From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/ice lake (client)"
(→Process Technology) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
== Process Technology== | == Process Technology== | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{see also|intel/microarchitectures/cannonlake#Process_Technology|l1=Cannonlake § Process Technology}} |
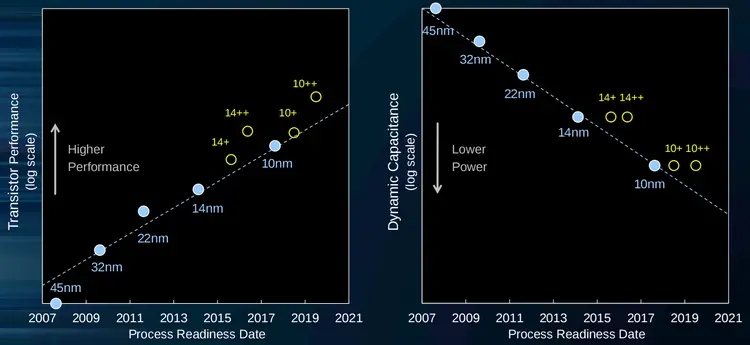
| − | Icelake | + | Icelake will use a second-generation enhanced [[10 nm process]] called "10 nm+". Versus the first generation 10nm which was used for Cannonlake, 10nm+ will feature higher performance through higher drive current for the same power envelope. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:intels 10+ and 10++.png|750px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 14 August 2017
| Edit Values | |
| Icelake µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | 2018 |
| Process | 10 nm |
| Succession | |
Icelake (ICL) is a planned microarchitecture by Intel as a successor to Cannonlake. Icelake is expected to be fabricated using a 10 nm process. Icelake is the "Architecture" microarchitecture as part of Intel's PAO model.
Process Technology
- See also: Cannonlake § Process Technology
Icelake will use a second-generation enhanced 10 nm process called "10 nm+". Versus the first generation 10nm which was used for Cannonlake, 10nm+ will feature higher performance through higher drive current for the same power envelope.
Architecture
Not much is known about Ice Lake's architecture.
Key changes from Cannonlake
Facts about "Ice Lake (client) - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | Icelake + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | 2018 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/ice lake (client) + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Icelake + |
| process | 10 nm (0.01 μm, 1.0e-5 mm) + |