From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "apple/ax"
(Testing changes in ic family template) |
(→PC processors) |
||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| proc 6 = 14 nm | | proc 6 = 14 nm | ||
| proc 7 = 10 nm | | proc 7 = 10 nm | ||
| + | | proc 8 = 7 nm | ||
| + | | proc 9 = 5 nm | ||
| tech = CMOS | | tech = CMOS | ||
| − | | clock min = | + | | clock min = 800 MHz |
| − | | clock max = | + | | clock max = 3.1 GHz |
| package = | | package = | ||
| socket = | | socket = | ||
| Line 38: | Line 40: | ||
| successor link = | | successor link = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
'''Ax''' is a family of high-performance {{arch|32}} and {{arch|64}} [[ARM]] system on chips designed by [[Apple]] exclusively for their consumer products. | '''Ax''' is a family of high-performance {{arch|32}} and {{arch|64}} [[ARM]] system on chips designed by [[Apple]] exclusively for their consumer products. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 52: | ||
== Members == | == Members == | ||
{{collist | {{collist | ||
| − | | count = | + | | count = 4 |
| | | | ||
| − | * {{\|A4}} | + | * {{\|A4}} (Cortex-A8) |
| − | * {{\|A5}} | + | * {{\|A5}} • {{\|A5X}} (Cortex-A9) |
| − | + | * {{\|A6}} • {{\|A6X}} (Swift) | |
| − | * {{\|A6}} | + | * {{\|A7}} (Cyclone) |
| − | + | ||
| − | * {{\|A7}} | + | * {{\|A8}} • {{\|A8X}} (Typhoon) |
| − | * {{\|A8}} | + | * {{\|A9}} • {{\|A9X}} (Twister) |
| − | + | * {{\|A10}} Fusion • {{\|A10X}} (Hurricane) | |
| − | * {{\|A9}} | + | * {{\|A11}} Bionic (Monsoon) |
| − | + | ||
| − | * {{\|A10}} | + | * {{\|A12}} Bionic (Vortex) |
| − | + | * {{\|A12X}} • {{\|A12Z}} | |
| − | * {{\|A11}} | + | * {{\|A13}} Bionic (Lightning) |
| − | * {{\|A12}} | + | * {{\|A14}} Bionic (Firestorm) |
| + | |||
| + | * {{\|A15}} Bionic (Avalanche) | ||
| + | * {{\|A16}} Bionic (Everest Gen 1) | ||
| + | * {{\|A17 Pro}} (Everest Gen 2) | ||
| + | * {{\|A18}} • {{\|A18 Pro}} (Everest Gen 3) | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Mobile processors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="width:100%; text-align:center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Model | ||
| + | ! CPU | ||
| + | ! GPU | ||
| + | ! NPU | ||
| + | ! RAM | ||
| + | ! Catalog number | ||
| + | ! Process | ||
| + | ! Release date | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A18 Pro]] | ||
| + | | 2x Everest @4.05GHz<br>4x Sawtooth @2.42GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(hexa-core)<br>(2227 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine<br>(35 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5x-7500 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @3750MHz <br>(60GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1V07 | ||
| + | | "[[3 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N3E | ||
| + | | 2024/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A18]] | ||
| + | | 2x Everest @4.05GHz<br>4x Sawtooth @2.42GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(penta-core)<br>(1789 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine<br>(35 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5x-7500 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @3750MHz <br>(60GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1V08 | ||
| + | | "[[3 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N3E | ||
| + | | 2024/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A17]] | ||
| + | | 2x Everest @3.78GHz <br>4x Sawtooth @2.11GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(hexa-core) <br>(2147 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(35 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @3200MHz <br>(51.2GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1V02 | ||
| + | | "[[3 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N3B | ||
| + | | 2023/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A16]] | ||
| + | | 2x Everest @3.46GHz <br>4x Sawtooth @2.02GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(penta-core) <br>(1789 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(17 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @3200MHz <br>(51.2GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1W10 | ||
| + | | "[[4 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N4P | ||
| + | | 2022/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A15]] | ||
| + | | 2x Avalanche @3.24GHz <br>4x Blizzard @2.0GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(penta-core) <br>(1712 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(15.8 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR4X-4266 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @2133MHz <br>(34.1GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1W07 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5P | ||
| + | | 2021/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A14]] | ||
| + | | 2x Firestorm @3.0GHz <br>4x Icestorm | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(quad-core) <br>(748.8 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(11 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR4X-4266 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @2133MHz <br>(34.1GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1W87 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5 | ||
