(→Cores: Fixed a spelling mistake: compArable) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
** 8-stage pipeline (from 5-7) | ** 8-stage pipeline (from 5-7) | ||
*** 10% higher frequency | *** 10% higher frequency | ||
| − | ** dual-issue | + | ** [[dual-issue]] (from [[single-issue]]) |
** Memory subsystem | ** Memory subsystem | ||
*** 0-cycle [[load-to-use latency]] (down from 1 cycle) | *** 0-cycle [[load-to-use latency]] (down from 1 cycle) | ||
*** 2-cycle [[SRAM]] access time worst case (down from 5 cycles) | *** 2-cycle [[SRAM]] access time worst case (down from 5 cycles) | ||
*** Fast I/O Port (FIO Port) | *** Fast I/O Port (FIO Port) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== New instructions ==== | ||
| + | 7 Series introduces the following new [[RISC-V]] extensions: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * <code>{{riscv|V}}</code> - Vector | ||
| + | |||
=== Block Diagram === | === Block Diagram === | ||
==== Cluster ==== | ==== Cluster ==== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 59: | ||
=== Core === | === Core === | ||
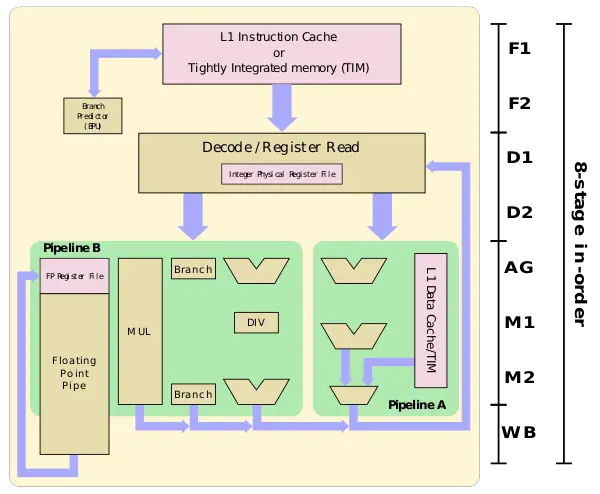
| − | 7 Series cores are based on a [[dual-issue]] [[in-order]] [[pipelined]] design. | + | 7 Series cores are based on a [[dual-issue]] [[in-order]] [[pipelined]] design. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:7 series pipeline.svg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The pipeline itself is one cycle longer than prior microarchitectures, enabling up to 10% higher frequency. SiFive reworked the execution units. The new design can handle up to two instruction being issued at once, this is double the prior design which brings along substantial performance improvement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Memory subsystem ==== | ||
| + | The largest change in the 7 Series is the overhaul of the memory subsystem. The data cache and the optional tightly integrated memory (TIM) can now span two cycles, enabling large SRAM/TIM to be included with the core. Additionally, two sets of ALUs have been incorporated into the pipeline in order to allow a zero cycle [[load-to-use latency]] where the first stage is used for the address generation and the last stage can be used to operate on the data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Fast I/O Port (FIO Port)===== | ||
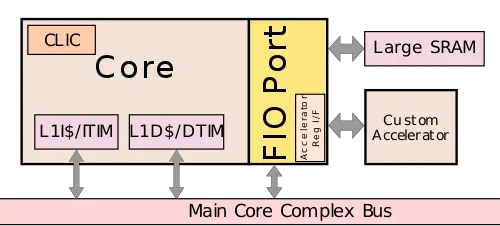
| + | 7 Series incorporates an optional fast I/O port (FIO port) which is tightly coupled to the core, enabling low-latency core-to-memory/accelerator operations. The FIO port can be used to incorporate much larger [[SRAM]] as well as custom accelerators via the accelerator register interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:sifive 7 series core with fio port.svg|500px]] | ||
=== Cluster === | === Cluster === | ||
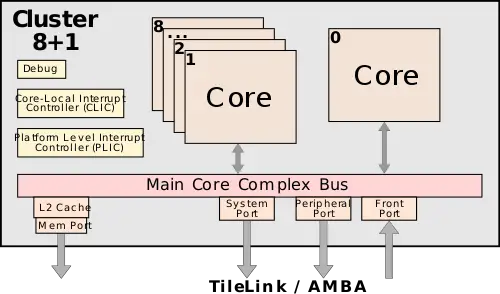
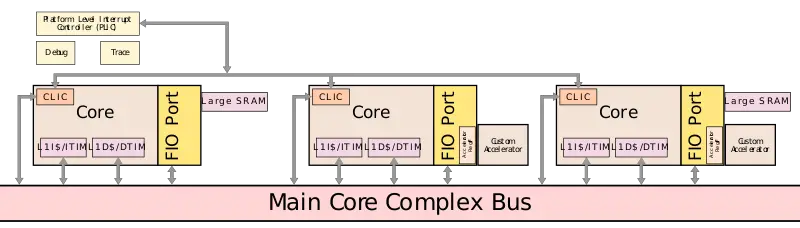
| − | The basic cluster comprises up to 9 cores configured as 8+1. The type of cores is fully customizable and may incorporate SiFive previous cores (e.g. the high-efficiency {{\\|2 Series}} cores). All the cores sit on a [[cache coherent]] bus. | + | The basic cluster comprises up to 9 cores configured as 8+1. The type of cores is fully customizable and may incorporate SiFive previous cores (e.g. the high-efficiency {{\\|2 Series}} cores). It's worth noting that any of the cores can be finely customized (e.g. one with SRAM while another might have an [[accelerator]] while a third core might have neither). All the cores sit on a [[cache coherent]] bus. All cores on the bus can see and access the FIO port on all the other cores as well, meaning they can also access the SRAM and possible custom [[accelerator]] sitting on any of the other cores. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:sifive 7 series cores with fio port.svg|800px]] | ||
== Cores == | == Cores == | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! Core !! Perf !! | + | ! Core !! Perf !! Comparable !! ISA |
|- | |- | ||
| E7 || 2.3 DMIPS/MHz<br>4.9 CoreMarks/MHz || {{armh|Cortex-M7|l=arch}} || RV32GCV | | E7 || 2.3 DMIPS/MHz<br>4.9 CoreMarks/MHz || {{armh|Cortex-M7|l=arch}} || RV32GCV | ||
