(Updated L2 banking and latency) |
(add tables) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|atype=CPU | |atype=CPU | ||
|name=Neoverse V1 | |name=Neoverse V1 | ||
| + | |codename=Zeus | ||
| + | |features={{\\|Zeus}} | ||
| + | |core name=[[Neoverse]] | ||
|designer=ARM Holdings | |designer=ARM Holdings | ||
|manufacturer=TSMC | |manufacturer=TSMC | ||
| − | |introduction=2021 | + | |introduction=April 27, 2021 |
|process=7 nm | |process=7 nm | ||
| + | |process 2=5 nm | ||
|oooe=Yes | |oooe=Yes | ||
|speculative=Yes | |speculative=Yes | ||
|renaming=Yes | |renaming=Yes | ||
| + | |isa=ARMv8.4 | ||
| + | |decode=5 | ||
|predecessor=Neoverse N1 | |predecessor=Neoverse N1 | ||
|predecessor link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse n1 | |predecessor link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse n1 | ||
| + | |predecessor 2=Neoverse E1 | ||
| + | |predecessor 2 link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse e1 | ||
| + | |predecessor 3=Neoverse E2 | ||
| + | |predecessor 3 link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse e2 | ||
| + | |successor=Neoverse N2 | ||
| + | |successor link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse n2 | ||
| + | |successor 2=Neoverse V2 | ||
| + | |successor 2 link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse v2 | ||
| + | |successor 3=Neoverse V3 | ||
| + | |successor 3 link=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/poseidon | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Neoverse V1''' (codename '' | + | |
| + | '''[[Neoverse V1]]''' (codename ''{{\\|Zeus}}'') is a high-performance [[ARM]] [[microarchitecture]] designed by [[ARM Holdings]] for the [[high-performance computing]] market. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable [[IP core]] and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | Definition for Zeus started in 2016. | + | [[File:arm server roadmap techcon 2018.jpg|thumb|left|Arm's server roadmap.]] |
| + | |||
| + | Definition for {{\\|Zeus}} started in [[2016]]. {{\\|Zeus}} was first announced by Drew Henry, [[Arm]]’s SVP and GM of Infrastructure Business Unit, at his TechCon [[2018]] keynote. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Codename ''{{\\|Poseidon}}'' was first used for the generation succeeding {{\\|Zeus}}, now V1, and targeted for [[2021]] on a [[5 nm]] node. | ||
== Release Dates == | == Release Dates == | ||
| − | Zeus was launched on April 27, 2021. | + | {{\\|Zeus}} was launched on April 27, 2021. |
| + | |||
| + | == Process Technology == | ||
| + | {{\\|Zeus}} specifically designed takes advantage of the power and area advantages of the [[5 nm process]]. | ||
| + | {{see also|Neoverse}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == All Neoverse V1/V2/V3 Processors == | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc4 tc6 tc9"> | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|9:List of Neoverse V1/V2/V3-based Processors}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|7:Main processor|2:ISA}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Part number|Family|Arch|Cores|%Frequency|Process|Launched|ISA|Bits}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:all microprocessor models]] [[microarchitecture::~*Neoverse V*]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?name | ||
| + | |?model_number | ||
| + | |?family | ||
| + | |?microarchitecture | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?process | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?isa | ||
| + | |?word_size | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=11 | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | |valuesep=, | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:all microprocessor models]] [[microarchitecture::~*Neoverse V*]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| − | The Neoverse V1 is an off-shoot of the {{\\|Neoverse N1}} that has been primarily optimized for the highest performance possible. | + | The [[Neoverse V1]] is an off-shoot of the {{\\|Neoverse N1}} that has been primarily optimized for the highest performance possible. |
=== Key changes from {{\\|Neoverse N1}} === | === Key changes from {{\\|Neoverse N1}} === | ||
| Line 29: | Line 91: | ||
** {{ARM|SVE}} support | ** {{ARM|SVE}} support | ||
* Higher performance | * Higher performance | ||
| − | ** [[Arm]] self-reported around 48% performance on average of [[SPEC CPU2006]]/[[SPEC CPU2017]] at iso-power/process | + | ** [[Arm]] self-reported around 48% performance on average<br>of [[SPEC CPU2006]]/[[SPEC CPU2017]] at iso-power/process |
* Front-end | * Front-end | ||
** Branch-prediction | ** Branch-prediction | ||
| Line 59: | Line 121: | ||
