From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/packages/lga-1567"
(→Intel CPU Sockets) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{title|LGA-1567}}[[File:FCLGA-8.svg|300px|right]] | + | {{intel title|Socket LGA-1567}} |
| − | + | [[File:FCLGA-8.svg|300px|right]] | |
| + | '''Socket LGA-1567''' is the socket for '''FCLGA-8'''-packaged microprocessor designed by [[Intel]] for their high-end enterprise server [[multiprocessors]]. | ||
| + | :This socket was used for chips manufactured based on the {{intel|Nehalem|l=arch}} and {{intel|Westmere|l=arch}} microarchitectures. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;[[Intel]] • [[Xeon]] | ||
| + | *[[intel/packages/lga-1151|Socket LGA-1151]] | ||
| + | *[[intel/packages/lga-1567|Socket LGA-1567]] | ||
== Socket LGA-1567 Models == | == Socket LGA-1567 Models == | ||
| Line 28: | Line 34: | ||
|?base frequency#GHz 1 | |?base frequency#GHz 1 | ||
|?turbo frequency (1 core) | |?turbo frequency (1 core) | ||
| − | |?max memory# | + | |?max memory#GiB |
|?max cpu count | |?max cpu count | ||
|?core count | |?core count | ||
|?thread count | |?thread count | ||
|?has x86 advanced encryption standard instruction set extension | |?has x86 advanced encryption standard instruction set extension | ||
| − | |?has intel turbo boost technology | + | |?has intel turbo boost technology 1_0 |
|?has simultaneous multithreading | |?has simultaneous multithreading | ||
|format=template | |format=template | ||
| Line 44: | Line 50: | ||
{{table count|col=18|ask=[[Category:all microprocessor models]] [[package::FCLGA-8]]}} | {{table count|col=18|ask=[[Category:all microprocessor models]] [[package::FCLGA-8]]}} | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Package == | ||
| + | :;[[intel/packages/lga-1567|Socket LGA-1567]] | ||
| + | * '''LGA 1567''' ''(FCLGA-8)'' • [[Xeon]] 65xx/75xx (Vector), [[Xeon]] E7 (Westmeer-EX) | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{packages/intel/lga-1567}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;[[intel/packages/lga-1151|Socket LGA-1151]] | ||
| + | *'''Socket H4''' (LGA 1151) • Desktop [[Core]] i (Gen 6/7), [[Xeon]] E3 v5/v6 (Skylake, Kaby Lake) | ||
| + | *'''Socket H5''' (LGA 1151 v2) • Desktop [[Core]] i (Gen 8/9) (Coffee Lake), [[Xeon]] E (Coffee Lake-E) | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{packages/intel/lga-1151}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;[[packages/socket-g1|Socket G1]] (rPGA-988A) | ||
| + | *Socket G1 (rPGA 988A) • Mobile Core i (Gen 1), Pentium, Celeron | ||
| + | *Socket G2 (rPGA 988B) • Mobile Core i (Gen 2/3), Pentium, Celeron | ||
| + | *Socket G3 (rPGA 946) • Mobile Core i (Gen 4), Pentium, Celeron | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{packages/intel/rpga-988a}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;[[packages/bga-1288|BGA-1288]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{packages/intel/bga-1288}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Intel CPU Sockets == | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;Type | ||
| + | *BGA (Ball Grid Array) • | ||
| + | **FCBGA (Flip Chip Ball Grid Array) • | ||
| + | *LGA (Land Grid Array) • | ||
| + | **OLGA (Organic Land Grid Array) • | ||
| + | **FC-OLGA (Flip Chip Organic Land Grid Array) • | ||
| + | *PGA (Pin Grid Array) • mPGA, rPGA | ||
| + | **CPGA (Ceramic Pin Grid Array) • Socket 940 - AMD | ||
| + | **OMPGA (Organic Micro Pin Grid Array) • Socket AM3, AM3 - AMD | ||
| + | |||
| + | Organic Micro Ball Grid Array | ||
| + | Ceramic Pin Grid Array (CPGA) | ||
| + | :;General line | ||
| + | |||
| + | *DIP socket (40 pins) • Intel 8086/8088 | ||
| + | *PLCC socket (68 pins) • Intel 80186 | ||
| + | *PLCC socket • Intel 80286 | ||
| + | *PLCC socket • Intel 80386 | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Socket 1 • Intel 80486 | ||
| + | *Socket 2 • Intel 80486 series | ||
| + | *Socket 3 • Intel 80486 series (3.3/5 V) | ||
| + | *Socket 4 • Intel Pentium (60/66 MHz) | ||
| + | *Socket 5 • Intel Pentium (75-133 MHz), AMD 5K86 (K5), Cyrix 6x86, IDT WinChip (C6/2) | ||
| + | *Socket 6 • Intel 80486 (Only very few were produced) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;[[Pentium]] | ||
| + | *Socket 7 • Intel Pentium (MMX), AMD K6, Cyrix 6x86 (MX/MII) | ||
| + | *Slot 1 • Pentium II, Pentium III, Celeron | ||
| + | *Socket 370 (FC-PGA370, PGA370) • Pentium III, Celeron, VIA C3 | ||
| + | *Socket 423 (OLGA423) • Pentium 4 (Early Willamette) | ||
| + | *Socket 478 (mPGA478) • Pentium 4 (EE), Celeron, Celeron D (Late Willamette/Northwood/Early Prescott) | ||
| + | *Socket 479 • Pentium M, Celeron M, VIA C7-M | ||
| + | *Socket T (LGA 775) | ||
| + | :Single Core • Pentium 4 (EE), Celeron (Conroe-L)/Celeron D (Prescott Late Model/Cedar Mill) | ||
| + | :Dual Core • Pentium D, Pentium XE (Smithfield/Pressler), Core 2 Duo, Dual Core, Celeron Dual Core (Conroe/Wolfdale) | ||
| + | :Quad Core • Core 2 Quad, Core 2 Extreme (Kentsfield/Yorkfield) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;[[Core]] | ||
| + | *Socket M (mPGA478MT) • Intel Core/Core2 for Mobile, Pentium Dual Core, Celeron M (Yonah, Merom) | ||
| + | *Socket P (mPGA478MN) • Intel Core 2 for Mobile, Pentium Dual Core, Celeron M (Penryn) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Socket G1 (rPGA 988A) • Mobile Core i (Gen 1), Pentium, Celeron | ||
| + | *Socket G2 (rPGA 988B) • Mobile Core i (Gen 2/3), Pentium, Celeron | ||
| + | *Socket G3 (rPGA 946) • Mobile Core i (Gen 4), Pentium, Celeron | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Socket H ('''LGA 1156''') • Desktop Core i (Gen 1), Xeon (Linfield, Clarkdale) | ||
| + | *Socket H2 ('''LGA 1155''') • Desktop Core i (Gen 2/3), Xeon E3 v1/v2 (Sandy Bridge, Ivy Bridge) | ||
| + | *Socket H3 ('''LGA 1150''') • Desktop Core i (Gen 4/5), Xeon E3 v3/v4 (Haswell, Broadwell) | ||
| + | *Socket H4 ('''LGA 1151''') • Desktop Core i (Gen 6/7), Xeon E3 v5/v6 (Skylake, Kaby Lake) | ||
| + | *Socket H5 ('''LGA 1151 v2''') • Desktop Core i (Gen 8/9) (Coffee Lake), Xeon E (Coffee Lake-E) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *FCBGA1356 (BGA 1356) • Low Power (Gen 6/7) Mobile CPU for Mobile | ||
| + | *FCBGA1440 (BGA 1440) • General Power (Gen 6-10) Mobile CPUs for Mobile | ||
| + | *FCBGA1515 (BGA 1515) • Ultra-low Power (Gen 6/7/8) Mobile CPU for Mobile | ||
| + | *FCBGA1528 (BGA 1528) • Low Power (Gen 8) CPU for select Mobile | ||
| + | *BGA2270 (BGA 2270) • Mobile APU | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''LGA 1200''' (2020) • Desktop Core i (Gen 10/11) (Comet Lake), Xeon E W 1xxx (Rocket Lake-E) | ||
| + | :Intel Comet Lake (10th gen), Intel Rocket Lake (11th gen) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 1700''' (2021) • Desktop Core i (Gen 12-14) (Alder Lake, Raptor Lake (Refresh)) | ||
| + | :Intel Alder Lake (12th gen), Raptor Lake (13th gen), Raptor Lake (14th gen) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 1851''' (2024) • Desktop Core Ultra Series 1 (Meteor Lake-PS) | ||
| + | :Intel Core Ultra (Gen 2) 200S Series (Arrow Lake) | ||
| + | |||
| + | :;Server/Workstation | ||
| + | *Socket 8 (CPGA) • [[Pentium]] Pro | ||
| + | *Slot 2 • [[Pentium]] II Xeon, III Xeon | ||
| + | *Socket 603 • [[Xeon]] (Netburst: Poster, some of Prestonia, some Gallatin) | ||
| + | *Socket 604 • [[Xeon]] (Netburst: Some of the Prestonia, some of the Gallatin, | ||
| + | :Nokona, Irwindale, Cranford, Potomac, Faxville, Core: Tiger, Dunnington) | ||
| + | *PAC418 • Itanium (Merced) | ||
| + | *PAC611 • Itanium 2 (McKinley, Madison, Montishito, Montbale) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 1248''' • Itanium 9300 (Tukwila) or higher series | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Socket J ('''LGA 771''') • Cion (Demn, Wood Crest, Clover Town, Harper Town) | ||
| + | *Socket B ('''LGA 1366''') • Desktop • Core i7 (Gen 1) Extreme (Bloomfield, Gulftown), | ||