| + | | 2020/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A13]] | ||
| + | | 2x Lightning @2.65GHz <br>4x Thunder @1.8GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(quad-core) <br>(806 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 8x Neural Engine <br>(6 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR4X-4266 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @2133MHz <br>(34.1GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1W85 | ||
| + | | "[[7 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N7P | ||
| + | | 2019/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A12]] | ||
| + | | 2x Vortex @2.5GHz <br>4x Tempest @1.6GHz | ||
| + | | 4x Apple G11P <br>(576 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 8x Neural Engine <br>(5 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR4X-4266 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @2133MHz <br>(34.1GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1W81 | ||
| + | | "[[7 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N7 | ||
| + | | 2018/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A11]] | ||
| + | | 2x Monsoon @2.4GHz<br> 4x Mistral | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(tri-core) <br>(408 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 2x Neural Engine <br>(0.6 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR4X-4266 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @2133MHz <br>(34.1GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1W72 | ||
| + | | "[[10 nm]]"<br>[[TSMC]] FinFET | ||
| + | | 2017/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A10]] | ||
| + | | 2x Hurricane @2.34GHz <br>2x Zephyr @1.05GHz | ||
| + | | 6x PowerVR <br>GT7600 Plus <br>@900MHz <br>(345.6 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR4-3200 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @1600MHz <br>(25.6GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1W24 | ||
| + | | "[[16 nm]]"<br>[[TSMC]] 16FFC | ||
| + | | 2016/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A9]] | ||
| + | | 2x Twister @1.85GHz | ||
| + | | 6x PowerVR <br>GT7600 <br>@650MHz <br>(249.6 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR4-3200 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit <br>@1600MHz <br>(25.6GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL0898 <br>APL1022 | ||
| + | | "[[14 nm]]" [[Samsung]] <br>"[[16 nm]]" [[TSMC]] | ||
| + | | 2015/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A8]] | ||
| + | | 2x Typhoon @1.5GHz | ||
| + | | 4x PowerVR <br>GXA6450 <br>@533MHz <br>(136.5 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR3-1600 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @800MHz <br>(12.8GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL1011 | ||
| + | | "[[20 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] | ||
| + | | 2014/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A7]] | ||
| + | | 2x Cyclone @1.3GHz | ||
| + | | 4x PowerVR <br>G6430 <br>@450MHz <br>(115.2 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR3-1600 <br>single-channel <br>64-bit @800MHz <br>(12.8GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL0698 <br>APL5698 <br>(S5L8960X) | ||
| + | | "[[28 nm]]" <br>[[Samsung]] HKMG | ||
| + | | 2013/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A6]] | ||
| + | | 2x Swift @1.3GHz | ||
| + | | 3x PowerVR <br>SGX543 <br>@266MHz <br>(25 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDRR2-1066 <br>dual-channel <br>32-bit @533MHz <br>(8.5GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL0598 <br>S5L8950X | ||
| + | | "[[32 nm]]" <br>[[Samsung]] HKMG | ||
| + | | 2012/09 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A5]] | ||
| + | | 2x ARM Cortex-A9 <br>@1.0GHz | ||
| + | | 2x PowerVR <br>SGX543 <br>@200MHz <br>(12.8 GFLOPS) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR2-800 <br>dual-channel <br>32-bit @400MHz <br>(6.4GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL0498 <br>APL2498 <br>(S5L8940X) | ||
| + | | "[[45 nm]]" [[Samsung]] <br>"[[32 nm]]" [[Samsung]] <br>HKMG | ||
| + | | 2011/03 <br>2012/03 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A4]] | ||
| + | | 1x ARM Cortex-A8 <br>@1.0GHz | ||
| + | | PowerVR SGX535 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR-400 <br>dual-channel <br>32-bit @200MHz <br>(3.2GB/s) | ||
| + | | APL0398 <br>(S5L8930X) | ||
| + | | "[[45 nm]]" <br>[[Samsung]] | ||
| + | | 2010/04 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Model | ||
| + | ! CPU | ||
| + | ! GPU | ||
| + | ! NPU | ||
| + | ! RAM | ||
| + | ! Catalog name | ||
| + | ! Lithography | ||
| + | ! Release date | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Tablet processors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="width:100%; text-align:center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Model | ||
| + | ! CPU | ||
| + | ! GPU | ||
| + | ! NPU | ||
| + | ! RAM | ||
| + | ! Modem | ||
| + | ! Catalog number | ||
| + | ! Lithography | ||
| + | ! Release date | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A12X]] | ||
| + | | 4x Vortex @2.49GHz <br>4x Tempest @1.6GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(hexa/octa-core) <br>(1200 GFLOPs) | ||
| + | | 8x Neural Engine <br>(6 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR4X-4266 <br>dual-channel <br>64-bit @2133MHz <br>(68.2GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1083 | ||
| + | | "[[7 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N7 | ||
| + | | 2018/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A10X]] | ||
| + | | 3x Hurricane @2.36GHz <br>3x Zephyr @1.0GHz | ||
| + | | 12x PowerVR <br>GT7500 Plus <br>@900MHz <br>(768 GFLOPs) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR4-3200 <br>dual-channel <br>64-bit @1600MHz <br>(51.2GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1071 | ||
| + | | "[[10 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] 10FF | ||
| + | | 2017/06 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A9X]] | ||
| + | | 2x Twister @2.26GHz | ||
| + | | 12x PowerVR <br>GTA7850 <br>@650MHz <br>(345.6 GFLOPs) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR4-3200 <br>dual-channel <br>64-bit @1600MHz <br>(51.2GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1021 | ||
| + | | "[[16 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] 16FF | ||
| + | | 2015/11 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A8X]] | ||
| + | | 3x Typhoon @1.5GHz | ||
| + | | 8x PowerVR <br>GXA6850 <br>@450MHz <br>(230.4 GFLOPs) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR3-1600 <br>dual-channel <br>64-bit @800MHz <br>(25.6GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1012 | ||
| + | | "[[20 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] | ||
| + | | 2014/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A6X]] | ||
| + | | 2x Swift @1.4GHz | ||
| + | | 4x PowerVR <br>SGX554 @266MHz <br>(68.1 GFLOPs) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR2-1066 <br>quad-channel <br>32-bit @533MHz <br>(17.1GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL5598 | ||
| + | | "[[32 nm]]" <br>[[Samsung]] <br>HKMG | ||
| + | | 2012/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple A5X]] | ||
| + | | 2x ARM Cortex-A9 <br>@1.0GHz | ||
| + | | 4x PowerVR <br>SGX543 @200MHz <br>(25 GFLOPs) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | LPDDR2-800 <br>quad-channel <br>32-bit @400MHz <br>(12.8GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL5498 | ||
| + | | "[[45 nm]]" <br>[[Samsung]] | ||
| + | | 2012/03 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Model | ||
| + | ! CPU | ||
| + | ! GPU | ||
| + | ! NPU | ||
| + | ! RAM | ||
| + | ! Modem | ||
| + | ! Catalog name | ||
| + | ! Lithography | ||
| + | ! Release date | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === PC processors === | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="width:100%; text-align:center" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Model | ||
| + | ! CPU | ||
| + | ! GPU | ||
| + | ! NPU | ||
| + | ! RAM | ||
| + | ! Modem | ||
| + | ! Catalog <br>number | ||
| + | ! Lithography | ||
| + | ! Release date | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M4]] | ||
| + | | 4x Everest @4.4GHz <br>6x Sawtooth @2.85GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(10 cores) <br>(3.7 TFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(38 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5x-7500 <br>128-bit <br>@3750MHz <br>(120GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1206 | ||
| + | | "[[3 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N3E | ||
| + | | 2024/05 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M3 Max]] | ||
| + | | 14x/16x Everest @4.05GHz <br>4x Sawtooth @2.75GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(30/40 cores) <br>(10.6/14.1 <br>TFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(18 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>384/512-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(307.2/<br>409.6GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1201 | ||
| + | | "[[3 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N3B | ||
| + | | 2023/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M3 Pro]] | ||
| + | | 5x/6x Everest @4.05GHz <br>6x Sawtooth @2.75GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(14/18 cores) <br>(4.9/6.4 TFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(18 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>192-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(153.6GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1201 | ||
| + | | "[[3 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N3B | ||
| + | | 2023/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M3]] | ||
| + | | 4x Everest @4.05GHz <br>4x Sawtooth @2.75GHz | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(8/10 cores) <br>(2.8 TFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(18 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>128-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(102.4GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1201 | ||
| + | | "[[3 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N3B | ||
| + | | 2023/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M2 Ultra]] | ||
| + | | 16x Avalanche <br>8x Blizzard | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(60/76 cores) <br>(27.19 TFLOPS)<br> | ||
| + | | 32x Neural Engine <br>(31.6 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>1024-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(800GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5P | ||
| + | | 2023/06 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M2 Max]] | ||
| + | | 8x Avalanche <br>4x Blizzard | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(38 cores) <br>(13.59 TFLOPS)<br> | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(15.8 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>512-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(400GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | T6021 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5P | ||
| + | | 2023/01 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M2 Pro]] | ||
| + | | 8x Avalanche <br>4x Blizzard | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(19 cores) <br>(6.79 TFLOPS) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(15.8 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>256-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(200GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | T6020 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5P | ||
| + | | 2023/01 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M2]] | ||
| + | | 4x Avalanche <br>4x Blizzard | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(10 cores) <br>(3.6 TFLOPs) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(15.8 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>128-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(100GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1109 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5P | ||
| + | | 2022/06 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M1 Ultra]] | ||
| + | | 16x Firestorm <br>4x Icestorm | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(64 cores) <br>(21 TFLOPs) | ||
| + | | 32x Neural Engine <br>(22 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>1024-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(800GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1W06 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5 | ||
| + | | 2022/03 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M1 Max]] | ||
| + | | 8x Firestorm <br>2x Icestorm | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(32 cores) <br>(10.4 TFLOPs) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(11 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>512-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(400GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1105 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5 | ||
| + | | 2021/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M1 Pro]] | ||
| + | | 8x Firestorm <br>2x Icestorm | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(16 cores) <br>(5.2 TFLOPs) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(11 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR5-6400 <br>256-bit <br>@3200MHz <br>(200GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1103 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5 | ||
| + | | 2021/10 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Apple M1]] | ||
| + | | 4x Firestorm @3.2GHz <br>4x Icestorm | ||
| + | | Proprietary <br>(octa-core) <br>(2.6 TFLOPs) | ||
| + | | 16x Neural Engine <br>(11 TOPS) | ||
| + | | LPDDR4X-4266 <br>dual-channel <br>64-bit <br>@2133MHz <br>(68.2GB/s) | ||
| + | | ''not available'' | ||
| + | | APL1102 | ||
| + | | "[[5 nm]]" <br>[[TSMC]] N5 | ||
| + | | 2020/11 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Model | ||
| + | ! CPU | ||
| + | ! GPU | ||
| + | ! NPU | ||
| + | ! RAM | ||
| + | ! Modem | ||
| + | ! Catalog name | ||
| + | ! Lithography | ||
| + | ! Release date | ||
| + | |} | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
| − | * | + | * [[HiSilicon]] |
| − | * MediaTek {{mediatek|Helio}} | + | * [[Intel]] • {{intel|Atom}} |
| − | * | + | * [[MediaTek]] • {{mediatek|Helio}} |
| + | * [[Qualcomm]] • {{qualcomm|Snapdragon 8}} | ||
| + | * [[Samsung]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| − | <!-- nop --> | + | <!-- nop 2 --> |
| + | [[Category:apple]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:49, 23 April 2025
| Apple Ax | |
| Developer | Apple, ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | Samsung, TSMC |
| Type | System on Chips |
| Architecture | High-performance ARM SoCs |
| ISA | ARM |
| Word size | 32 bit 4 octets , 64 bit8 nibbles 8 octets
16 nibbles |
| Process | 45 nm 0.045 μm , 32 nm4.5e-5 mm 0.032 μm , 28 nm3.2e-5 mm 0.028 μm , 20 nm2.8e-5 mm 0.02 μm , 16 nm2.0e-5 mm 0.016 μm , 14 nm1.6e-5 mm 0.014 μm , 10 nm1.4e-5 mm 0.01 μm , 7 nm1.0e-5 mm 0.007 μm , 5 nm7.0e-6 mm 0.005 μm
5.0e-6 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 800 MHz-3.1 GHz |
Ax is a family of high-performance 32-bit and 64-bit ARM system on chips designed by Apple exclusively for their consumer products.
Contents
Overview[edit]
Since the introduction of the original iPhone in 2007, Apple has been developing a series of chips designed exclusively for their own consumer products. Those system on chips are found in all iPhones, iPod Touches, iPads, Apple TVs, and Apple Watches. While initial models used IP cores licensed from ARM Holdings, since the introduction of the A6 in 2012, Apple has been developing their own microarchitecture for their chips which have become considerably more powerful than other ARM-based microprocessors.
Analysis[edit]
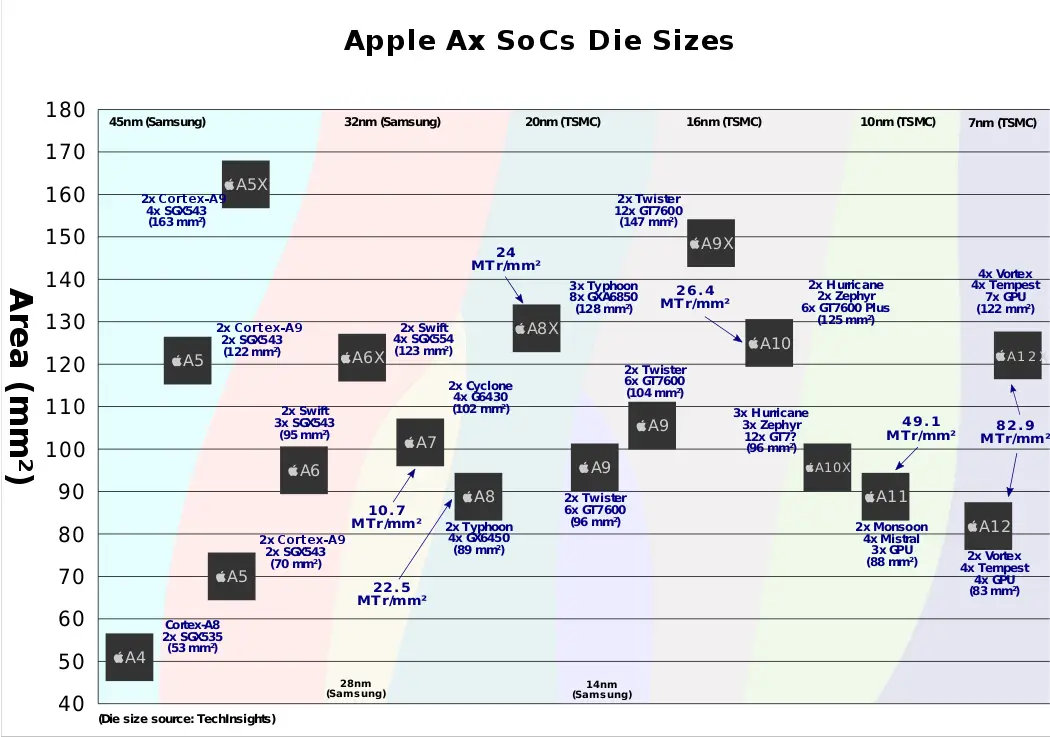
Die size comparison[edit]
Members[edit]
Mobile processors[edit]
| Model | CPU | GPU | NPU | RAM | Catalog number | Process | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple A18 Pro | 2x Everest @4.05GHz 4x Sawtooth @2.42GHz |
Proprietary (hexa-core) (2227 GFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (35 TOPS) |
LPDDR5x-7500 single-channel 64-bit @3750MHz (60GB/s) |
APL1V07 | "3 nm" TSMC N3E |
2024/09 |
| Apple A18 | 2x Everest @4.05GHz 4x Sawtooth @2.42GHz |
Proprietary (penta-core) (1789 GFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (35 TOPS) |
LPDDR5x-7500 single-channel 64-bit @3750MHz (60GB/s) |
APL1V08 | "3 nm" TSMC N3E |
2024/09 |
| Apple A17 | 2x Everest @3.78GHz 4x Sawtooth @2.11GHz |
Proprietary (hexa-core) (2147 GFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (35 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 single-channel 64-bit @3200MHz (51.2GB/s) |
APL1V02 | "3 nm" TSMC N3B |
2023/09 |
| Apple A16 | 2x Everest @3.46GHz 4x Sawtooth @2.02GHz |
Proprietary (penta-core) (1789 GFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (17 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 single-channel 64-bit @3200MHz (51.2GB/s) |
APL1W10 | "4 nm" TSMC N4P |
2022/09 |
| Apple A15 | 2x Avalanche @3.24GHz 4x Blizzard @2.0GHz |
Proprietary (penta-core) (1712 GFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (15.8 TOPS) |
LPDDR4X-4266 single-channel 64-bit @2133MHz (34.1GB/s) |
APL1W07 | "5 nm" TSMC N5P |
2021/09 |
| Apple A14 | 2x Firestorm @3.0GHz 4x Icestorm |
Proprietary (quad-core) (748.8 GFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (11 TOPS) |
LPDDR4X-4266 single-channel 64-bit @2133MHz (34.1GB/s) |
APL1W87 | "5 nm" TSMC N5 |
2020/09 |
| Apple A13 | 2x Lightning @2.65GHz 4x Thunder @1.8GHz |
Proprietary (quad-core) (806 GFLOPS) |
8x Neural Engine (6 TOPS) |