:[[File:neoverse n1 soc block diagram.svg|850px]] | :[[File:neoverse n1 soc block diagram.svg|850px]] | ||
| − | + | The Neoverse N1 is also expected to be integrated along with {{\\|Neoverse E1}} <br>high-efficiency cores and possibly other custom IP blocks. | |
| − | The Neoverse N1 is also expected to be integrated along with {{\\|Neoverse E1}} high-efficiency cores and possibly other custom IP blocks. | ||
| − | |||
:[[File:neoverse e1 n1 soc example.svg|750px]] | :[[File:neoverse e1 n1 soc example.svg|750px]] | ||
| Line 97: | Line 157: | ||
*** 2 MiB to 4 MiB, 16-way set associative | *** 2 MiB to 4 MiB, 16-way set associative | ||
| − | The Neoverse N1 TLB consists of a dedicated L1 TLB for instruction cache (ITLB) and another one for data cache (DTLB). Additionally, there is a unified L2 TLB (STLB). | + | The Neoverse N1 TLB consists of a dedicated L1 TLB for instruction cache (ITLB) and <br>another one for data cache (DTLB). Additionally, there is a unified L2 TLB (STLB). |
* TLBs | * TLBs | ||
| Line 112: | Line 172: | ||
Formerly known as Zeus, the Neoverse V1 is an offshoot of the initial {{\\|Neoverse N1}} microarchitecture design that has been heavily modified and optimized for performance. Historically, [[Arm]] has imposed major power and area restrictions on their core in order to meet the market requirement for their client devices. With the Neoverse V1, those requirements were finally relaxed in order to extract additional performance. In addition to general integer and floating-point performance, Zeus has also been optimized for HPC workloads with wider vector execution as well as {{arm|Scalable Vector Extension}} (SVE) support. | Formerly known as Zeus, the Neoverse V1 is an offshoot of the initial {{\\|Neoverse N1}} microarchitecture design that has been heavily modified and optimized for performance. Historically, [[Arm]] has imposed major power and area restrictions on their core in order to meet the market requirement for their client devices. With the Neoverse V1, those requirements were finally relaxed in order to extract additional performance. In addition to general integer and floating-point performance, Zeus has also been optimized for HPC workloads with wider vector execution as well as {{arm|Scalable Vector Extension}} (SVE) support. | ||
| − | The Neoverse V1 is designed for the absolute highest performance such as that found in high-performance computing systems. The Neoverse V1 is an 11-stage out-of-order core with private L1 and L2 caches as well as an ultra-wide front-end and back-end. The core itself is intended to leverage Arm's Coherent Mesh Network 700 (CMN-700) interconnect to enable scaling from as little as a quad-core design to as much as 256 cores and from a dual DDR channel all the way up to twelve channels, depending on the kind of workload being addressed | + | The Neoverse V1 is designed for the absolute highest performance such as that found in high-performance computing systems. The Neoverse V1 is an 11-stage out-of-order core with private L1 and L2 caches as well as an ultra-wide front-end and back-end. The core itself is intended to leverage Arm's Coherent Mesh Network 700 (CMN-700) interconnect to enable scaling from as little as a quad-core design to as much as 256 cores and from a dual DDR channel all the way up to twelve channels, depending on the kind of workload being addressed. |
| − | + | Extending the base design is a framework for multiprocessing support as well as chiplets support which can be used by companies who are looking to improve yield and manufacturability with large SoC designs. The V1 is also designed to work seamlessly with the {{\\|Neoverse E1}} which was introduced at the same time as N1 but is optimized for high throughput multithreaded workloads as well as other types of accelerators that may be integrated on the mesh network. | |
| − | == | + | === Core === |
== Die == | == Die == | ||
| Line 125: | Line 185: | ||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
* Arm Neoverse Tech Day, 2021 | * Arm Neoverse Tech Day, 2021 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:arm holdings]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:34, 23 March 2025
| Edit Values | |
| Neoverse V1 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | April 27, 2021 |
| Process | 7 nm, 5 nm |
| Pipeline | |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Decode | 5 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv8.4 |
| Features | Zeus |
| Cores | |
| Core Names | Neoverse |
| Succession | |
Neoverse V1 (codename Zeus) is a high-performance ARM microarchitecture designed by ARM Holdings for the high-performance computing market.
