From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/airmont"
(→Multithreading) |
m |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| extension 10 = AES-NI | | extension 10 = AES-NI | ||
| extension 11 = CLMUL | | extension 11 = CLMUL | ||
| + | | extension 12 = RDRAND | ||
| cache = Yes | | cache = Yes | ||
Revision as of 10:18, 10 April 2016
| Edit Values | |
| Airmont µarch | |
| General Info |
Airmont is Intel's 14 nm microarchitecture for the Atom family of system on chips. Introduced in 2015, Airmont is a shrink of Silvermont.
Contents
Codenames
| Platform | Core | Target |
|---|---|---|
| Cherry Trail | Cherry Trail | Smartphones, Tablets |
| Braswell | Braswell | Tablets, PCs |
Architecture
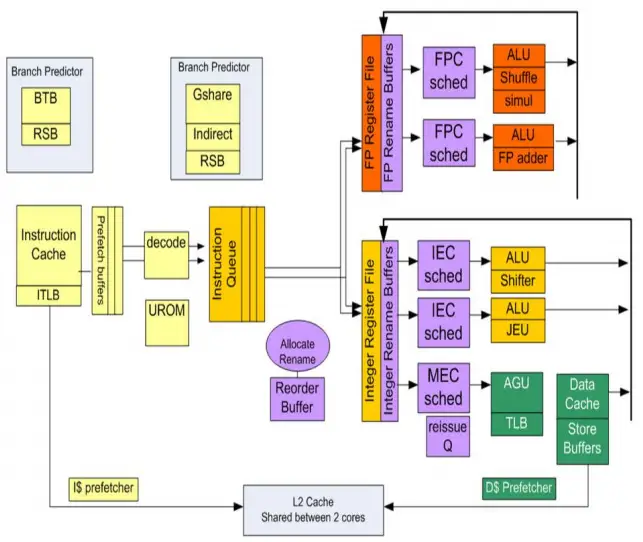
Airmont is for the most part identical to Silvermont with some higher number of execution units to the GPU in some of the higher-end models.
Key changes from Silvermont
- DTLB table size doubled (128 entries -> 256 entries)
- L2 latency increased
- Reorder Buffer was increased (from 32 entries to 48)
- Gen 8 GPUs
Block Diagram
Memory Hierarchy
- Cache
- Hardware prefetchers
- L1 Cache:
- 32 KB 8-way set associative instruction, 64 B line size
- 24 KB 6-way set associative data, 64 B line size
- Per core
- L2 Cache:
- 1 MB 16-way set associative, 64 B line size
- Per 2 cores
- L3 Cache:
- No level 3 cache
- RAM
- Maximum of 1GB, 2 GB, and 4 GB
- dual 32-bit channels, 1 or 2 ranks per channel
Multithreading
Airmont, like Silvermont has no support for Intel Hyper-Threading Technology.
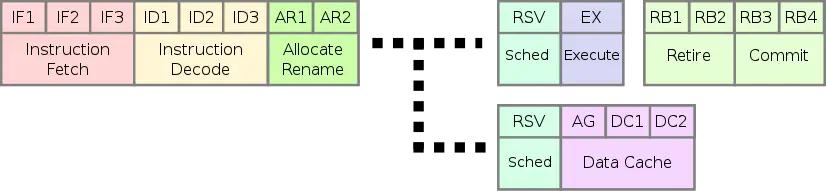
Pipeline
- Main article: Silvermont's Pipeline
Airmont's pipeline is identical to Silvermont's.
Cores
- Cherry Trail - SoCs for Smartphones/Tablets
- Braswell - SoCs for low-end PCs