| Edit Values | |
| Vulcan µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Broadcomm, Cavium |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | 2018 |
| Process | 16 nm |
| Core Configs | 16, 20, 24, 28, 30, 32 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar, Superpipeline |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Stages | 13-15 |
| Decode | 4-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv8.1 |
| Extensions | NEON |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 32 KiB/core 8-way set associative |
| L1D Cache | 32 KiB/core 8-way set associative |
| L2 Cache | 256 KiB/core 8-way set associative |
| L3 Cache | 1 MiB/core |
| Succession | |
Vulcan is a 16 nm high-performance 64-bit ARM microarchitecture designed by Broadcom and later Cavium for the server market.
Introduced in 2018, Vulcan-based microprocessors are branded as part of the ThunderX2 family.
Contents
History
Vulcan can trace its roots all the way back to Raza Microelectronics XLR family of MIPS processors from 2006. With the introduction of their XLR family in 2009, Raza (and later NetLogic) moved to a high-performance superscalar design with fine-grained 4-way multithreading support. In 2011, Broadcom acquired NetLogic Microsystems and integrated them Broadcom's Embedded Processor Group.
In 2013, Broadcom announced that they have licensed the ARMv7 and ARMv8 architectures, allowing them to develop their own microarchitectures based on the ISA. Vulcan is the outcome of this effort which involved adopting the ARM ISA instead of MIPS and enhancing the cores in various ways.
In 2017 Cavium acquired Vulcan from broadcom which was introduced later that year. In early 2018, Vulcan-based microprocessor entered general availability under the ThunderX2 brand.
Architecture
Vulcan builds on the prior MIPS-based XLP II microarchitecture. The design has been substantially improved and changed to execute ARM (based on the ARMv8.1 ISA).
Key changes from XLP II
- Converted to ARM ISA (from MIPS)
- Aarch64, Aarch32
- 16nm FinFET process (from 28 nm planar)
- 40% IPC improvement
- 25% higher clock (2.5 GHz, up from 2 GHz)
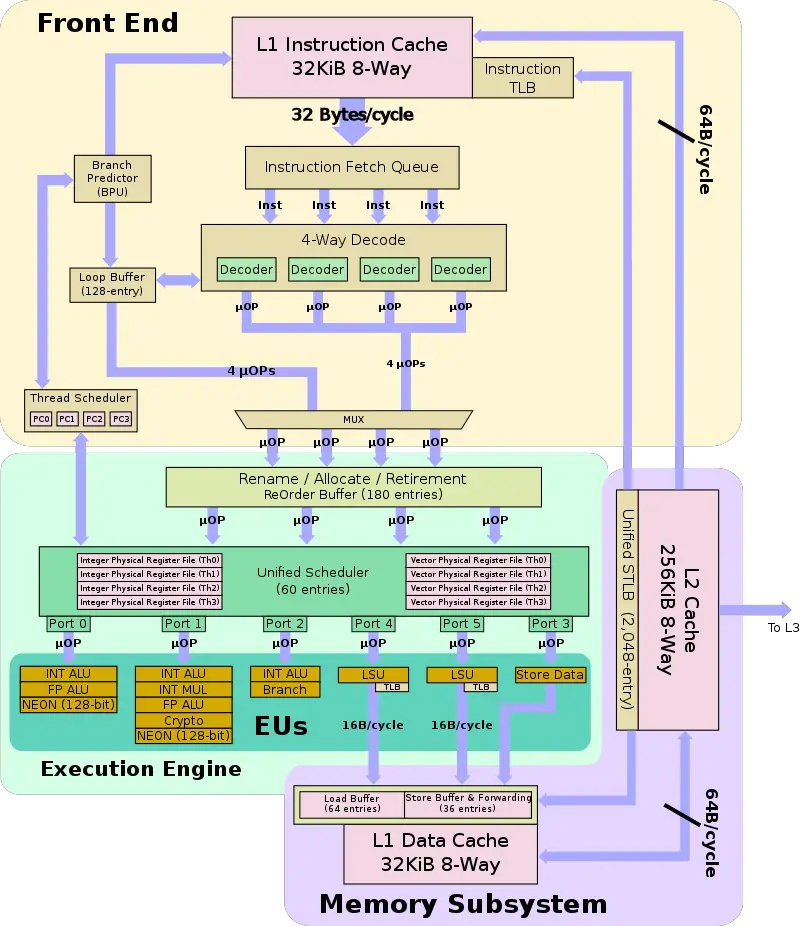
- Core
- Longer pipeline (15 stages, up from 13)
- Improved branch predictor
- Double fetch throughput (4, up from 2)
- New Decoder
- Decodes ARMv8.1 (Instead of MIPS64 R5)
- Decodes to micro-ops
- Roughly 10-20% more µOPs
- New loop buffer
- Execution Engine
- New scheduler
- Unified schedule (from distributed)
- 60 entries
- Unified schedule (from distributed)
- Large ROB (180 entries, up from 128)
- Execution Units
- New FP Unit (2, up from 1)
- Wider FP Units (128-bit, up from 64-bit)
- New scheduler
- Memory Subsystem
- Double load bandwidth (128-bit, up from 64-bit)
- New Store Data Unit
- Half L2 Cache Size (256 KiB, down form 512 KiB)
- Memory Controller
- DDR3 → DDR4
- 4 → 8 channels
- 1600 MT/s → 2666 MT/s
- 47.68 GiB/s → 158.9 GiB/s
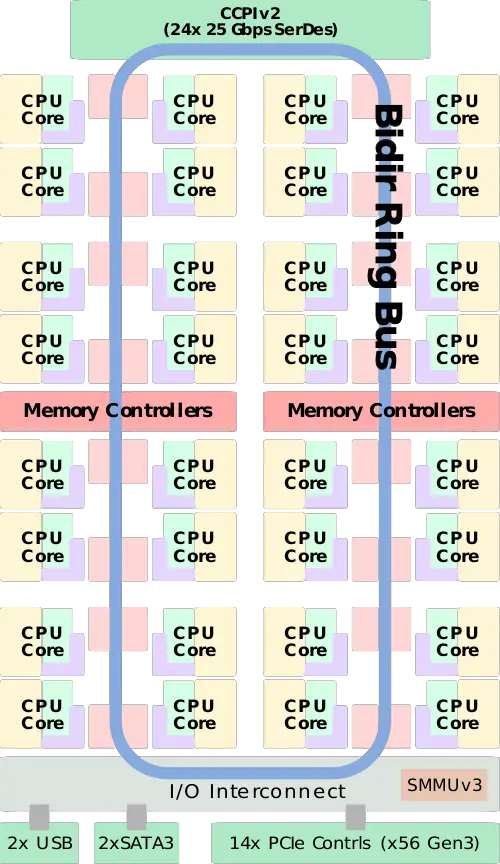
Block Diagram
Entire Chip
Individual Core
Memory Hierarchy
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Overview
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Core
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
All Vulcan Chips
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
References
- Some information was obtained directly from Broadcom
- Some information was obtained directly from Cavium
See also
| codename | Vulcan + |
| core count | 16 +, 20 +, 24 +, 28 +, 30 + and 32 + |
| designer | Cavium + and Broadcom + |
| first launched | 2018 + |
| full page name | cavium/microarchitectures/vulcan + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv8.1 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Vulcan + |
| pipeline stages (max) | 15 + |
| pipeline stages (min) | 13 + |
| process | 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) + |