This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable IP core and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips.
Contents
History[edit]
Definition for Zeus started in 2016. Zeus was first announced by Drew Henry, Arm’s SVP and GM of Infrastructure Business Unit, at his TechCon 2018 keynote.
Codename Poseidon was first used for the generation succeeding Zeus, now V1, and targeted for 2021 on a 5 nm node.
Release Dates[edit]
Zeus was launched on April 27, 2021.
Process Technology[edit]
Zeus specifically designed takes advantage of the power and area advantages of the 5 nm process.
- See also: Neoverse
All Neoverse V1/V2/V3 Processors[edit]
| List of Neoverse V1/V2/V3-based Processors | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | ISA | ||||||||
| Model | Part number | Family | Arch | Cores | Frequency | Process | Launched | ISA | Bits |
| AWS Graviton3 | ALC13B00 | Graviton | Neoverse V1 | 64 | 2.6 GHz 2,600 MHz 2,600,000 kHz | 5 nm 0.005 μm 5.0e-6 mm | 30 November 2021 | ARMv8.4-A | 64 bit 8 octets 16 nibbles |
| AWS Graviton4 | ALC14C00 | Graviton | Neoverse V2 | 96 | 2.8 GHz 2,800 MHz 2,800,000 kHz | 4 nm 0.004 μm 4.0e-6 mm | 28 November 2023 | ARMv9.0-A | 64 bit 8 octets 16 nibbles |
| Count: 2 | |||||||||
Architecture[edit]
The Neoverse V1 is an off-shoot of the Neoverse N1 that has been primarily optimized for the highest performance possible.
Key changes from Neoverse N1[edit]
- Architecture
- Higher performance