Latest revision as of 09:16, 28 November 2018
| Edit Values | |
| 7 Series µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | SiFive |
| Manufacturer | TSMC, GlobalFoundries |
| Introduction | October 21, 2018 |
| Core Configs | 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar, Pipelined |
| OoOE | No |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | No |
| Stages | 8 |
| Decode | 2 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | RISC-V |
| Cores | |
| Core Names | E76, E76-MC, S76, S76-MC, U74, U74-MC |
| Succession | |
7 Series is a series of high-performance RISC-V IP cores designed by SiFive.
Contents
Architecture[edit]
Key changes from 5 Series[edit]
- Core
- 8-stage pipeline (from 5-7)
- 10% higher frequency
- dual-issue (from single-issue)
- Memory subsystem
- 0-cycle load-to-use latency (down from 1 cycle)
- 2-cycle SRAM access time worst case (down from 5 cycles)
- Fast I/O Port (FIO Port)
- 8-stage pipeline (from 5-7)
New instructions[edit]
7 Series introduces the following new RISC-V extensions:
-
V- Vector
Block Diagram[edit]
Cluster[edit]
Core[edit]
Overview[edit]
The 7 Series is based on an improved version of the 5 Series which SiFive claims to provide 60% improvement in CoreMarks/MHz as well as 40% improvement in DMIPS/MHz. Series 7 base design is a cluster of up to 9 cores (8+1). Cores can be a mix of 7 Series cores as well as SiFive other existing cores. Everything in the cluster is cache coherent - including any extended SRAM options as well as any custom accelerator attached to the cores. The cluster can be further scaled up through the use of AMBA or TileLink which allows for up to 64 clusters to be integrated onto a single chip. Multi-chip support is also possible via ChipLink.
Core[edit]
7 Series cores are based on a dual-issue in-order pipelined design.
The pipeline itself is one cycle longer than prior microarchitectures, enabling up to 10% higher frequency. SiFive reworked the execution units. The new design can handle up to two instruction being issued at once, this is double the prior design which brings along substantial performance improvement.
Memory subsystem[edit]
The largest change in the 7 Series is the overhaul of the memory subsystem. The data cache and the optional tightly integrated memory (TIM) can now span two cycles, enabling large SRAM/TIM to be included with the core. Additionally, two sets of ALUs have been incorporated into the pipeline in order to allow a zero cycle load-to-use latency where the first stage is used for the address generation and the last stage can be used to operate on the data.
Fast I/O Port (FIO Port)[edit]
7 Series incorporates an optional fast I/O port (FIO port) which is tightly coupled to the core, enabling low-latency core-to-memory/accelerator operations. The FIO port can be used to incorporate much larger SRAM as well as custom accelerators via the accelerator register interface.
Cluster[edit]
The basic cluster comprises up to 9 cores configured as 8+1. The type of cores is fully customizable and may incorporate SiFive previous cores (e.g. the high-efficiency 2 Series cores). It's worth noting that any of the cores can be finely customized (e.g. one with SRAM while another might have an accelerator while a third core might have neither). All the cores sit on a cache coherent bus. All cores on the bus can see and access the FIO port on all the other cores as well, meaning they can also access the SRAM and possible custom accelerator sitting on any of the other cores.
Cores[edit]
| Core | Perf | Comparable | ISA |
|---|---|---|---|
| E7 | 2.3 DMIPS/MHz 4.9 CoreMarks/MHz |
Cortex-M7 | RV32GCV |
| S7 | 2.5 DMIPS/MHz 4.9 CoreMarks/MHz |
Cortex-R8 | RV64GCV |
| U7 | 2.5 DMIPS/MHz 4.9 CoreMarks/MHz |
Cortex-A55 | RV64GCV |
| codename | 7 Series + |
| core count | 1 +, 2 +, 4 +, 6 + and 8 + |
| designer | SiFive + |
| first launched | October 21, 2018 + |
| full page name | sifive/microarchitectures/7 series + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | RISC-V + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + and GlobalFoundries + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | 7 Series + |
| pipeline stages | 8 + |