| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
PEZY-SCx is a family of high-performance, low-power many-core microprocessors designed by [[PEZY]] for a series of supercomputer developed in [[Japan]]. PEZY collaborates closely with ExaScaler, a company that provides immersion cooling systems. Together, they have developed a series of supercomputers called [[ZettaScaler]]. | PEZY-SCx is a family of high-performance, low-power many-core microprocessors designed by [[PEZY]] for a series of supercomputer developed in [[Japan]]. PEZY collaborates closely with ExaScaler, a company that provides immersion cooling systems. Together, they have developed a series of supercomputers called [[ZettaScaler]]. | ||
| − | + | === Architecture === | |
| + | The basic architecture of all the PEZY-SCx chips is fairly similar. At the heart is the Processing Element. Depending on the model, 1000s of those PEs are then integrated on a single [[die]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Processing Element (PE) ==== | ||
| + | [[File:pezy-sc pe.svg|right|200px]] | ||
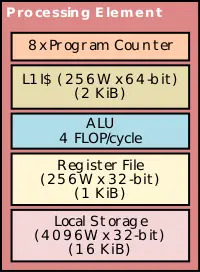
| + | The [[physical core|cores]] are called the '''processing elements''' ('''PE'''). The PEs are designed to be very simple [[RISC]] cores that support [[MIMD]]. Each PE is a 16-stage [[in-order]] [[superscalar]] capable of issuing two instructions per cycle with [[out-of-order]] completion whenever possible supporting 8-way fine-grain [[simultaneous multithreading]]. A processing element supports 8-way SMT with dedicated register files for each thread. Threads are are interleaved each cycle with switching done to reduce [[forwarding]] and [[branch prediction]]. Explicit switching of active threads is also done in order to hide high latency operations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The instruction set architecture implemented is a proprietary one designed by PEZY. The PEs do not maintain cache-coherency and there is no per-PE data cache. A fair amount of sacrifices were made in order to ensure the cores remain small enough so that a large amount of them can be packed into a small area. | ||
=== 1st generation === | === 1st generation === | ||
| − | The first series of supercomputers, [[ZettaScaler | + | {{main|pezy/pezy-scx/pezy-sc|l1=PEZY-SC}} |
| + | The first series of supercomputers, [[ZettaScaler#ZettaScaler-1.x|ZettaScaler-1.x]], were based on the {{\\|PEZY-SC}}. | ||
=== 2nd generation === | === 2nd generation === | ||
| − | The first series of supercomputers, [[ZettaScaler | + | {{main|pezy/pezy-scx/pezy-sc2|l1=PEZY-SC2}} |
| + | The first series of supercomputers, [[ZettaScaler#ZettaScaler-2.x|ZettaScaler-2.x]], were based on the {{\\|PEZY-SC2}}. | ||
=== future generations === | === future generations === | ||
Revision as of 22:54, 1 November 2017
| PEZY-SCx | |
| Developer | PEZY Computing |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Type | Microprocessors |
| Introduction | 2014 (announced) 2014 (launch) |
| Architecture | Many-core architecture |
| Process | 28 nm 0.028 μm , 16 nm2.8e-5 mm 0.016 μm , 7 nm1.6e-5 mm 0.007 μm , 5 nm7.0e-6 mm 0.005 μm
5.0e-6 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 733 MHz-1,600 MHz |
PEZY-SCx (PEZY-SuperComputerx) is a family of many-core microprocessors designed by PEZY. Those processors power many of Japan's most efficient supercomputers.
Contents
Overview
PEZY-SCx is a family of high-performance, low-power many-core microprocessors designed by PEZY for a series of supercomputer developed in Japan. PEZY collaborates closely with ExaScaler, a company that provides immersion cooling systems. Together, they have developed a series of supercomputers called ZettaScaler.
Architecture
The basic architecture of all the PEZY-SCx chips is fairly similar. At the heart is the Processing Element. Depending on the model, 1000s of those PEs are then integrated on a single die.
Processing Element (PE)
The cores are called the processing elements (PE). The PEs are designed to be very simple RISC cores that support MIMD. Each PE is a 16-stage in-order superscalar capable of issuing two instructions per cycle with out-of-order completion whenever possible supporting 8-way fine-grain simultaneous multithreading. A processing element supports 8-way SMT with dedicated register files for each thread. Threads are are interleaved each cycle with switching done to reduce forwarding and branch prediction. Explicit switching of active threads is also done in order to hide high latency operations.
The instruction set architecture implemented is a proprietary one designed by PEZY. The PEs do not maintain cache-coherency and there is no per-PE data cache. A fair amount of sacrifices were made in order to ensure the cores remain small enough so that a large amount of them can be packed into a small area.
1st generation
- Main article: PEZY-SC
The first series of supercomputers, ZettaScaler-1.x, were based on the PEZY-SC.
2nd generation
- Main article: PEZY-SC2
The first series of supercomputers, ZettaScaler-2.x, were based on the PEZY-SC2.
future generations
PEZY has laid out future generations based on TSMC's 7nm and 5nm processes.
Summary
| List of PEZY-SCx Processors | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Process | Launched | Cores | Threads | Die | Frequency |
| PEZY-SC4 | 5 nm 0.005 μm 5.0e-6 mm | 2020 | 16,384 | 131,072 | 740 mm² 1.147 in² 7.4 cm² 740,000,000 µm² | 1,600 MHz 1.6 GHz 1,600,000 kHz |
| PEZY-SC3 | 7 nm 0.007 μm 7.0e-6 mm | 2019 | 8,192 | 65,536 | 700 mm² 1.085 in² 7 cm² 700,000,000 µm² | 1,333.333 MHz 1.333 GHz 1,333,333 kHz |
| PEZY-SC2 | 16 nm 0.016 μm 1.6e-5 mm | 2017 | 2,048 | 16,384 | 620 mm² 0.961 in² 6.2 cm² 620,000,000 µm² | 1,000 MHz 1 GHz 1,000,000 kHz |
| PEZY-SC | 28 nm 0.028 μm 2.8e-5 mm | September 2014 | 1,024 | 8,192 | 411.6 mm² 0.638 in² 4.116 cm² 411,600,000 µm² | 733.33 MHz 0.733 GHz 733,330 kHz |
| PEZY-SCnp | 28 nm 0.028 μm 2.8e-5 mm | 6 May 2016 | 1,024 | 8,192 | 766.66 MHz 0.767 GHz 766,660 kHz | |
| Count: 5 | ||||||
See also
- Intel Xeon Phi
| designer | PEZY Computing + |
| first announced | 2014 + |
| first launched | 2014 + |
| full page name | pezy/pezy-scx + |
| instance of | microprocessor family + |
| main designer | PEZY Computing + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| name | PEZY-SCx + |
| process | 28 nm (0.028 μm, 2.8e-5 mm) +, 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) +, 7 nm (0.007 μm, 7.0e-6 mm) + and 5 nm (0.005 μm, 5.0e-6 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |