| (17 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{intel title|Saltwell}} | + | {{intel title|Saltwell|arch}} |
{{microarchitecture | {{microarchitecture | ||
| + | | atype = CPU | ||
| name = Saltwell | | name = Saltwell | ||
| + | | designer = Intel | ||
| manufacturer = Intel | | manufacturer = Intel | ||
| introduction = 2011 | | introduction = 2011 | ||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
| pipeline = Yes | | pipeline = Yes | ||
| type = Superscalar | | type = Superscalar | ||
| + | | type 2 = Superpipeline | ||
| OoOE = No | | OoOE = No | ||
| − | | | + | | speculative = No |
| − | | isa | + | | renaming = No |
| + | |isa=x86-64 | ||
| stages = 16 | | stages = 16 | ||
| issues = 2 | | issues = 2 | ||
| inst = Yes | | inst = Yes | ||
| − | | feature = MMX | + | | feature = |
| − | | extension | + | | extension = MOVBE |
| − | | extension | + | | extension 2 = MMX |
| − | | extension | + | | extension 3 = SSE |
| − | | extension | + | | extension 4 = SSE2 |
| + | | extension 5 = SSE3 | ||
| + | | extension 6 = SSSE3 | ||
| cache = Yes | | cache = Yes | ||
| − | | l1i = 32 | + | | l1i = 32 KiB |
| l1i per = Core | | l1i per = Core | ||
| l1i desc = 8-way set associative | | l1i desc = 8-way set associative | ||
| − | | l1d = 24 | + | | l1d = 24 KiB |
| l1d per = Core | | l1d per = Core | ||
| l1d desc = 6-way set associative | | l1d desc = 6-way set associative | ||
| − | | l2 = 512 | + | | l2 = 512 KiB |
| l2 per = Cores | | l2 per = Cores | ||
| l2 desc = 8-way set associative | | l2 desc = 8-way set associative | ||
| Line 45: | Line 51: | ||
| succession = Yes | | succession = Yes | ||
| predecessor = Bonnell | | predecessor = Bonnell | ||
| − | | predecessor link = intel/bonnell | + | | predecessor link = intel/microarchitectures/bonnell |
| successor = Silvermont | | successor = Silvermont | ||
| − | | successor link = intel/silvermont | + | | successor link = intel/microarchitectures/silvermont |
}} | }} | ||
'''Saltwell''' was a [[microarchitecture]] for [[Intel]]'s [[32 nm]] ultra-low power [[system on chip]]s first introduced in late 2011 for the {{intel|Atom}} family. Saltwell is a shrink of {{intel|Bonnell}} which also incorporated all support chips on-die. Saltwell, unlike its predecessor was aimed directly at smartphones (as opposed to MIDs). | '''Saltwell''' was a [[microarchitecture]] for [[Intel]]'s [[32 nm]] ultra-low power [[system on chip]]s first introduced in late 2011 for the {{intel|Atom}} family. Saltwell is a shrink of {{intel|Bonnell}} which also incorporated all support chips on-die. Saltwell, unlike its predecessor was aimed directly at smartphones (as opposed to MIDs). | ||
| Line 56: | Line 62: | ||
! Platform !! Core !! Target | ! Platform !! Core !! Target | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | {{intel|Medfield}} || {{intel|Penwell}} || Smartphones | + | | {{intel|Medfield|l=platform}} || {{intel|Penwell}} || Smartphones |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | {{intel|Cedar Trail}} || {{intel| | + | | {{intel|Cedar Trail}} || {{intel|Cedar Trail}}|| Netbooks |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | {{intel|Clover Trail+}} || {{intel| | + | | {{intel|Clover Trail+}} || {{intel|Cedar Trail+}} || Tablets |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{intel|Medfield|l=platform}} || {{intel|Medfield}} || Tablet / Smartphone | ||
|- | |- | ||
| {{intel|Bordenville}} || {{intel|Centerton}} || Microservers | | {{intel|Bordenville}} || {{intel|Centerton}} || Microservers | ||
| Line 66: | Line 74: | ||
| {{intel|Bordenville}} || {{intel|Briarwood}} || Microservers | | {{intel|Bordenville}} || {{intel|Briarwood}} || Microservers | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | || {{intel|Berryville}} || CE (set-tops) | + | | || {{intel|Berryville|l=core}} || CE (set-tops) |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 77: | Line 85: | ||
## Burst frequencies | ## Burst frequencies | ||
| + | === Key changes from Bonnell === | ||
| + | * L2$ increase rate | ||
| + | * L2$ now seperate rail | ||
| + | * New low-power SRAM for machine state | ||
| + | * Larger instruction fetch | ||
| + | * Double the size of the branch prediction history table | ||
=== Memory Hierarchy === | === Memory Hierarchy === | ||
* Cache | * Cache | ||
** Hardware prefetchers | ** Hardware prefetchers | ||
** L1 Cache: | ** L1 Cache: | ||
| − | *** 32 | + | *** 32 [[KiB]] 8-way [[set associative]] instruction |
**** 1 read and 1 write port | **** 1 read and 1 write port | ||
| − | *** 24 | + | *** 24 KiB 6-way set associative data |