LPDDR4X-4266 single-channel 64-bit @2133MHz (34.1GB/s) |
APL1W85 | "7 nm" TSMC N7P |
2019/09 |
| Apple A12 | 2x Vortex @2.5GHz 4x Tempest @1.6GHz |
4x Apple G11P (576 GFLOPS) |
8x Neural Engine (5 TOPS) |
LPDDR4X-4266 single-channel 64-bit @2133MHz (34.1GB/s) |
APL1W81 | "7 nm" TSMC N7 |
2018/09 |
| Apple A11 | 2x Monsoon @2.4GHz 4x Mistral |
Proprietary (tri-core) (408 GFLOPS) |
2x Neural Engine (0.6 TOPS) |
LPDDR4X-4266 single-channel 64-bit @2133MHz (34.1GB/s) |
APL1W72 | "10 nm" TSMC FinFET |
2017/09 |
| Apple A10 | 2x Hurricane @2.34GHz 2x Zephyr @1.05GHz |
6x PowerVR GT7600 Plus @900MHz (345.6 GFLOPS) |
LPDDR4-3200 single-channel 64-bit @1600MHz (25.6GB/s) |
APL1W24 | "16 nm" TSMC 16FFC |
2016/09 | |
| Apple A9 | 2x Twister @1.85GHz | 6x PowerVR GT7600 @650MHz (249.6 GFLOPS) |
LPDDR4-3200 single-channel 64-bit @1600MHz (25.6GB/s) |
APL0898 APL1022 |
"14 nm" Samsung "16 nm" TSMC |
2015/09 | |
| Apple A8 | 2x Typhoon @1.5GHz | 4x PowerVR GXA6450 @533MHz (136.5 GFLOPS) |
LPDDR3-1600 single-channel 64-bit @800MHz (12.8GB/s) |
APL1011 | "20 nm" TSMC |
2014/09 | |
| Apple A7 | 2x Cyclone @1.3GHz | 4x PowerVR G6430 @450MHz (115.2 GFLOPS) |
LPDDR3-1600 single-channel 64-bit @800MHz (12.8GB/s) |
APL0698 APL5698 (S5L8960X) |
"28 nm" Samsung HKMG |
2013/09 | |
| Apple A6 | 2x Swift @1.3GHz | 3x PowerVR SGX543 @266MHz (25 GFLOPS) |
LPDRR2-1066 dual-channel 32-bit @533MHz (8.5GB/s) |
APL0598 S5L8950X |
"32 nm" Samsung HKMG |
2012/09 | |
| Apple A5 | 2x ARM Cortex-A9 @1.0GHz |
2x PowerVR SGX543 @200MHz (12.8 GFLOPS) |
LPDDR2-800 dual-channel 32-bit @400MHz (6.4GB/s) |
APL0498 APL2498 (S5L8940X) |
"45 nm" Samsung "32 nm" Samsung HKMG |
2011/03 2012/03 | |
| Apple A4 | 1x ARM Cortex-A8 @1.0GHz |
PowerVR SGX535 | LPDDR-400 dual-channel 32-bit @200MHz (3.2GB/s) |
APL0398 (S5L8930X) |
"45 nm" Samsung |
2010/04 | |
| Model | CPU | GPU | NPU | RAM | Catalog name | Lithography | Release date |
Tablet processors[edit]
| Model | CPU | GPU | NPU | RAM | Modem | Catalog number | Lithography | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple A12X | 4x Vortex @2.49GHz 4x Tempest @1.6GHz |
Proprietary (hexa/octa-core) (1200 GFLOPs) |
8x Neural Engine (6 TOPS) |
LPDDR4X-4266 dual-channel 64-bit @2133MHz (68.2GB/s) |
not available | APL1083 | "7 nm" TSMC N7 |
2018/10 |
| Apple A10X | 3x Hurricane @2.36GHz 3x Zephyr @1.0GHz |
12x PowerVR GT7500 Plus @900MHz (768 GFLOPs) |
LPDDR4-3200 dual-channel 64-bit @1600MHz (51.2GB/s) |
not available | APL1071 | "10 nm" TSMC 10FF |