| + | :Xeon 55xx/56xx (Gainstown, Westmere-EP) | ||
| + | *Socket B2 ('''LGA 1356''') • Desktop • Xeon E5 v1/v2 | ||
| + | *Socket LS ('''LGA 1567''') (2010) • Server • Xeon 65xx/75xx (Vector), Xeon E7 (Westmeer-EX) | ||
| + | *Socket R ('''LGA 2011''') • Desktop • Core i7 (Gen 2/3) Extreme (Sandy Bridge-E, Ivy Bridge-E), | ||
| + | :Xeon E5 v1/v2 (Sandy Bridge-EP, Ivy Bridge-EP) | ||
| + | *Socket R3 ('''LGA 2011-V3''') • Core i7 (Gen 4) Extreme (Haswell-E, Broadwell-E), | ||
| + | :Xeon E5 v3/v4 (Haswell-EP, Broadwell-EP) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 2011-1''' • [[Xeon]] E7 V2/V3/V4 (Ivy Bridge-EX, Haswell-EX, Broadwell-EX) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''LGA 2066''' • [[Core]] X (Gen 1/2) (Skylake-X, Kaby Lake-X, Cascade Lake-X), [[Xeon]] W (Gen 1/2) (Skylake-W) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 3647''' • [[Xeon]] Scalable (Gen 1/2) (Skylake-SP, Cascade Lake-SP) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 4189''' (2020) • [[Xeon]] Scalable (Gen 3), [[Xeon]] W (Gen 3) (Cooper Lake/Ice Lake-SP) [0.99] (Desktop/Server) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 4677''' (2022) • [[Xeon]] Scalable (Gen 4) (Sapphire Rapids-SP), | ||
| + | :[[Xeon]] W (Gen 4) (Sapphire Rapid-64L/112L), [[Xeon]] Max (Server) | ||
| + | *'''LGA 7529''' (2024) • Intel Sierra Forest (Server) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===80x86=== | ||
| + | '''Table legend:''' | ||
| + | {{legend|#cdf|Intel only}} | ||
| + | {{legend|#fdc|AMD only}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size: 90%; text-align: center; width: 100%;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! style="width:8em" | Socket name | ||
| + | ! style="width:2em" | Year of introduction | ||
| + | ! style="width:14em" |CPU families | ||
| + | ! Computer type | ||
| + | ! Package | ||
| + | ! data-sort-type="number" | Pin count | ||
| + | ! Pin pitch<br>(mm) | ||
| + | ! Bus clock &<br>transfers | ||
| + | ! style="width:18em" | Notes | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| DIP <!-- Dual In-line Package --> | ||
| + | | 1970s | ||
| + | | [[Intel]] [[8086]]<br>[[Intel]] [[8088]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | DIP | ||
| + | | 40 | ||
| + | | 2.54 | ||
| + | | 5/10 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| PLCC <!-- Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier --> | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Intel [[80186]]<br>Intel [[80286]]<br>Intel [[80386]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PLCC | ||
| + | | 68 - 132 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 6–40 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;| PGA68 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | [[Intel 80286]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA <!-- Pin Grid Array --> | ||
| + | | 68 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;| PGA132 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | [[Intel 80386]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 132 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;" | PGA168 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | [[Intel]] 80486<br>AMD]] [[486<br>[[Cyrix]] 486 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 168 | ||
| + | | 2.54 | ||
| + | | 16–50 MHz | ||
| + | | Sometimes referred to as Socket 0 or Socket 486 | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;| Socket 1 | ||
| + | | 1989 | ||
| + | | Intel 80486<br>AMD 486<br>AMD 5x86<br>Cyrix 486<br>Cyrix 5x86 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 169 | ||
| + | | 2.54 | ||
| + | | 16–50 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; " | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;| Socket 2 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Intel 80486<br>Intel [[Pentium <br>OverDrive]] (P24T)<br>Intel DX4<br>AMD 486<br>AMD 5x86<br>Cyrix 486<br>Cyrix 5x86 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 238 | ||
| + | | 2.54 | ||
| + | | 16–50 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;"| Socket 3 | ||
| + | | 1991 | ||
| + | | Intel 80486<br>Intel Pentium <br>OverDrive (P24T)<br>Intel DX4<br>AMD 486<br>AMD 5x86<br>Cyrix 486<br>Cyrix 5x86<br> IBM Blue Lightning | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 237 | ||
| + | | 2.54 | ||
| + | | 16–50 MHz <!--"66MHz486"--> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 4 | ||
| + | | 1993 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Pentium]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 273 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 60–100 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;"| Socket 5 | ||
| + | | 1994 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium<br>[[AMD]] K5<br>[[Cyrix]] 6x86<br>[[IDT]] WinChip C6<br>IDT WinChip 2 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 320 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 50–100 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 6 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Intel 80486 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 235 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Designed but not used | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;" | Socket 463<br>(Socket NexGen) | ||
| + | | 1994 | ||
| + | | [[NexGen]] Nx586 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 463 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 37.5–66 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;"| Socket 7 | ||
| + | | 1994 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium<br>Intel Pentium MMX<br>AMD K6 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 321 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 50–66 MHz | ||
| + | | It is possible to use Socket 7 processors in a Socket 5. <!-- An adapter is required, or if one is careful, a socket 7 can be pulled off its pins and put onto a socket 5 board, allowing the use of socket 7 processors.--> | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 8 | ||
| + | | 1995 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium Pro | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 387 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 60–66 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Slot 1 | ||
| + | | 1997 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium II<br>Intel Pentium III | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | Slot | ||
| + | | 242 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 66–133 MHz | ||
| + | | Celeron <br>(Covington, Mendocino)<br>Pentium II <br>(Klamath, Deschutes)<br>Pentium III <br>(Katmai) - all versions <br>Pentium III <br>(Coppermine) | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;| [[Super Socket 7]] | ||
| + | | 1998 | ||
| + | | [[AMD]] K6-2<br>AMD [[AMD]] K6-III<br>[[Rise Technology|Rise]] mP6<br>[[Cyrix]] 6x86 (MII) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 321 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 66–100 MHz | ||
| + | | Backward compatible with Socket 5 and Socket 7 processors. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Slot 2 | ||
| + | | 1998 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium II Xeon<br>Intel Pentium III Xeon | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | Slot | ||
| + | | 330 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 100–133 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;" | Socket 615 | ||
| + | | 1999 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Mobile Pentium II]]<br>Intel [[Mobile Celeron]] | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 615 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 66 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| Slot A | ||
| + | | 1999 | ||
| + | | AMD [[Athlon]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | Slot | ||
