | MG_DQS_L[6] | USB_1_SS_3RXN |
| D10 | MG_DQS_L[7] | USB_1_SS_3TXP |
| CW10 | MG_DQS_L[9] | USB_0_SS_2TXP |
| BL10 | MG_RESET_L | VSS |
| misc. | Memory channel H | Memory channel D |
| misc. | P1 interface | All pins RSVD |
| CF29 | P1A_ZVSS | USB_0_3_ZVSS |
| misc. | P2 interface | P1 interface |
| misc. | P3 interface | All pins RSVD |
| CT28 | P3B_ZVSS | USB_0_2_ZVSS |
| A23 | PCIE_RST1_L/EGPIO26_1 | RSVD |
| B28 | PCIE_RST2_L/EGPIO26_2 | PCIE_RST1_L/EGPIO26_1 |
| DB21 | PCIE_RST3_L/EGPIO26_3 | RSVD |
| CY44 | PM_INTR_L/AGPIO89 | GENINT1_L/AGPIO89 |
| AY28 | REFCLK100SSC_N | GPP_CLK00N |
| BA27 | REFCLK100SSC_P | GPP_CLK00P |
| E23 | S0A3_GPIO_1/AGPIO10_1/SGPIO1_CLK/MDIO2_SCL | RSVD |
| E26 | S0A3_GPIO_2/AGPIO10_2/SGPIO2_CLK/MDIO4_SCL | S0A3_GPIO_1/EGPIO10_1/SGPIO1_CLK/MDIO2_SCL |
| DA43 | S0A3_GPIO_3/AGPIO10_3/SGPIO3_CLK/MDIO6_SCL | RSVD |
| D34 | TEST41[1] | RSVD |
| B16 | TEST41[2] | TEST41[1] |
| CY20 | TEST41[3] | RSVD |
| CW36 | TEST47[0] | BLINK/AGPIO11 |
| E29 | TEST47[1] | RSVD |
| D18 | TEST47[2] | TEST47[0] |
| CW21 | TEST47[3] | TEST47[1] |
| AC33 | TEST4[1] | RSVD |
| AC23 | TEST4[2] | TEST4[1] |
| CA21 | TEST4[3] | RSVD |
| AB34 | TEST5[1] | RSVD |
| AB24 | TEST5[2] | TEST5[1] |
| BY22 | TEST5[3] | RSVD |
| DB12 | USB0_0_ZVSS | USB_0_0_ZVSS |
| CY12 | USB1_0_ZVSS | USB_0_1_ZVSS |
| D16 | USB2_1_ZVSS | USB_1_0_ZVSS |
| E16 | USB3_1_ZVSS | USB_1_1_ZVSS |
| C17 | USB_1_HSD2N | USB_1_HSD0N |
| C16 | USB_1_HSD2P | USB_1_HSD0P |
| B18 | USB_1_HSD3N | USB_1_HSD1N |
| A17 | USB_1_HSD3P | USB_1_HSD1P |
| E13 | USB_1_SS_2RXN | USB_1_SS_0RXN |
| D13 | USB_1_SS_2RXP | USB_1_SS_0RXP |
| A13 | USB_1_SS_2TXN | USB_1_SS_0TXN |
| B13 | USB_1_SS_2TXP | USB_1_SS_0TXP |
| D15 | USB_1_SS_3RXN | USB_1_SS_1RXN |
| E14 | USB_1_SS_3RXP | USB_1_SS_1RXP |
| B15 | USB_1_SS_3TXN | USB_1_SS_1TXN |
| A14 | USB_1_SS_3TXP | USB_1_SS_1TXP |
| CY15 | USB_OC0_L/AGPIO16_0 | USB_0_OC0_L/AGPIO16_0 |
| CY14 | USB_OC1_L/AGPIO17_0 | USB_0_OC1_L/AGPIO17_0 |
| C13 | USB_OC2_L/EGPIO16_1 | USB_1_OC0_L/EGPIO16_1 |
| C14 | USB_OC3_L/EGPIO17_1 | USB_1_OC1_L/EGPIO17_1 |
| misc. | VDDIO_MEM_S3_ABCD | VDDIO_MEM_S3_AB |
| AP38 | VDDIO_MEM_S3_ABCD_FB_H | VDDIO_MEM_S3_AB_FB_H |
| AN38 | VDDIO_MEM_S3_ABCD_FB_L | VDDIO_MEM_S3_AB_FB_L |
| misc. | VDDIO_MEM_S3_EFGH | VDDIO_MEM_S3_CD |
| BJ18 | VDDIO_MEM_S3_EFGH_FB_H | VDDIO_MEM_S3_CD_FB_H |