2017/06 | |
| Apple A9X | 2x Twister @2.26GHz | 12x PowerVR GTA7850 @650MHz (345.6 GFLOPs) |
LPDDR4-3200 dual-channel 64-bit @1600MHz (51.2GB/s) |
not available | APL1021 | "16 nm" TSMC 16FF |
2015/11 | |
| Apple A8X | 3x Typhoon @1.5GHz | 8x PowerVR GXA6850 @450MHz (230.4 GFLOPs) |
LPDDR3-1600 dual-channel 64-bit @800MHz (25.6GB/s) |
not available | APL1012 | "20 nm" TSMC |
2014/10 | |
| Apple A6X | 2x Swift @1.4GHz | 4x PowerVR SGX554 @266MHz (68.1 GFLOPs) |
LPDDR2-1066 quad-channel 32-bit @533MHz (17.1GB/s) |
not available | APL5598 | "32 nm" Samsung HKMG |
2012/10 | |
| Apple A5X | 2x ARM Cortex-A9 @1.0GHz |
4x PowerVR SGX543 @200MHz (25 GFLOPs) |
LPDDR2-800 quad-channel 32-bit @400MHz (12.8GB/s) |
not available | APL5498 | "45 nm" Samsung |
2012/03 | |
| Model | CPU | GPU | NPU | RAM | Modem | Catalog name | Lithography | Release date |
PC processors[edit]
| Model | CPU | GPU | NPU | RAM | Modem | Catalog number |
Lithography | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple M4 | 4x Everest @4.4GHz 6x Sawtooth @2.85GHz |
Proprietary (10 cores) (3.7 TFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (38 TOPS) |
LPDDR5x-7500 128-bit @3750MHz (120GB/s) |
not available | APL1206 | "3 nm" TSMC N3E |
2024/05 |
| Apple M3 Max | 14x/16x Everest @4.05GHz 4x Sawtooth @2.75GHz |
Proprietary (30/40 cores) (10.6/14.1 TFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (18 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 384/512-bit @3200MHz (307.2/ 409.6GB/s) |
not available | APL1201 | "3 nm" TSMC N3B |
2023/10 |
| Apple M3 Pro | 5x/6x Everest @4.05GHz 6x Sawtooth @2.75GHz |
Proprietary (14/18 cores) (4.9/6.4 TFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (18 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 192-bit @3200MHz (153.6GB/s) |
not available | APL1201 | "3 nm" TSMC N3B |
2023/10 |
| Apple M3 | 4x Everest @4.05GHz 4x Sawtooth @2.75GHz |
Proprietary (8/10 cores) (2.8 TFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (18 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 128-bit @3200MHz (102.4GB/s) |
not available | APL1201 | "3 nm" TSMC N3B |
2023/10 |
| Apple M2 Ultra | 16x Avalanche 8x Blizzard |
Proprietary (60/76 cores) (27.19 TFLOPS) |
32x Neural Engine (31.6 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 1024-bit @3200MHz (800GB/s) |
not available | "5 nm" TSMC N5P |
2023/06 | |
| Apple M2 Max | 8x Avalanche 4x Blizzard |