| + | | 242 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 100 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left;"| Socket 370 | ||
| + | | 1999 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium III<br>Intel [[Celeron]]<br>[[VIA]] Cyrix III<br>[[VIA]] C3 | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 370 | ||
| + | | 1.27 <ref>{{cite book |title=Intel 815 Chipset Family |url=http://www.intel.com/design/chipsets/designex/29071401.pdf |website=Intel |access-date=May 4, 2009}}</ref> | ||
| + | | 66–133 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| Socket A <br>Socket 462 | ||
| + | | 2000 | ||
| + | | AMD Athlon<br>AMD [[Duron]]<br>AMD [[Athlon XP]]<br>AMD [[Athlon XP-M]]<br>AMD [[Athlon MP]]<br>AMD [[Sempron]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 462 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 100–200 MHz<br>400 MT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 423 | ||
| + | | 2000 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium 4 | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 423 | ||
| + | | 1 | ||
| + | | 100 MHz<br />400 MT/s | ||
| + | | Willamette core only.<br>Can accept some of Socket 478 CPU with an adapter. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 495 | ||
| + | | 2000 | ||
| + | | Intel Celeron<br>Intel Pentium III | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 495 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 66–133 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 603 | ||
| + | | 2001 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Xeon]] | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 603 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 100–133 MHz<br>400–533 MT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 478<br>Socket N | ||
| + | | 2001 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium 4<br>Intel Celeron<br>Intel Pentium 4 EE<br>Intel Pentium 4 M | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 478 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 100–200 MHz<br>400–800 MT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| Socket 563 | ||
| + | | 2002 | ||
| + | | AMD Athlon XP-M | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 563 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 333 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 604 | ||
| + | | 2002 | ||
| + | | Intel Xeon | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 604 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 100–266 MHz<br>400–1066 MT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| Socket 754 | ||
| + | | 2003 | ||
| + | | AMD [[Athlon 64]]<br>AMD Sempron<br>AMD [[Turion 64]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 754 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 200–800 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| Socket 940 | ||
| + | | 2003 | ||
| + | | AMD [[Opteron]]<br>AMD [[Athlon 64 FX]] | ||
| + | | Desktop<br>Server | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 940 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 200–1000 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket 479 | ||
| + | | 2003 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Pentium M]]<br>Intel [[Celeron M]] | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 479 <ref name="479note">CPU only has 478 pins, but the socket has 479.</ref> | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 100–133 MHz<br>400–533 MT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| Socket 939 | ||
| + | | 2004 | ||
| + | | AMD Athlon 64<br>AMD Athlon 64 FX<br>AMD [[Athlon 64 X2]]<br>AMD Opteron | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 939 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 200–1000 MHz | ||
| + | | Support of Athlon 64 FX to 1 GHz<br>Support of Opteron limited to 100-series only | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| LGA 775/<br>Socket T | ||
| + | | 2004 | ||
| + | | Intel Pentium 4<br>Intel Pentium D<br>Intel Celeron<br>Intel Celeron D<br>Intel Pentium XE<br>Intel Core 2 Duo<br> Intel Core 2 Quad<br>Intel Xeon | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 775 | ||
| + | | 1.09 x 1.17 | ||
| + | | 1600 MHz | ||
| + | | Can accept LGA 771 CPU with slight modification and use of an adapter. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| Socket M | ||
| + | | 2006 | ||
| + | | Intel Core Solo<br>Intel Core Duo<br>Intel Dual-Core Xeon<br>Intel Core 2 Duo | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 478 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 133–166 MHz<br />533–667 MT/s | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket 479 | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| LGA 771<br />Socket J | ||
| + | | 2006 | ||
| + | | Intel Xeon | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 771 | ||
| + | | 1.09 x 1.17<ref>{{cite web |title=LGA771 Socket Mechanical Design Guide |url=http://www.intel.com/Assets/PDF/designguide/313871.pdf |website=Intel |language=en-US |access-date=May 3, 2009}}</ref> | ||
| + | | 1600 MHz | ||
| + | | See LGA 775/Socket T above | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket S1]] | ||
| + | | 2006 | ||
| + | | AMD [[Turion 64 X2]] | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 638 | ||
| + | | 1.27<ref>{{cite web |title=Low-Profile Socket S1 Design Specification |url=https://www.amd.com/us-en/assets/content_type/white_papers_and_tech_docs/31839.pdf |website=AMD |access-date=May 3, 2009}}</ref> | ||
| + | | 200–800 MHz | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM2]] | ||
| + | | 2006 | ||
| + | | AMD Athlon 64<br />AMD Athlon 64 X2 | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 940 | ||
| + | | 1.27<ref name="amd.com">{{cite web |title=AMD Opteron Processor Product Data Sheet |url=https://www.amd.com/us-en/assets/content_type/white_papers_and_tech_docs/23932.pdf |website=AMD |access-date=May 3, 2009}}</ref> | ||
| + | | 200–1000 MHz | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket 754 and Socket 939 | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket F]]/<br />[[Socket L]] ([[Socket 1207FX]]) | ||
| + | | 2006 | ||
| + | | AMD Athlon 64 FX<br />AMD Opteron<br />(Socket L only support Athlon 64 FX) | ||
| + | | Desktop<br />Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1207 | ||
| + | | 1.1<ref>{{cite web |title=Thermal Design Guide for Socket F (1207) Processors |url=https://www.amd.com/us-en/assets/content_type/white_papers_and_tech_docs/32800.pdf |website=AMD |access-date=May 6, 2009}}</ref> | ||
| + | | Socket L: 1000 MHz in Single CPU mode,<br />2000 MHz in Dual CPU mode | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket 940<br />Socket L was intended for enthusiasts who wanted server power in a desktop PC. It is just a re-branded Socket F that doesn't need special RAM, and may have only been used in the Asus L1N64-SLI WS Motherboard. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM2+]] | ||
| + | | 2007 | ||
| + | | AMD Athlon 64<br />AMD [[Athlon X2]]<br />AMD [[AMD Phenom|Phenom]]<br />AMD [[Phenom II]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 940 | ||
| + | | 1.27<ref name="amd.com"/> | ||
| + | | 200–2600 MHz | ||
| + | | Separated power planes<br />Replaces Socket AM2<br />AM2+ Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2<br />AM2 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2+ | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[Socket P]] | ||
| + | | 2007 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Core 2]] | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 478 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 133–266 MHz<br />533–1066 MT/s | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket M | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1366]]/<br />[[Socket B]] | ||
| + | | 2008 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Core i7]] (900 series)<br />Intel Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series) | ||