| BK18 | VDDIO_MEM_S3_EFGH_FB_L | VDDIO_MEM_S3_CD_FB_L |
| AG18 | VDD_18_S5_1 | VDDIO_AUDIO |
| F12 | VSS | SP3R2 |
| A16 | WAFL1_ZVSS | RSVD |
| C28 | WAFL2_ZVSS | WAFL1_ZVSS |
| DB17 | WAFL3_ZVSS | RSVD |
| E43 | X156M_H[1] | RSVD |
| F44 | X156M_L[1] | RSVD |
| D19 | X156M_H[2] | X156M_H[1] |
| E19 | X156M_L[2] | X156M_L[1] |
| CW19 | X156M_H[3] | RSVD |
| CV20 | X156M_L[3] | RSVD |
Bibliography[edit]
- David. S. (March 2018). "ISSCC 2018: AMD’s Zeppelin; Multi-chip routing and packaging"
- "Socket SP3 Design Specification", AMD Publ. #55260, Rev. 1.16, August 2020
- "SP3r2 Processor Platform Thermal Design Guide", AMD Publ. #55815, Rev. 1.03, July 2018
- "SP3r2 Processor Functional Data Sheet", AMD Publ. #55814, Rev. 1.03, June 2017
- "Electrical Data Sheet (EDS) for AMD Family 17h Models 00h-0Fh SP3r2 Processors", AMD Publ. #55443, Rev. 0.51, June 2019
- "SP3r2 Processor Infrastructure Roadmap", AMD Publ. #55557, Rev. 1.01, April 2017
- "SP3r2 Processor Motherboard Design Guide", AMD Publ. #55809, Rev. 1.03, October 2017
- "Revision Guide for AMD Family 17h Models 00h-0Fh Processors", AMD Publ. #55449, Rev. 1.19, December 2019
- Beck, Noah; White, Sean; Paraschou, Milam; Naffziger, Samuel (2018). ‘Zeppelin’: An SoC for multichip architectures. Proceedings of IEEE ISSCC 2018. pp. 40-42. doi:10.1109/ISSCC.2018.8310173
See also[edit]
- Socket AM4 • (Zen • Ryzen 3/5)
- Socket SP3 • Socket SP3 (EPYC 7001)
- Socket TR4 • Socket SP3r2 (Ryzen Threadripper 1900/2900)
- Socket sTRX4 • Socket SP3r3 (Ryzen Threadripper 3000X)
- Socket sWRX8 • Socket SP3r4 (Ryzen Threadripper Pro 3000WX/5000WX)
- Package SP4 • Package SP4r2 • BGA (EPYC 3000)
- Socket SP5 • (EPYC 9004)
| designer | AMD + |
| first announced | May 16, 2017 + |
| first launched | August 10, 2017 + |
| instance of | package + |
| market segment | Desktop + and Workstation + |
| microarchitecture | Zen + and Zen+ + |
| name | Socket TR4 + |
| package | TR4 + and FCLGA-4094 + |
| package contacts | 4,094 + |
| package height | 6.26 mm (0.246 in) + |
| package length | 75.4 mm (7.54 cm, 2.969 in) + |
| package pitch | 0.87 mm (0.0343 in) + and 1 mm (0.0394 in) + |
| package type | FC-OLGA + |
| package width | 58.5 mm (5.85 cm, 2.303 in) + |
| socket | TR4 +, SP3r2 + and sTR4 + |
| tdp | 180 W (180,000 mW, 0.241 hp, 0.18 kW) + and 250 W (250,000 mW, 0.335 hp, 0.25 kW) + |