Proprietary (38 cores) (13.59 TFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (15.8 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 512-bit @3200MHz (400GB/s) |
not available | T6021 | "5 nm" TSMC N5P |
2023/01 |
| Apple M2 Pro | 8x Avalanche 4x Blizzard |
Proprietary (19 cores) (6.79 TFLOPS) |
16x Neural Engine (15.8 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 256-bit @3200MHz (200GB/s) |
not available | T6020 | "5 nm" TSMC N5P |
2023/01 |
| Apple M2 | 4x Avalanche 4x Blizzard |
Proprietary (10 cores) (3.6 TFLOPs) |
16x Neural Engine (15.8 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 128-bit @3200MHz (100GB/s) |
not available | APL1109 | "5 nm" TSMC N5P |
2022/06 |
| Apple M1 Ultra | 16x Firestorm 4x Icestorm |
Proprietary (64 cores) (21 TFLOPs) |
32x Neural Engine (22 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 1024-bit @3200MHz (800GB/s) |
not available | APL1W06 | "5 nm" TSMC N5 |
2022/03 |
| Apple M1 Max | 8x Firestorm 2x Icestorm |
Proprietary (32 cores) (10.4 TFLOPs) |
16x Neural Engine (11 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 512-bit @3200MHz (400GB/s) |
not available | APL1105 | "5 nm" TSMC N5 |
2021/10 |
| Apple M1 Pro | 8x Firestorm 2x Icestorm |
Proprietary (16 cores) (5.2 TFLOPs) |
16x Neural Engine (11 TOPS) |
LPDDR5-6400 256-bit @3200MHz (200GB/s) |
not available | APL1103 | "5 nm" TSMC N5 |
2021/10 |
| Apple M1 | 4x Firestorm @3.2GHz 4x Icestorm |
Proprietary (octa-core) (2.6 TFLOPs) |
16x Neural Engine (11 TOPS) |
LPDDR4X-4266 dual-channel 64-bit @2133MHz (68.2GB/s) |
not available | APL1102 | "5 nm" TSMC N5 |
2020/11 |
| Model | CPU | GPU | NPU | RAM | Modem | Catalog name | Lithography | Release date |
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Facts about "Ax - Apple"
| designer | Apple + and ARM Holdings + |
| full page name | apple/ax + |
| instance of | system on a chip family + |
| instruction set architecture | ARM + |
| main designer | Apple + |
| manufacturer | Samsung + and TSMC + |
| name | Apple Ax + |
| process | 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) +, 32 nm (0.032 μm, 3.2e-5 mm) +, 28 nm (0.028 μm, 2.8e-5 mm) +, 20 nm (0.02 μm, 2.0e-5 mm) +, 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) +, 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) +, 10 nm (0.01 μm, 1.0e-5 mm) +, 7 nm (0.007 μm, 7.0e-6 mm) + and 5 nm (0.005 μm, 5.0e-6 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 32 bit (4 octets, 8 nibbles) + and 64 bit (8 octets, 16 nibbles) + |