| + | | Desktop<br />Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1366 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket J (LGA 771) in the entry level. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM3]] | ||
| + | | 2009 | ||
| + | | AMD Phenom II<br />AMD [[Athlon II]]<br />AMD Sempron<br />AMD Opteron (1300 series) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 941<ref name="941note">CPU only has 938 pins, but the socket has 941.</ref> or 940<ref name="940note">AMD Documentation {{cite web |title=Socket AM3 design Specification |url=http://support.amd.com/us/Processor_TechDocs/40523.pdf |website=AMD |access-date=January 5, 2012}}</ref> | ||
| + | | 1.27<ref name="amd.com"/> | ||
| + | | 200–3200 MHz | ||
| + | | Separated power planes<br />Replaces Socket AM2+<br />AM3 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2/AM2+<br />Sempron 140 only | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;" | [[rPGA 988A]]/<br />[[Socket G1]] | ||
| + | | 2009 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Clarksfield (microprocessor)|Clarksfield]]<br />Intel [[Arrandale]] | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | [[Pin grid array#rPGA|rPGA]] | ||
| + | | 988 | ||
| + | | 1 | ||
| + | | 2.5 GT/s | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket P | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1156]]/<br />[[Socket H]] | ||
| + | | 2009 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Nehalem (microarchitecture)|Nehalem]] (1st gen)<br />Intel [[Westmere (microarchitecture)|Westmere]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1156 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 2.5 GT/s | ||
| + | | [[Direct Media Interface|DMI]] bus is a (perhaps modified) [[PCI Express|PCIe]] x4 v1.1 interface | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket G34]] | ||
| + | | 2010 | ||
| + | | AMD Opteron (6000 series) | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1974 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 200–3200 MHz | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket F | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket C32]] | ||
| + | | 2010 | ||
| + | | AMD Opteron (4000 series) | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1207 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 200–3200 MHz | ||
| + | | Replaces Socket F, Socket AM3 | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1567]]/<br />[[Socket LS]] | ||
| + | | 2010 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Beckton (microprocessor)#Beckton|Xeon 6500/7500-series]] | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1567 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1155]]/<br />[[Socket H2]] | ||
| + | | 2011/Q1<br />2011.01.09 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Sandy Bridge (microarchitecture)|Sandy Bridge]] (2nd gen)<br />Intel [[Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture)|Ivy Bridge]] (3rd gen) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1155 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 5.7 GT/s | ||
| + | | used for Intel 2nd generation, 3rd generation processors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sandy Bridge supports 20 PCIe 2.0 lanes.<br />Ivy Bridge supports 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes.<br />Intel Mainstream Socket. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 2011]]/<br />[[Socket R]] | ||
| + | | 2011/Q3<br />2011.11.14 | ||
| + | | Intel Core i7 3xxx [[Sandy Bridge-E]]<br />Intel Core i7 4xxx [[Ivy Bridge-E]]<br />Intel Xeon E5 2xxx/4xxx (Sandy Bridge EP) (2/4S)<br />Intel Xeon E5-2xxx/4xxx v2 (Ivy Bridge EP) (2/4S) | ||
| + | | Desktop<br />Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 2011 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | ||
| + | | Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP both support 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes.<br />Using the Xeon focused 2011 socket gives also 4 memory Channels. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[rPGA 988B]]/<br />[[Socket G2]] | ||
| + | | 2011 | ||
| + | | Intel Core i7<br />Intel [[Core i5]]<br />Intel [[Core i3]]<br />(2000, 3000 series) | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | rPGA | ||
| + | | 988 | ||
| + | | 1 | ||
| + | | 2.5 GT/s, 4.8 GT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FM1]] | ||
| + | | 2011 | ||
| + | | AMD [[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#K10 architecture (2011): Llano|Llano Processors]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 905 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 5.2 GT/s | ||
| + | | used for 1st generation APUs | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FS1]] | ||
| + | | 2011 | ||
| + | | AMD Llano Processors | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 722 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 3.2 GT/s | ||
| + | | used for 1st generation Mobile APUs | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM3+]] | ||
| + | | 2011 | ||
| + | | AMD [[Bulldozer (processor)#2nd Generation Piledriver core|FX Vishera]]{{Broken anchor|date=2024-09-19|bot=User:Cewbot/log/20201008/configuration|target_link=Bulldozer (processor)#2nd Generation Piledriver core|reason= The anchor (2nd Generation Piledriver core) [[Special:Diff/546495333|has been deleted]].}}<br />AMD [[Bulldozer (microarchitecture)|FX Zambezi]]<br />AMD Phenom II<br />AMD [[Athlon II]]<br />AMD Sempron | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 942 (CPU 71pin) | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | 3.2 GT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1356]]/<br />[[Socket B2]] | ||
| + | | 2012 | ||
| + | | Intel Xeon (E5 1400 & 2400 series) | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1356 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 3.2–4.0 GT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FM2]] | ||
| + | | 2012 | ||
| + | | AMD [[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Trinity|Trinity Processors]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 904 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | used for 2nd generation APUs | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1150]]/<br />[[Socket H3]] | ||
| + | | 2013 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Haswell (microarchitecture)|Haswell]] (4th gen)<br />Intel [[Haswell (microarchitecture)#REFRESH|Haswell Refresh]]<br />Intel [[Broadwell (microarchitecture)|Broadwell]] (5th gen) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1150 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | used for Intel's 4th generation (Haswell/Haswell Refresh), the handful of intel 5th generation processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[rPGA 946B/947]]/<br />[[Intel Socket G3|Socket G3]] | ||
| + | | 2013 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Haswell (microarchitecture)|Haswell]] | ||
| + | | Notebook | ||
| + | | rPGA | ||
| + | | 946 | ||
| + | | 1 | ||
| + | | 5.0 GT/s | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket FM2+]] | ||
| + | | 2014 | ||
| + | | AMD [[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Steamroller architecture (2014):_Kaveri|Kaveri]]<br />AMD [[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Steamroller architecture (Q2–Q3 2015): Godavari|Godavari]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 906 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Compatible with [[AMD APU]]s such as "[[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Richland|Richland" and "Trinity]]" | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM1]] | ||
| + | | 2014 | ||
| + | | AMD Athlon<br />AMD Sempron | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 721 | ||
| + | | 1.27 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Compatible with AMD APUs such as "[[AMD Accelerated Processing Unit#Kabini|Kabini]]" | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;" | [[LGA 2011-v3]] | ||
| + | | 2014<br />(August and September) | ||
| + | | [[Haswell-E]]<br />[[Haswell-EP]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 2011 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Up to 68 GB/sec.<br />Depends on DDR4 speed and channel count. | ||
| + | | Up to 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes.<br />Up to 4 memory Channels. | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1151]]/<br />[[Socket H4]] | ||
| + | | 2015 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Skylake (microarchitecture)|Skylake]] (6th gen)<br />Intel [[Kaby Lake (microarchitecture)|Kaby Lake]] (7th gen)<br />Intel [[Coffee Lake (microarchitecture)|Coffee Lake]] (8th gen)<br />Intel [[Coffee Lake|Coffee Lake Refresh]] (9th gen) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1151 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | 5 GT/s - 8 GT/s | ||
| + | | used for Intel's 6th generation (Skylake), 7th generation (Kaby Lake), 8th generation (Coffee Lake) processors, and 9th generation (Coffee Lake Refresh) processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 3647]] | ||
| + | | 2016 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Xeon Phi]]<br />Intel Skylake-SP | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 3647 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | used for Intel's Xeon Phi x200 and Xeon Scalable processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM4]] | ||
| + | | 2016 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | AMD Athlon [[List of AMD Athlon processors#"Bristol Ridge" (2016)|Bristol Ridge]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | AMD Athlon [[List of AMD Athlon processors#"Raven Ridge", 14 nm|Raven Ridge 14nm]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | AMD Athlon [[List of AMD Athlon processors#"Picasso", 12 nm|Picasso 12nm]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 1000 series|1000 series]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 2000 series|2000 series]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 3000 series|3000 series]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 4000 series|4000 series]] | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 5000 series|5000 series]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | PGA | ||
| + | | 1331 | ||
| + | | 1 | ||
| + | | Depends on DDR4 speed | ||
| + | | compatible with AMD [[Ryzen]] 9, Ryzen 7, Ryzen 5 & Ryzen 3 Zen based processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket SP3]] | ||
| + | | 2017 | ||
| + | | AMD Epyc [[Epyc#First generation Epyc (Naples)|Naples]]<br /> AMD Epyc [[Epyc#Second generation Epyc (Rome)|Rome]]<br /> AMD Epyc [[Epyc#Third generation Epyc (Milan)|Milan]] | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4094 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Depends on DDR4 speed | ||
| + | | compatible with AMD Epyc processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket TR4]]/<br />Socket SP3r2 | ||
| + | | 2017 | ||
| + | | AMD Ryzen Threadripper ([[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Whitehaven (Threadripper 1000 series, Zen based)|1000 series]])<br />AMD Ryzen Threadripper ([[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Colfax (Threadripper 2000 series, Zen+ based)|2000 series]]) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4094 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Depends on DDR4 speed | ||
| + | | compatible with AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 2066]]/<br />[[Socket R4]] | ||
| + | | 2017 | ||
| + | | Intel Skylake-X<br />Intel Kaby Lake-X<br />Intel Cascade Lake-X | ||
| + | | Desktop<br />Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 2066 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Used for Intel's 7th generation (Skylake-X & Kaby Lake-X & Cascade Lake-X) series of Core-X processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sTRX4]]/<br />Socket SP3r3 | ||
| + | | 2019 | ||
| + | | AMD Ryzen Threadripper ([[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Castle Peak (Threadripper 3000 series, Zen 2 based)|3000 series]]) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4094 | ||
| + | | ? | ||
| + | | Depends on DDR4 speed | ||
| + | | compatible with 3rd generation AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 4189]] | ||
| + | | 2020 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Cooper Lake (microprocessor)|Cooper Lake]]<br />Intel [[Ice Lake (microprocessor)|Ice Lake-SP]] | ||
| + | | Desktop<br />Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4189<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=LGA 4189 Socket and Hardware |url=https://www.mouser.com/pdfDocs/LGA4189.pdf}}</ref> | ||
| + | | 0.99<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1200]] | ||
| + | | 2020 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Comet Lake]] (10th gen)<br />Intel [[Rocket Lake]] (11th gen) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1200 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| [[LGA 1700]] | ||
| + | | 2021 | ||
| + | | Intel [[Alder Lake]] (12th gen)<br />Intel [[Raptor Lake]] (13th gen) | ||
| + | Intel Raptor Lake (14th gen) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1700 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket sWRX8]] | ||
| + | | 2022 | ||
| + | | AMD Ryzen Threadripper Pro ([[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Chagall (Threadripper 5000 series, Zen 3 based)|5000 series]]) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4094 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket AM5]] | ||
| + | | 2022 | ||
| + | | AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 7000 series|7000 series]]<br/> AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 8000 series|8000 series]] (APU)<br/>AMD Ryzen [[List of AMD Ryzen processors#Ryzen 9000 series|9000 series]] | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1718 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Zen 4 Ryzen CPUs | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket SP5]] | ||
| + | | 2022 | ||
| + | | AMD [[Epyc#Fourth generation Epyc (Genoa, Bergamo and Siena)| Epyc Genoa]] | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 6096 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | Used for [[EPYC]] Genoa and Milan | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| LGA 4677 | ||
| + | | 2022 | ||
| + | | [[Intel]] <br>[[Sapphire Rapids]] | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4677 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| [[Socket SP6]] | ||
| + | | 2023 | ||
| + | | [[AMD]] [[EPYC]] Siena <!--Epyc 4 Gen (Genoa, Bergamo and Siena)--> | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4844 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#fdc;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#fdc;"| Socket sTR5 | ||
| + | | 2023 | ||
| + | | [[AMD]] [[Ryzen Threadripper]]<br> AMD Ryzen Threadripper Pro <br>Storm Peak (7000 series, Zen 4) | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 4844 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| LGA 1851 | ||
| + | | 2024 | ||
| + | | Intel Meteor Lake-PS <br>(Core Ultra Series 1)<br>Intel [[Arrow Lake]] <br>(Core Ultra 200S Series)<br>{{abbr|TBA|to be announced}} | ||
| + | | Desktop | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 1851 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- style="vertical-align:top; background:#cdf;" | ||
| + | ! style="text-align:left; background:#cdf;"| LGA 7529 | ||
| + | | 2024 | ||
| + | | [[Intel]] Sierra Forest | ||
| + | | Server | ||
| + | | LGA | ||
| + | | 7529 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! style="width:8em" | Socket name | ||
| + | ! style="width:4em" | Year of introduction | ||
