From WikiChip
Cortex-A7 - Microarchitectures - ARM
| Edit Values | |
| Cortex-A7 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | October 19, 2011 |
| Process | 40 nm, 28 nm |
| Succession | |
Cortex-A7 (codename Kingfisher) is the successor to the Cortex-A9, a high efficiency ARM microarchitecture designed by ARM Holdings for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable IP core and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-A7 was introduced along with the big.LITTLE technology so that it could be integrated along with the a higher-performance core such as the Cortex-A15 or the Cortex-A17 for better energy and power efficiency.
Contents
Architecture
Key changes from Cortex-A9
- 28 nm process (from 40 nm)
- New in-order pipeline (form out-of-order)
- Shorter pipeline (8, down from 9-12)
- 0.5x frequency (1 GHz, down from 2 GHz)
- Shorter pipeline (8, down from 9-12)
- Integer
- Hardware division support
- Hardware Fused Multiply-Accumulate
- VFPv4 (from VFPv3)
- NEONv2 (from NEON)
- Memory subsystem
- Level 1 instruction cache reduced to 2-way set associative (down from 4-way)
- Added LPAE support
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Block Diagram
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Memory Hierarchy
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Licensees
Arm named the following companies as licensees.
Die
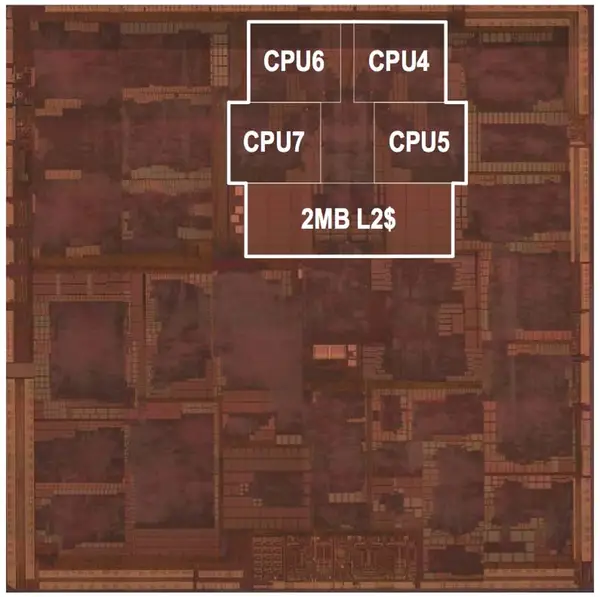
MediaTek MT6595
- TSMC 28 nm process
- 89 mm² die size
- Quad-core Cortex-A7
- ~0.48 mm² per core
- Quad-core Cortex-A17 + 2 MiB L2
- ~1.93 mm² per core
- ~3.93 mm² for 2 MiB L2
(small quad-core is unlabeled below the big core cluster)
Bibliography
- Mair, Hugh, et al. "23.3 A highly integrated smartphone SoC featuring a 2.5 GHz octa-core CPU with advanced high-performance and low-power techniques." Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2015 IEEE International. IEEE, 2015.
Facts about "Cortex-A7 - Microarchitectures - ARM"
| codename | Cortex-A7 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | October 19, 2011 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/cortex-a7 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Cortex-A7 + |
| process | 40 nm (0.04 μm, 4.0e-5 mm) + and 28 nm (0.028 μm, 2.8e-5 mm) + |