**** 1 read and 1 write port | **** 1 read and 1 write port | ||
*** 8 transistors (instead of 6) to reduce voltage | *** 8 transistors (instead of 6) to reduce voltage | ||
*** Per core | *** Per core | ||
** L2 Cache: | ** L2 Cache: | ||
| − | *** 512 | + | *** 512 KiB 8-way set associative |
*** ECC | *** ECC | ||
| − | *** Shrinkable from 512 | + | *** Shrinkable from 512 KiB to 128 KiB (2-way) |
*** 32B/cycle and 32 outstanding cache requests | *** 32B/cycle and 32 outstanding cache requests | ||
*** separate voltage rail, fixed @ 1.05V | *** separate voltage rail, fixed @ 1.05V | ||
| Line 97: | Line 111: | ||
*** No level 3 cache | *** No level 3 cache | ||
** Non-Cache Shared State Memory | ** Non-Cache Shared State Memory | ||
| − | *** | + | *** 256 KiB low-power SRAM |
*** separate voltage plane | *** separate voltage plane | ||
*** always-on block that stores architectural states while in various power saving modes | *** always-on block that stores architectural states while in various power saving modes | ||
** RAM | ** RAM | ||
| − | *** Maximum of | + | *** Maximum of 1 [[GiB]], 2 GiB, and 4 GiB |
*** dual 32-bit channels, 1 or 2 ranks per channel | *** dual 32-bit channels, 1 or 2 ranks per channel | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Functional Units === | === Functional Units === | ||
| Line 110: | Line 122: | ||
* 2 Integer [[ALU]]s (1 for jumps, 1 for shifts) | * 2 Integer [[ALU]]s (1 for jumps, 1 for shifts) | ||
* 2 FP ALUs (1 adder, 1 for others) | * 2 FP ALUs (1 adder, 1 for others) | ||
| − | * No Integer multiplier & divider | + | * No Integer multiplier & divider (shared with FP ALU instead) |
| + | |||
=== Pipeline === | === Pipeline === | ||
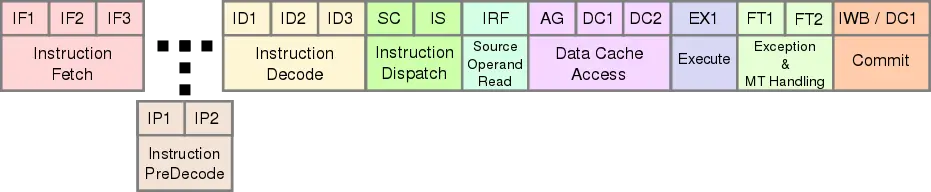
Saltwell has an almost identical pipeline to {{intel|Bonnell|Bonnell's}} with a 16-stage pipeline with a 13-stage miss penalty. It's also still a dual-issue [[superscalar]] but with in-order execution. Reordering logic is was still omitted due to power and area restrictions. | Saltwell has an almost identical pipeline to {{intel|Bonnell|Bonnell's}} with a 16-stage pipeline with a 13-stage miss penalty. It's also still a dual-issue [[superscalar]] but with in-order execution. Reordering logic is was still omitted due to power and area restrictions. | ||
| Line 164: | Line 177: | ||
* '''{{intel|Briarwood}}''' - SoCs for Microservers | * '''{{intel|Briarwood}}''' - SoCs for Microservers | ||
* '''{{intel|Berryville}}''' - SoCs for consumer electronics (e.g. set-tops) | * '''{{intel|Berryville}}''' - SoCs for consumer electronics (e.g. set-tops) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == All Saltwell Chips == | ||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: http://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <table class="wikitable sortable"> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="11" style="background:#D6D6FF;">Saltwell Chips</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th colspan="8">CPU</th><th colspan="3">IGP</th></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><th>Model</th><th>µarch</th><th>Platform</th><th>Core</th><th>Launched</th><th>SDP</th><th>Freq</th><th>Max Mem</th><th>Name</th><th>Freq</th><th>Max Freq</th></tr> | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[microarchitecture::Saltwell]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?microarchitecture | ||
| + | |?platform | ||
| + | |?core name | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?sdp | ||
| + | |?base frequency | ||
| + | |?max memory | ||
| + | |?integrated gpu | ||
| + | |?integrated gpu base frequency | ||
| + | |?integrated gpu max frequency | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 2 | ||
| + | |userparam=12 | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:42, 30 November 2017
| Edit Values | |
| Saltwell µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | 2011 |
| Phase-out | 2013 |
| Process | 32 nm |
| Core Configs | 1, 2 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar, Superpipeline |
| Speculative | No |
| Reg Renaming | No |
| Stages | 16 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Extensions | MOVBE, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3 |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 32 KiB/Core 8-way set associative |
| L1D Cache | 24 KiB/Core 6-way set associative |
| L2 Cache | 512 KiB/Cores 8-way set associative |
| Cores | |
| Core Names | Penwell, Cedarview, Cloverview, Centerton, Briarwood, Berryville |
| Succession | |
Saltwell was a microarchitecture for Intel's 32 nm ultra-low power system on chips first introduced in late 2011 for the Atom family. Saltwell is a shrink of Bonnell which also incorporated all support chips on-die. Saltwell, unlike its predecessor was aimed directly at smartphones (as opposed to MIDs).