| + | ! style="width:12em" | CPU families | ||
| + | ! Computer type | ||
| + | ! Package | ||
| + | ! Pin count | ||
| + | ! Pin pitch<br>(mm) | ||
| + | ! Bus clock &<br>transfers | ||
| + | ! style="width:18em" | Notes | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === [[Intel]] CPU Packages === | ||
| + | * [[packages/bga-1288|BGA-1288]] ([[Intel]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Semiconductor packages]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:37, 26 May 2025
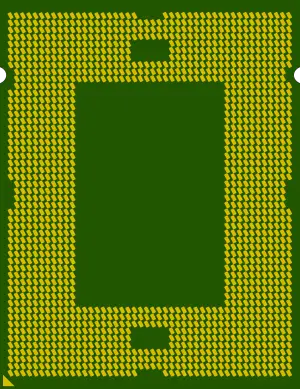
Socket LGA-1567 is the socket for FCLGA-8-packaged microprocessor designed by Intel for their high-end enterprise server multiprocessors.
- Socket LGA-1151
- Socket LGA-1567
Contents
[hide]Socket LGA-1567 Models[edit]
| LGA-1567 Chips | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | Features | ||||||||||||||||
| Model | Family | Price | Core | Launched | S | C | T | TDP | Freq | Turbo | Max Mem | S | C | T | AES | TBT 1.0 | HT |
| E7-8870 | Xeon E7 | $ 4,616.00 € 4,154.40 £ 3,738.96 ¥ 476,971.28 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,399.99 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,399,990 kHz | 2,799.99 MHz 2.8 GHz 2,799,990 kHz | 4,096 GiB 4,194,304 MiB 4,294,967,296 KiB 4,398,046,511,104 B 4 TiB | 8 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-8867L | Xeon E7 | $ 4,172.00 € 3,754.80 £ 3,379.32 ¥ 431,092.76 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 105 W 105,000 mW 0.141 hp 0.105 kW | 2,133.33 MHz 2.133 GHz 2,133,330 kHz | 2,533.33 MHz 2.533 GHz 2,533,330 kHz | 4,096 GiB 4,194,304 MiB 4,294,967,296 KiB 4,398,046,511,104 B 4 TiB | 8 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-8860 | Xeon E7 | $ 4,061.00 € 3,654.90 £ 3,289.41 ¥ 419,623.13 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,266.66 MHz 2.267 GHz 2,266,660 kHz | 2,666.66 MHz 2.667 GHz 2,666,660 kHz | 4,096 GiB 4,194,304 MiB 4,294,967,296 KiB 4,398,046,511,104 B 4 TiB | 8 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-8850 | Xeon E7 | $ 3,059.00 € 2,753.10 £ 2,477.79 ¥ 316,086.47 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,000 MHz 2 GHz 2,000,000 kHz | 2,400 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,400,000 kHz | 4,096 GiB 4,194,304 MiB 4,294,967,296 KiB 4,398,046,511,104 B 4 TiB | 8 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-8837 | Xeon E7 | $ 2,280.00 € 2,052.00 £ 1,846.80 ¥ 235,592.40 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,666.66 MHz 2.667 GHz 2,666,660 kHz | 2,799.99 MHz 2.8 GHz 2,799,990 kHz | 4,096 GiB 4,194,304 MiB 4,294,967,296 KiB 4,398,046,511,104 B 4 TiB | 8 | 8 | 8 | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
| E7-8830 | Xeon E7 | $ 2,280.00 € 2,052.00 £ 1,846.80 ¥ 235,592.40 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 105 W 105,000 mW 0.141 hp 0.105 kW | 2,133.33 MHz 2.133 GHz 2,133,330 kHz | 2,399.99 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,399,990 kHz | 4,096 GiB 4,194,304 MiB 4,294,967,296 KiB 4,398,046,511,104 B 4 TiB | 8 | 8 | 16 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-4870 | Xeon E7 | $ 4,394.00 € 3,954.60 £ 3,559.14 ¥ 454,032.02 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 4 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,399.99 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,399,990 kHz | 2,799.99 MHz 2.8 GHz 2,799,990 kHz | 2,048 GiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2 TiB | 4 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-4860 | Xeon E7 | $ 3,838.00 € 3,454.20 £ 3,108.78 ¥ 396,580.54 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 4 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,266.66 MHz 2.267 GHz 2,266,660 kHz | 2,666.66 MHz 2.667 GHz 2,666,660 kHz | 2,048 GiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2 TiB | 4 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-4850 | Xeon E7 | $ 2,837.00 € 2,553.30 £ 2,297.97 ¥ 293,147.21 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 4 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 1,999.99 MHz 2 GHz 1,999,990 kHz | 2,399.99 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,399,990 kHz | 2,048 GiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2 TiB | 4 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-4830 | Xeon E7 | $ 2,059.00 € 1,853.10 £ 1,667.79 ¥ 212,756.47 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 105 W 105,000 mW 0.141 hp 0.105 kW | 2,133.33 MHz 2.133 GHz 2,133,330 kHz | 2,399.66 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,399,660 kHz | 2,048 GiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2 TiB | 4 | 8 | 16 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-4820 | Xeon E7 | $ 1,446.00 € 1,301.40 £ 1,171.26 ¥ 149,415.18 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 105 W 105,000 mW 0.141 hp 0.105 kW | 1,999.99 MHz 2 GHz 1,999,990 kHz | 2,266.66 MHz 2.267 GHz 2,266,660 kHz | 2,048 GiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2 TiB | 4 | 8 | 16 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-4807 | Xeon E7 | $ 890.00 € 801.00 £ 720.90 ¥ 91,963.70 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 4 | 6 | 12 | 95 W 95,000 mW 0.127 hp 0.095 kW | 1,866.66 MHz 1.867 GHz 1,866,660 kHz | 2,048 GiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2 TiB | 4 | 6 | 12 | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | |
| E7-2870 | Xeon E7 | $ 4,227.00 € 3,804.30 £ 3,423.87 ¥ 436,775.91 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,399.99 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,399,990 kHz | 2,799.99 MHz 2.8 GHz 2,799,990 kHz | 1,024 GiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1 TiB | 2 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-2860 | Xeon E7 | $ 3,670.00 € 3,303.00 £ 2,972.70 ¥ 379,221.10 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 2,266.66 MHz 2.267 GHz 2,266,660 kHz | 2,666.66 MHz 2.667 GHz 2,666,660 kHz | 1,024 GiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1 TiB | 2 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-2850 | Xeon E7 | $ 2,558.00 € 2,302.20 £ 2,071.98 ¥ 264,318.14 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 2 | 10 | 20 | 130 W 130,000 mW 0.174 hp 0.13 kW | 1,999.99 MHz 2 GHz 1,999,990 kHz | 2,666.66 MHz 2.667 GHz 2,666,660 kHz | 1,024 GiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1 TiB | 2 | 10 | 20 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-2830 | Xeon E7 | $ 1,779.00 € 1,601.10 £ 1,440.99 ¥ 183,824.07 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 105 W 105,000 mW 0.141 hp 0.105 kW | 2,133.33 MHz 2.133 GHz 2,133,330 kHz | 2,399.99 MHz 2.4 GHz 2,399,990 kHz | 1,024 GiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1 TiB | 2 | 8 | 16 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-2820 | Xeon E7 | $ 1,334.00 € 1,200.60 £ 1,080.54 ¥ 137,842.22 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 105 W 105,000 mW 0.141 hp 0.105 kW | 1,999.99 MHz 2 GHz 1,999,990 kHz | 2,266.66 MHz 2.267 GHz 2,266,660 kHz | 1,024 GiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1 TiB | 2 | 8 | 16 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| E7-2803 | Xeon E7 | $ 774.00 € 696.60 £ 626.94 ¥ 79,977.42 | Westmere EX | 5 April 2011 | 2 | 6 | 12 | 105 W 105,000 mW 0.141 hp 0.105 kW | 1,733.33 MHz 1.733 GHz 1,733,330 kHz | 1,024 GiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1 TiB | 2 | 6 | 12 | ✔ | ✘ | ✔ | |
| Count: 18 | |||||||||||||||||
Package[edit]
- Socket LGA-1567
| Package | FCLGA-8 (LGA) |  |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | 49.1 mm x 56.4 mm x 4.2 mm | |
| Pitch | 1 mm | |
| Pin Count | 1567 | |
| Socket | LGA-1567 |
- Socket H4 (LGA 1151) • Desktop Core i (Gen 6/7), Xeon E3 v5/v6 (Skylake, Kaby Lake)
- Socket H5 (LGA 1151 v2) • Desktop Core i (Gen 8/9) (Coffee Lake), Xeon E (Coffee Lake-E)
| Package | FCLGA-1151 (LGA) FC-LGA14C |  |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | 37.5 mm x 37.5 mm x 4.4 mm | |
