From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/knights ferry"
(add links) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|predecessor=Rock Creek | |predecessor=Rock Creek | ||
|predecessor link=intel/microarchitectures/rock creek | |predecessor link=intel/microarchitectures/rock creek | ||
| + | |predecessor 2=Larrabee | ||
| + | |predecessor 2 link=intel/microarchitectures/larrabee | ||
|successor=Knights Corner | |successor=Knights Corner | ||
|successor link=intel/microarchitectures/knights_corner | |successor link=intel/microarchitectures/knights_corner | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Knights Ferry''' ('''KNF''') was the successor to {{\\|Rock Creek}}, a [[45 nm]] [[many-core]] microarchitecture designed by [[ | + | '''Knights Ferry''' ('''KNF''') was the successor to {{\\|Rock Creek}}, a [[45 nm]] [[many-core]] microarchitecture designed by [[Intel]] for high performance computing. |
| − | Note that Intel gave the | + | Note that [[Intel]] gave the PCIe expansion card the codename '''Aubrey Isle''' (die, components, board). |
| + | |||
| + | === {{intel|CPUID}} === | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Microarchitecture !! Core !! Extended <br>Family !! Family !! Extended <br>Model !! Model !! Family • Model | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{intel|Knights Corner|l=arch}} ([[2011]]) || [[62 cores]] ([[22 nm]]) || 0 || 0xB || 0x0 || 0x1 || [[Family 11 Model 1]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{intel|Knights Ferry|l=arch}} ([[2010]]) || [[32 cores]] ([[45 nm]]) || 0 || 0xB || 0x0 || 0x0 || [[Family 11 Model 0]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| − | |||
{{empty section}} | {{empty section}} | ||
== Die == | == Die == | ||
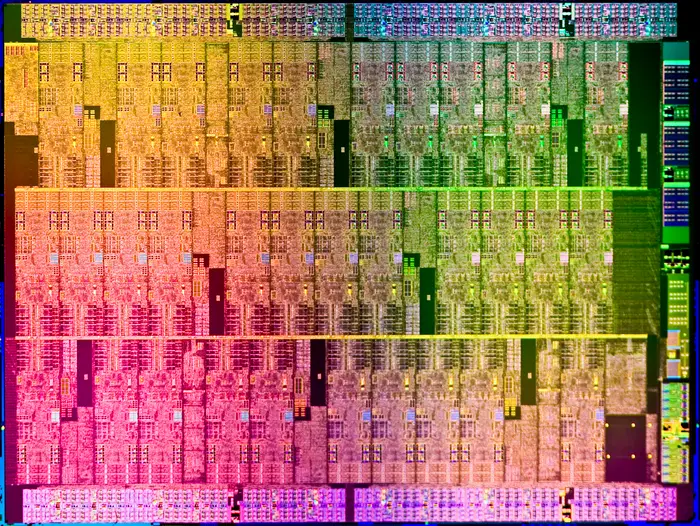
| + | * [[45 nm process]] | ||
| + | * 32 CPU cores | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:[[File:knights ferry die.png|class=wikichip_ogimage|700px]] | :[[File:knights ferry die.png|class=wikichip_ogimage|700px]] | ||
== Documents == | == Documents == | ||
* [[:File:ISC 2010 Skaugen keynote.pdf|Petascale to Exascale, Extending Intel's HPC Commitment]] | * [[:File:ISC 2010 Skaugen keynote.pdf|Petascale to Exascale, Extending Intel's HPC Commitment]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | :;[[Intel]] • {{intel|MIC Architecture}} | ||
| + | * {{intel|Knights Ferry|l=arch}} | ||
| + | * {{intel|Knights Corner|l=arch}} | ||
| + | * {{intel|Knights Landing|l=arch}} | ||
| + | * {{intel|Knights Mill|l=arch}} | ||
| + | * <s>{{intel|Knights Hill|l=arch}}</s> | ||
| + | * <s>{{intel|Knights Peak|l=arch}}</s> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:48, 4 May 2025
| Edit Values | |
| Knights Ferry µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | May 31, 2010 |
| Phase-out | 2011 |
| Process | 45 nm |
| Core Configs | 32 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86 |
| Extensions | L1OM |
| Succession | |
Knights Ferry (KNF) was the successor to Rock Creek, a 45 nm many-core microarchitecture designed by Intel for high performance computing.
Note that Intel gave the PCIe expansion card the codename Aubrey Isle (die, components, board).
Contents
CPUID[edit]
| Microarchitecture | Core | Extended Family |
Family | Extended Model |
Model | Family • Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knights Corner (2011) | 62 cores (22 nm) | 0 | 0xB | 0x0 | 0x1 | Family 11 Model 1 |
| Knights Ferry (2010) | 32 cores (45 nm) | 0 | 0xB | 0x0 | 0x0 | Family 11 Model 0 |
Architecture[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Die[edit]
- 45 nm process
- 32 CPU cores
Documents[edit]
See also[edit]
- Knights Ferry
- Knights Corner
- Knights Landing
- Knights Mill
-
Knights Hill -
Knights Peak
Facts about "Knights Ferry - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | Knights Ferry + |
| core count | 32 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | May 31, 2010 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/knights ferry + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Knights Ferry + |
| phase-out | 2011 + |
| process | 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) + |