| Edit Values | |
| Cannon Lake µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | May 15, 2018 |
| Process | 10 nm |
| Core Configs | 2 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Stages | 14-19 |
| Decode | 5-way? |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Extensions | MOVBE, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, POPCNT, AVX, AVX2, AES, PCLMUL, FSGSBASE, RDRND, FMA3, F16C, BMI, BMI2, VT-x, VT-d, TXT, TSX, RDSEED, ADCX, PREFETCHW, CLFLUSHOPT, XSAVE, SGX, MPX, AVX-512, AVX-512F, AVX-512CD, AVX-512BW, AVX-512DQ, AVX-512VL, AVX-512IFMA, AVX-512VBMI, SHA, UMIP |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 32 KiB/core 8-way set associative |
| L1D Cache | 32 KiB/core 8-way set associative |
| L2 Cache | 256 KiB/core 4-way set associative |
| L3 Cache | 2 MiB/core Up to 16-way set associative |
| Succession | |
| Contemporary | |
| Coffee Lake | |
Cannon Lake (CNL) (formerly Skymont) is a planned microarchitecture by Intel as a successor to Kaby Lake. Cannon Lake is expected to be fabricated using a 10 nm process and is set to be introduced in the second half of 2018. Cannon Lake is the "Process" microarchitecture as part of Intel's PAO model.
For mobile, Cannon Lake is expected to be branded as 8th Generation Intel Core i3, Core i5. and Core i7 processors.
Contents
Codenames[edit]
| Core | Abbrev | Description | Graphics | Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cannon Lake U | CNL-U | Ultra-low Power | GT2/GT3 | Light notebooks, portable All-in-Ones (AiOs), Minis, and conference room |
Release Dates[edit]
Initial Cannon Lake models were introduced in May 2018 with additional models planned throughout the year.
Process Technology[edit]
Cannon Lake is manufactured on Intel's 10 nm process (P1274). Intel's 10 nm process is among the first high-volume manufacturing processes to employ Self-Aligned Quad Patterning (SAQP) (goes under the "Hyper-Scaling" marketing name). Intel's 10nm features a 0.0367 µm² SRAM bit cell.
| Broadwell | Cannon Lake |
Δ | 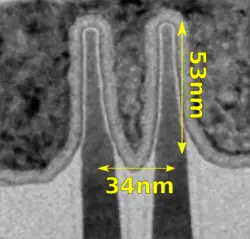
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 nm | 10 nm | |||
| Fin Pitch | 42 nm | 34 nm | 0.81x | |
| Fin Width | 8 nm | 7 nm | 0.88x | |
| Fin Height | 42 nm | 53 nm | 1.24x | |
| Gate Pitch | 70 nm | 54 nm | 0.77x | |
| Interconnect Pitch | 52 nm | 36 nm | 0.69x | |
| Cell Height | 399 nm | 272 nm | 0.68x |
Compiler support[edit]
Support for Cannon Lake was added in GCC 8.1 and LLVM 6.0.
| Compiler | Arch-Specific | Arch-Favorable |
|---|---|---|
| ICC | -march=cannonlake |
-mtune=cannonlake
|
| GCC | -march=cannonlake |
-mtune=cannonlake
|
| LLVM | -march=cannonlake |
-mtune=cannonlake
|
| Visual Studio | ? |
?
|
CPUID[edit]
| Core | Extended Family |
Family | Extended Model |
Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U | 0 | 0x6 | 0x6 | 0x6 |
| Family 6 Model 102 | ||||
Architecture[edit]
Key changes from Skylake[edit]
- 10 nm process (from 14 nm)
- Palm Cove core (from Skylake)
- See Palm Cove for microarchitectural details and changes
- Mainstream chipset
- Mobile Processors
- LPDDR4/LPDDR4X memory support (from LPDDR3)
- Rates up to 2400 MT/s
- LPDDR4/LPDDR4X memory support (from LPDDR3)
- New Integration
- New Gaussian Neural Accelerator 1.0 (Unclear to what extent)
New instructions[edit]
Cannon Lake introduced a number of new instructions. See Palm Cove § New Instructions for details.
Block Diagram[edit]
Entire SoC Overview[edit]
Individual Core[edit]
See Palm Cove § Block Diagram.
Gen11 Graphics[edit]
See Gen10 Graphics § Block Diagram.
Die[edit]
Dual-core[edit]
- 10 nm process
- 13 metal layers
- ~8.2 mm x ~8.6 mm
- ~70.52 mm² die size
- 2 CPU cores + 40 GPU EUs
All Cannon Lake Chips[edit]
References[edit]
- Some information was obtained directly from Intel.
- Mark Bohr, Intel. Intel Technology and Manufacturing Day. Mar 28, 2017.
See also[edit]
- AMD's Zen
| codename | Cannon Lake + |
| core count | 2 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | May 15, 2018 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/cannon lake + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Cannon Lake + |
| pipeline stages (max) | 19 + |
| pipeline stages (min) | 14 + |
| process | 10 nm (0.01 μm, 1.0e-5 mm) + |