| Pitch | 0.914 mm | |
| Contacts | 1151 | |
| Socket | LGA-1151 |
- Socket G1 (rPGA-988A)
- Socket G1 (rPGA 988A) • Mobile Core i (Gen 1), Pentium, Celeron
- Socket G2 (rPGA 988B) • Mobile Core i (Gen 2/3), Pentium, Celeron
- Socket G3 (rPGA 946) • Mobile Core i (Gen 4), Pentium, Celeron
| Package | rPGA-988A (rPGA) |  |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | 36 mm x 35 mm x 2.12 mm | |
| Pitch | 1 mm | |
| Pin Count | 988 | |
| Socket | Socket-G1 (PGA) |
| Package | BGA-1288 (BGA) |  |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | 34 mm x 28 mm x 2.1 mm | |
| Pitch | 0.7 mm | |
| Pin Count | 1288 |
Intel CPU Sockets[edit]
- Type
- BGA (Ball Grid Array) •
- FCBGA (Flip Chip Ball Grid Array) •
- LGA (Land Grid Array) •
- OLGA (Organic Land Grid Array) •
- FC-OLGA (Flip Chip Organic Land Grid Array) •
- PGA (Pin Grid Array) • mPGA, rPGA
- CPGA (Ceramic Pin Grid Array) • Socket 940 - AMD
- OMPGA (Organic Micro Pin Grid Array) • Socket AM3, AM3 - AMD
Organic Micro Ball Grid Array Ceramic Pin Grid Array (CPGA)
- General line
- DIP socket (40 pins) • Intel 8086/8088
- PLCC socket (68 pins) • Intel 80186
- PLCC socket • Intel 80286
- PLCC socket • Intel 80386
- Socket 1 • Intel 80486
- Socket 2 • Intel 80486 series
- Socket 3 • Intel 80486 series (3.3/5 V)
- Socket 4 • Intel Pentium (60/66 MHz)
- Socket 5 • Intel Pentium (75-133 MHz), AMD 5K86 (K5), Cyrix 6x86, IDT WinChip (C6/2)
- Socket 6 • Intel 80486 (Only very few were produced)
- Socket 7 • Intel Pentium (MMX), AMD K6, Cyrix 6x86 (MX/MII)
- Slot 1 • Pentium II, Pentium III, Celeron
- Socket 370 (FC-PGA370, PGA370) • Pentium III, Celeron, VIA C3
- Socket 423 (OLGA423) • Pentium 4 (Early Willamette)
- Socket 478 (mPGA478) • Pentium 4 (EE), Celeron, Celeron D (Late Willamette/Northwood/Early Prescott)
- Socket 479 • Pentium M, Celeron M, VIA C7-M
- Socket T (LGA 775)
- Single Core • Pentium 4 (EE), Celeron (Conroe-L)/Celeron D (Prescott Late Model/Cedar Mill)
- Dual Core • Pentium D, Pentium XE (Smithfield/Pressler), Core 2 Duo, Dual Core, Celeron Dual Core (Conroe/Wolfdale)
- Quad Core • Core 2 Quad, Core 2 Extreme (Kentsfield/Yorkfield)
- Socket M (mPGA478MT) • Intel Core/Core2 for Mobile, Pentium Dual Core, Celeron M (Yonah, Merom)
- Socket P (mPGA478MN) • Intel Core 2 for Mobile, Pentium Dual Core, Celeron M (Penryn)
- Socket G1 (rPGA 988A) • Mobile Core i (Gen 1), Pentium, Celeron
- Socket G2 (rPGA 988B) • Mobile Core i (Gen 2/3), Pentium, Celeron
- Socket G3 (rPGA 946) • Mobile Core i (Gen 4), Pentium, Celeron
- Socket H (LGA 1156) • Desktop Core i (Gen 1), Xeon (Linfield, Clarkdale)
- Socket H2 (LGA 1155) • Desktop Core i (Gen 2/3), Xeon E3 v1/v2 (Sandy Bridge, Ivy Bridge)
- Socket H3 (LGA 1150) • Desktop Core i (Gen 4/5), Xeon E3 v3/v4 (Haswell, Broadwell)
- Socket H4 (LGA 1151) • Desktop Core i (Gen 6/7), Xeon E3 v5/v6 (Skylake, Kaby Lake)
- Socket H5 (LGA 1151 v2) • Desktop Core i (Gen 8/9) (Coffee Lake), Xeon E (Coffee Lake-E)
- FCBGA1356 (BGA 1356) • Low Power (Gen 6/7) Mobile CPU for Mobile
- FCBGA1440 (BGA 1440) • General Power (Gen 6-10) Mobile CPUs for Mobile
- FCBGA1515 (BGA 1515) • Ultra-low Power (Gen 6/7/8) Mobile CPU for Mobile
- FCBGA1528 (BGA 1528) • Low Power (Gen 8) CPU for select Mobile
- BGA2270 (BGA 2270) • Mobile APU
- LGA 1200 (2020) • Desktop Core i (Gen 10/11) (Comet Lake), Xeon E W 1xxx (Rocket Lake-E)
- Intel Comet Lake (10th gen), Intel Rocket Lake (11th gen)
- LGA 1700 (2021) • Desktop Core i (Gen 12-14) (Alder Lake, Raptor Lake (Refresh))
- Intel Alder Lake (12th gen), Raptor Lake (13th gen), Raptor Lake (14th gen)
- LGA 1851 (2024) • Desktop Core Ultra Series 1 (Meteor Lake-PS)
- Intel Core Ultra (Gen 2) 200S Series (Arrow Lake)
- Server/Workstation
- Socket 8 (CPGA) • Pentium Pro
- Slot 2 • Pentium II Xeon, III Xeon
- Socket 603 • Xeon (Netburst: Poster, some of Prestonia, some Gallatin)
- Socket 604 • Xeon (Netburst: Some of the Prestonia, some of the Gallatin,
- Nokona, Irwindale, Cranford, Potomac, Faxville, Core: Tiger, Dunnington)
- PAC418 • Itanium (Merced)
- PAC611 • Itanium 2 (McKinley, Madison, Montishito, Montbale)
- LGA 1248 • Itanium 9300 (Tukwila) or higher series
- Socket J (LGA 771) • Cion (Demn, Wood Crest, Clover Town, Harper Town)
- Socket B (LGA 1366) • Desktop • Core i7 (Gen 1) Extreme (Bloomfield, Gulftown),
- Xeon 55xx/56xx (Gainstown, Westmere-EP)
- Socket B2 (LGA 1356) • Desktop • Xeon E5 v1/v2
- Socket LS (LGA 1567) (2010) • Server • Xeon 65xx/75xx (Vector), Xeon E7 (Westmeer-EX)
- Socket R (LGA 2011) • Desktop • Core i7 (Gen 2/3) Extreme (Sandy Bridge-E, Ivy Bridge-E),
- Xeon E5 v1/v2 (Sandy Bridge-EP, Ivy Bridge-EP)
- Socket R3 (LGA 2011-V3) • Core i7 (Gen 4) Extreme (Haswell-E, Broadwell-E),
- Xeon E5 v3/v4 (Haswell-EP, Broadwell-EP)
- LGA 2011-1 • Xeon E7 V2/V3/V4 (Ivy Bridge-EX, Haswell-EX, Broadwell-EX)
- LGA 2066 • Core X (Gen 1/2) (Skylake-X, Kaby Lake-X, Cascade Lake-X), Xeon W (Gen 1/2) (Skylake-W)
- LGA 3647 • Xeon Scalable (Gen 1/2) (Skylake-SP, Cascade Lake-SP)
- LGA 4189 (2020) • Xeon Scalable (Gen 3), Xeon W (Gen 3) (Cooper Lake/Ice Lake-SP) [0.99] (Desktop/Server)
- LGA 4677 (2022) • Xeon Scalable (Gen 4) (Sapphire Rapids-SP),
- LGA 7529 (2024) • Intel Sierra Forest (Server)
80x86[edit]
Table legend: Template:legend Template:legend
| Socket name | Year of introduction | CPU families | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIP | 1970s | Intel 8086 Intel 8088 |
DIP | 40 | 2.54 | 5/10 MHz | ||
| PLCC | ? | Intel 80186 Intel 80286 Intel 80386 |
PLCC | 68 - 132 | 1.27 | 6–40 MHz | ||
| PGA68 | ? | Intel 80286 | PGA | 68 | ||||
| PGA132 | ? | Intel 80386 | PGA | 132 | ||||
| PGA168 | ? | Intel 80486 AMD]] [[486 Cyrix 486 |
PGA | 168 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz | Sometimes referred to as Socket 0 or Socket 486 | |
| Socket 1 | 1989 | Intel 80486 AMD 486 AMD 5x86 Cyrix 486 Cyrix 5x86 |
PGA | 169 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz | ||
| Socket 2 | ? | Intel 80486 Intel [[Pentium OverDrive]] (P24T) Intel DX4 AMD 486 AMD 5x86 Cyrix 486 Cyrix 5x86 |
PGA | 238 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz | ||
| Socket 3 | 1991 | Intel 80486 Intel Pentium OverDrive (P24T) Intel DX4 AMD 486 AMD 5x86 Cyrix 486 Cyrix 5x86 IBM Blue Lightning |
PGA | 237 | 2.54 | 16–50 MHz | ||
| Socket 4 | 1993 | Intel Pentium | PGA | 273 | ? | 60–100 MHz | ||
| Socket 5 | 1994 | Intel Pentium AMD K5 Cyrix 6x86 IDT WinChip C6 IDT WinChip 2 |
PGA | 320 | ? | 50–100 MHz | ||
| Socket 6 | ? | Intel 80486 | PGA | 235 | ? | ? | Designed but not used | |
| Socket 463 (Socket NexGen) |
1994 | NexGen Nx586 | PGA | 463 | ? | 37.5–66 MHz | ||
| Socket 7 | 1994 | Intel Pentium Intel Pentium MMX AMD K6 |
PGA | 321 | ? | 50–66 MHz | It is possible to use Socket 7 processors in a Socket 5. | |
| Socket 8 | 1995 | Intel Pentium Pro | PGA | 387 | ? | 60–66 MHz | ||
| Slot 1 | 1997 | Intel Pentium II Intel Pentium III |
Desktop | Slot | 242 | ? | 66–133 MHz | Celeron (Covington, Mendocino) Pentium II (Klamath, Deschutes) Pentium III (Katmai) - all versions Pentium III (Coppermine) |
| Super Socket 7 | 1998 | AMD K6-2 AMD AMD K6-III Rise mP6 Cyrix 6x86 (MII) |
PGA | 321 | ? | 66–100 MHz | Backward compatible with Socket 5 and Socket 7 processors. | |
| Slot 2 | 1998 | Intel Pentium II Xeon Intel Pentium III Xeon |
Server | Slot | 330 | ? | 100–133 MHz | |
| Socket 615 | 1999 | Intel Mobile Pentium II Intel Mobile Celeron |
Notebook | PGA | 615 | ? | 66 MHz | |
| Slot A | 1999 | AMD Athlon | Desktop | Slot | 242 | ? | 100 MHz | |
| Socket 370 | 1999 | Intel Pentium III Intel Celeron VIA Cyrix III VIA C3 |
Desktop | PGA | 370 | 1.27 [1] | 66–133 MHz | |
| Socket A Socket 462 |
2000 | AMD Athlon AMD Duron AMD Athlon XP AMD Athlon XP-M AMD Athlon MP AMD Sempron |
Desktop | PGA | 462 | ? | 100–200 MHz 400 MT/s |
|
| Socket 423 | 2000 | Intel Pentium 4 | Desktop | PGA | 423 | 1 | 100 MHz 400 MT/s |