- Arm self-reported around 48% performance on average
of SPEC CPU2006/SPEC CPU2017 at iso-power/process
- Arm self-reported around 48% performance on average
- Front-end
- Branch-prediction
- Improved accuracy
- 6x nano BTB (96 entries, up from 16)
- 1.33x larger BTB (8K-entry, up from 6K-entry)
- Up to 90% reduction in branch mispredictions (for BTB misses)
- Up to 50% reduction in front-end stalls
- Faster fetch recovery
- 2x Runahead bandwidth (2x32B/cycle, up from 32B/cycle)
- 2x code regions that are able to be tracked in the front-end
- New L0 MOP cache
- 2x wider decoded instruction fetch (8 instrs/cycle, up from 4 traditional)
- 1 stage shorter
- Decode
- 1.25 wider decode (5-way decode, up from 4)
- Execution engine
- 2x ReOrder Buffer size (256-entry, up from 128)
- New compression capabilities
- Additional instruction fusion cases
- 2x-wide vector units (2x256b/clk, up from 2x128
- 2x256b/cycle SVE or 4x128b/cycle Neon/FP
- 2x ReOrder Buffer size (256-entry, up from 128)
- Memory Subsystem
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Block Diagram[edit]
Typical SoC[edit]
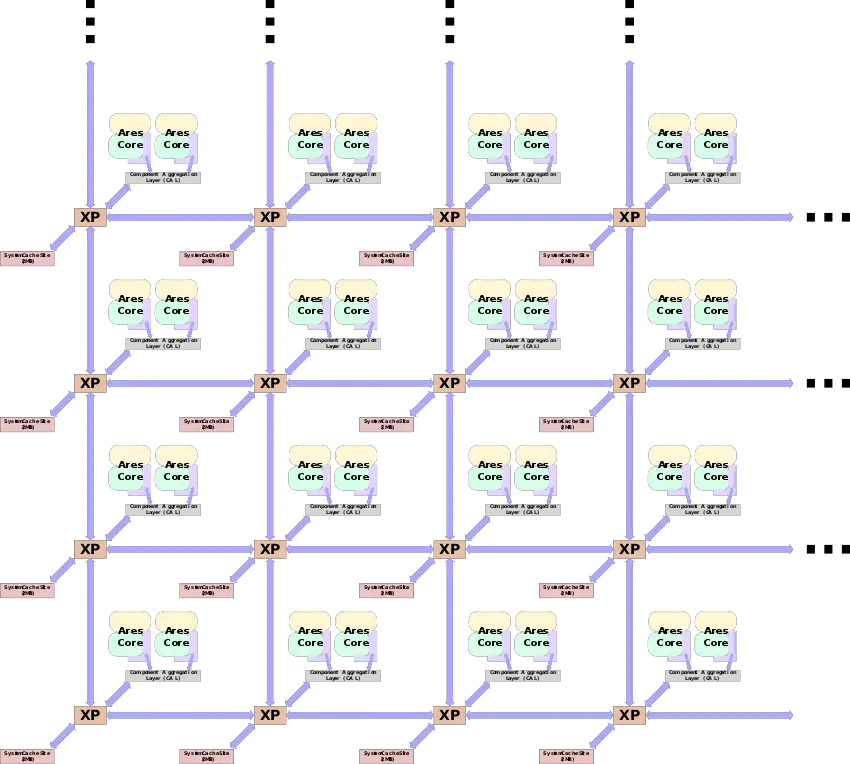
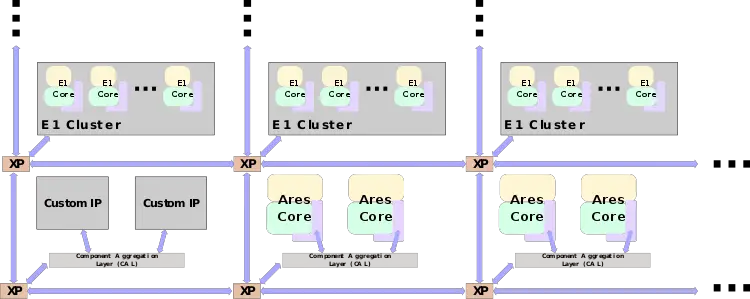
The Neoverse N1 is also expected to be integrated along with Neoverse E1
high-efficiency cores and possibly other custom IP blocks.
Individual Core[edit]
Memory Hierarchy[edit]
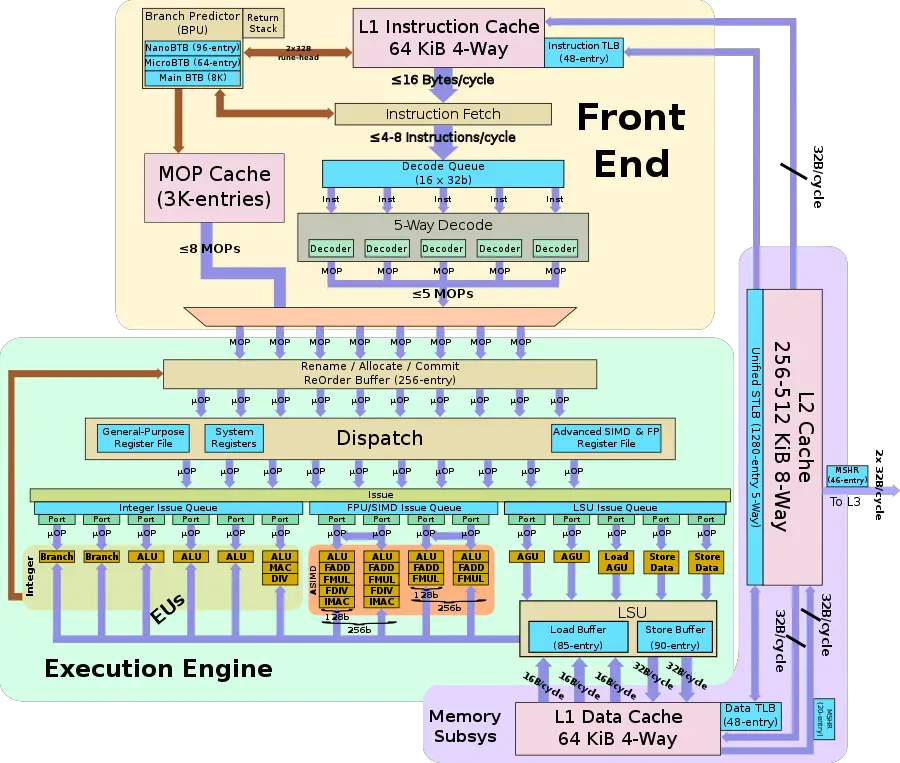
The Neoverse N1 has a private L1I, L1D, and L2 cache.
- Cache
- L1I Cache
- 64 KiB, 4-way set associative
- 64-byte cache lines
- SECDED ECC
- Write-back
- L1D Cache
- 64 KiB, 4-way set associative
- 64-byte cache lines
- 4-cycle fastest load-to-use latency
- SECDED ECC
- Write-back
- L2 Cache
- 512 KiB OR 1 MiB (4 banks)
- 8-way set associative
- 10 cycle
- 10-cycle fastest load-to-use latency
- ECC protection per 64 bits
- Modified Exclusive Shared Invalid (MESI) coherency
- Strictly inclusive of the L1 data cache & non-inclusive of the L1 instruction cache
- Write-back
- System-level cache (SLC)
- 1 Bank per core duplex
- 2 MiB to 4 MiB, 16-way set associative
- L1I Cache
The Neoverse N1 TLB consists of a dedicated L1 TLB for instruction cache (ITLB) and
another one for data cache (DTLB). Additionally, there is a unified L2 TLB (STLB).
- TLBs
- ITLB
- 4 KiB, 16 KiB, 64 KiB, 2 MiB, and 32 MiB page sizes
- 48-entry fully associative
- DTLB
- 48-entry fully associative
- 4 KiB, 16 KiB, 64 KiB, 2 MiB, and 512 MiB page sizes
- STLB
- 1280-entry 5-way set associative
- ITLB
Overview[edit]
Formerly known as Zeus, the Neoverse V1 is an offshoot of the initial Neoverse N1 microarchitecture design that has been heavily modified and optimized for performance. Historically, Arm has imposed major power and area restrictions on their core in order to meet the market requirement for their client devices. With the Neoverse V1, those requirements were finally relaxed in order to extract additional performance. In addition to general integer and floating-point performance, Zeus has also been optimized for HPC workloads with wider vector execution as well as Scalable Vector Extension (SVE) support.
The Neoverse V1 is designed for the absolute highest performance such as that found in high-performance computing systems. The Neoverse V1 is an 11-stage out-of-order core with private L1 and L2 caches as well as an ultra-wide front-end and back-end. The core itself is intended to leverage Arm's Coherent Mesh Network 700 (CMN-700) interconnect to enable scaling from as little as a quad-core design to as much as 256 cores and from a dual DDR channel all the way up to twelve channels, depending on the kind of workload being addressed.
Extending the base design is a framework for multiprocessing support as well as chiplets support which can be used by companies who are looking to improve yield and manufacturability with large SoC designs. The V1 is also designed to work seamlessly with the Neoverse E1 which was introduced at the same time as N1 but is optimized for high throughput multithreaded workloads as well as other types of accelerators that may be integrated on the mesh network.
Core[edit]
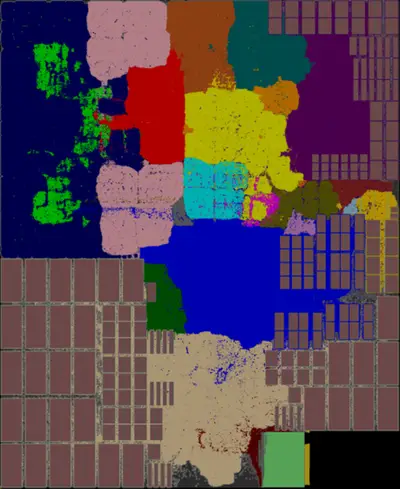
Die[edit]
- Die plot (core + 1 MiB L2 cache)
Bibliography[edit]
- Arm Neoverse Tech Day, 2021
| codename | Neoverse V1 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | April 27, 2021 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/neoverse v1 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv8.4 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Neoverse V1 + |
| process | 7 nm (0.007 μm, 7.0e-6 mm) + and 5 nm (0.005 μm, 5.0e-6 mm) + |