Contents
Codenames[edit]
| Platform | Core | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Medfield | Penwell | Smartphones |
| Cedar Trail | Cedar Trail | Netbooks |
| Clover Trail+ | Cedar Trail+ | Tablets |
| Medfield | Medfield | Tablet / Smartphone |
| Bordenville | Centerton | Microservers |
| Bordenville | Briarwood | Microservers |
| Berryville | CE (set-tops) |
Architecture[edit]
Saltwell's primary goals were:
- Improve on Bonnell by getting rid of older support chips
- Add enhancements using 32 nm process while transitioning to 22 nm
- Improve GPU, power
- Burst frequencies
Key changes from Bonnell[edit]
- L2$ increase rate
- L2$ now seperate rail
- New low-power SRAM for machine state
- Larger instruction fetch
- Double the size of the branch prediction history table
Memory Hierarchy[edit]
- Cache
- Hardware prefetchers
- L1 Cache:
- 32 KiB 8-way set associative instruction
- 1 read and 1 write port
- 24 KiB 6-way set associative data
- 1 read and 1 write port
- 8 transistors (instead of 6) to reduce voltage
- Per core
- 32 KiB 8-way set associative instruction
- L2 Cache:
- 512 KiB 8-way set associative
- ECC
- Shrinkable from 512 KiB to 128 KiB (2-way)
- 32B/cycle and 32 outstanding cache requests
- separate voltage rail, fixed @ 1.05V
- Per core
- L3 Cache:
- No level 3 cache
- Non-Cache Shared State Memory
- 256 KiB low-power SRAM
- separate voltage plane
- always-on block that stores architectural states while in various power saving modes
- RAM
- Maximum of 1 GiB, 2 GiB, and 4 GiB
- dual 32-bit channels, 1 or 2 ranks per channel
Functional Units[edit]
The number of functional units were kept to minimum to cut on power consumption.
- 2 Integer ALUs (1 for jumps, 1 for shifts)
- 2 FP ALUs (1 adder, 1 for others)
- No Integer multiplier & divider (shared with FP ALU instead)
Pipeline[edit]
Saltwell has an almost identical pipeline to Bonnell's with a 16-stage pipeline with a 13-stage miss penalty. It's also still a dual-issue superscalar but with in-order execution. Reordering logic is was still omitted due to power and area restrictions.
The longer pipeline allows a more evenly spreading of heat across the chip with more units. This also allows a higher clock rate.
- Instruction Fetch
- 3 stages
- 48 Bytes/Cycle (lower if SMT)
- Instruction Decode
- 3 stages
- Instructions with up to 3 prefixes/Cycle
- Instruction Dispatch
- 2 stages
- Source Operand Read
- 1 stage
- reading register operand
- 1 stage
- Data Cache Access
- 3 stages
- 1 stage for calculating
- 2 stages for reading cache
- 3 stages
- Execution
- 2 clusters
- integers
- quick cache access due to direct connection
- floating point & SIMD
- integers
- 2 clusters
- Exception & MT Handling
- 2 stages
- Commit
- 1 stage
Multithreading[edit]
Saltwell has support for multithreading - up to two threads per core. However each thread compete for the same resources which does inherently means they run slower than they would if they were to run alone.
Branch Prediction[edit]
- Two-level adaptive predictor
- 12-bit branch history register
- Pattern history table has 8192 entries (shared between threads), twice that of Bonnell
- Branch buffer target has 128 entries (4-way, 32 sets)
- Unconditional jumps are ignored
- Always-taken and never-taken are marked in the table
- Penalties:
- 13 stages for miss prediction
- 7 stages for correct prediction but missing branch target buffer (BTB)
Cores[edit]
- Penwell - SoCs specifically for smartphones
- Cedarview - SoCs for netbooks
- Cloverview - SoCs for tablets
- Centerton - SoCs for Microservers; added support for Intel VT and ECC memory
- Briarwood - SoCs for Microservers
- Berryville - SoCs for consumer electronics (e.g. set-tops)
All Saltwell Chips[edit]
| Saltwell Chips | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | IGP | |||||||||
| Model | µarch | Platform | Core | Launched | SDP | Freq | Max Mem | Name | Freq | Max Freq |
| codename | Saltwell + |
| core count | 1 + and 2 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | 2011 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/saltwell + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Saltwell + |
| phase-out | 2013 + |
| pipeline stages | 16 + |
| process | 32 nm (0.032 μm, 3.2e-5 mm) + |