Willamette core only. Can accept some of Socket 478 CPU with an adapter. |
| Socket 495 | 2000 | Intel Celeron Intel Pentium III |
Notebook | PGA | 495 | 1.27 | 66–133 MHz | |
| Socket 603 | 2001 | Intel Xeon | Server | PGA | 603 | 1.27 | 100–133 MHz 400–533 MT/s |
|
| Socket 478 Socket N |
2001 | Intel Pentium 4 Intel Celeron Intel Pentium 4 EE Intel Pentium 4 M |
Desktop | PGA | 478 | 1.27 | 100–200 MHz 400–800 MT/s |
|
| Socket 563 | 2002 | AMD Athlon XP-M | Notebook | PGA | 563 | ? | 333 MHz | |
| Socket 604 | 2002 | Intel Xeon | Server | PGA | 604 | 1.27 | 100–266 MHz 400–1066 MT/s |
|
| Socket 754 | 2003 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Sempron AMD Turion 64 |
Desktop | PGA | 754 | 1.27 | 200–800 MHz | |
| Socket 940 | 2003 | AMD Opteron AMD Athlon 64 FX |
Desktop Server |
PGA | 940 | 1.27 | 200–1000 MHz | |
| Socket 479 | 2003 | Intel Pentium M Intel Celeron M |
Notebook | PGA | 479 [2] | ? | 100–133 MHz 400–533 MT/s |
|
| Socket 939 | 2004 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Athlon 64 FX AMD Athlon 64 X2 AMD Opteron |
Desktop | PGA | 939 | 1.27 | 200–1000 MHz | Support of Athlon 64 FX to 1 GHz Support of Opteron limited to 100-series only |
| LGA 775/ Socket T |
2004 | Intel Pentium 4 Intel Pentium D Intel Celeron Intel Celeron D Intel Pentium XE Intel Core 2 Duo Intel Core 2 Quad Intel Xeon |
Desktop | LGA | 775 | 1.09 x 1.17 | 1600 MHz | Can accept LGA 771 CPU with slight modification and use of an adapter. |
| Socket M | 2006 | Intel Core Solo Intel Core Duo Intel Dual-Core Xeon Intel Core 2 Duo |
Notebook | PGA | 478 | ? | 133–166 MHz 533–667 MT/s |
Replaces Socket 479 |
| LGA 771 Socket J |
2006 | Intel Xeon | Server | LGA | 771 | 1.09 x 1.17[3] | 1600 MHz | See LGA 775/Socket T above |
| Socket S1 | 2006 | AMD Turion 64 X2 | Notebook | PGA | 638 | 1.27[4] | 200–800 MHz | |
| Socket AM2 | 2006 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Athlon 64 X2 |
Desktop | PGA | 940 | 1.27[5] | 200–1000 MHz | Replaces Socket 754 and Socket 939 |
| Socket F/ Socket L (Socket 1207FX) |
2006 | AMD Athlon 64 FX AMD Opteron (Socket L only support Athlon 64 FX) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 1207 | 1.1[6] | Socket L: 1000 MHz in Single CPU mode, 2000 MHz in Dual CPU mode |
Replaces Socket 940 Socket L was intended for enthusiasts who wanted server power in a desktop PC. It is just a re-branded Socket F that doesn't need special RAM, and may have only been used in the Asus L1N64-SLI WS Motherboard. |
| Socket AM2+ | 2007 | AMD Athlon 64 AMD Athlon X2 AMD Phenom AMD Phenom II |
Desktop | PGA | 940 | 1.27[5] | 200–2600 MHz | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2 AM2+ Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2 AM2 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2+ |
| Socket P | 2007 | Intel Core 2 | Notebook | PGA | 478 | ? | 133–266 MHz 533–1066 MT/s |
Replaces Socket M |
| LGA 1366/ Socket B |
2008 | Intel Core i7 (900 series) Intel Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 1366 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | Replaces Socket J (LGA 771) in the entry level. |
| Socket AM3 | 2009 | AMD Phenom II AMD Athlon II AMD Sempron AMD Opteron (1300 series) |
Desktop | PGA | 941[7] or 940[8] | 1.27[5] | 200–3200 MHz | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2+ AM3 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2/AM2+ Sempron 140 only |
| rPGA 988A/ Socket G1 |
2009 | Intel Clarksfield Intel Arrandale |
Notebook | rPGA | 988 | 1 | 2.5 GT/s | Replaces Socket P |
| LGA 1156/ Socket H |
2009 | Intel Nehalem (1st gen) Intel Westmere |
Desktop | LGA | 1156 | ? | 2.5 GT/s | DMI bus is a (perhaps modified) PCIe x4 v1.1 interface |
| Socket G34 | 2010 | AMD Opteron (6000 series) | Server | LGA | 1974 | ? | 200–3200 MHz | Replaces Socket F |
| Socket C32 | 2010 | AMD Opteron (4000 series) | Server | LGA | 1207 | ? | 200–3200 MHz | Replaces Socket F, Socket AM3 |
| LGA 1567/ Socket LS |
2010 | Intel Xeon 6500/7500-series | Server | LGA | 1567 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | |
| LGA 1155/ Socket H2 |
2011/Q1 2011.01.09 |
Intel Sandy Bridge (2nd gen) Intel Ivy Bridge (3rd gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1155 | ? | 5.7 GT/s | used for Intel 2nd generation, 3rd generation processors.
Sandy Bridge supports 20 PCIe 2.0 lanes. |
| LGA 2011/ Socket R |
2011/Q3 2011.11.14 |
Intel Core i7 3xxx Sandy Bridge-E Intel Core i7 4xxx Ivy Bridge-E Intel Xeon E5 2xxx/4xxx (Sandy Bridge EP) (2/4S) Intel Xeon E5-2xxx/4xxx v2 (Ivy Bridge EP) (2/4S) |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 2011 | ? | 4.8–6.4 GT/s | Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP both support 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes. Using the Xeon focused 2011 socket gives also 4 memory Channels. |
| rPGA 988B/ Socket G2 |
2011 | Intel Core i7 Intel Core i5 Intel Core i3 (2000, 3000 series) |
Notebook | rPGA | 988 | 1 | 2.5 GT/s, 4.8 GT/s | |
| Socket FM1 | 2011 | AMD Llano Processors | Desktop | PGA | 905 | 1.27 | 5.2 GT/s | used for 1st generation APUs |
| Socket FS1 | 2011 | AMD Llano Processors | Notebook | PGA | 722 | 1.27 | 3.2 GT/s | used for 1st generation Mobile APUs |
| Socket AM3+ | 2011 | AMD FX VisheraTemplate:Broken anchor AMD FX Zambezi AMD Phenom II AMD Athlon II AMD Sempron |
Desktop | PGA | 942 (CPU 71pin) | 1.27 | 3.2 GT/s | |
| LGA 1356/ Socket B2 |
2012 | Intel Xeon (E5 1400 & 2400 series) | Server | LGA | 1356 | ? | 3.2–4.0 GT/s | |
| Socket FM2 | 2012 | AMD Trinity Processors | Desktop | PGA | 904 | 1.27 | ? | used for 2nd generation APUs |
| LGA 1150/ Socket H3 |
2013 | Intel Haswell (4th gen) Intel Haswell Refresh Intel Broadwell (5th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1150 | ? | ? | used for Intel's 4th generation (Haswell/Haswell Refresh), the handful of intel 5th generation processors |
| rPGA 946B/947/ Socket G3 |
2013 | Intel Haswell | Notebook | rPGA | 946 | 1 | 5.0 GT/s | |
| Socket FM2+ | 2014 | AMD Kaveri AMD Godavari |
Desktop | PGA | 906 | 1.27 | ? | Compatible with AMD APUs such as "Richland" and "Trinity" |
| Socket AM1 | 2014 | AMD Athlon AMD Sempron |
Desktop | PGA | 721 | 1.27 | ? | Compatible with AMD APUs such as "Kabini" |
| LGA 2011-v3 | 2014 (August and September) |
Haswell-E Haswell-EP |
Desktop | LGA | 2011 | ? | Up to 68 GB/sec. Depends on DDR4 speed and channel count. |
Up to 40 PCIe 3.0 lanes. Up to 4 memory Channels. |
| LGA 1151/ Socket H4 |
2015 | Intel Skylake (6th gen) Intel Kaby Lake (7th gen) Intel Coffee Lake (8th gen) Intel Coffee Lake Refresh (9th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1151 | ? | 5 GT/s - 8 GT/s | used for Intel's 6th generation (Skylake), 7th generation (Kaby Lake), 8th generation (Coffee Lake) processors, and 9th generation (Coffee Lake Refresh) processors |
| LGA 3647 | 2016 | Intel Xeon Phi Intel Skylake-SP |
Server | LGA | 3647 | ? | ? | used for Intel's Xeon Phi x200 and Xeon Scalable processors |
| Socket AM4 | 2016 |
AMD Athlon Bristol Ridge
|
Desktop | PGA | 1331 | 1 | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Ryzen 9, Ryzen 7, Ryzen 5 & Ryzen 3 Zen based processors |
| Socket SP3 | 2017 | AMD Epyc Naples AMD Epyc Rome AMD Epyc Milan |
Server | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Epyc processors |
| Socket TR4/ Socket SP3r2 |
2017 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper (1000 series) AMD Ryzen Threadripper (2000 series) |
Desktop | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| LGA 2066/ Socket R4 |
2017 | Intel Skylake-X Intel Kaby Lake-X Intel Cascade Lake-X |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 2066 | ? | ? | Used for Intel's 7th generation (Skylake-X & Kaby Lake-X & Cascade Lake-X) series of Core-X processors |
| Socket sTRX4/ Socket SP3r3 |
2019 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper (3000 series) | Desktop | LGA | 4094 | ? | Depends on DDR4 speed | compatible with 3rd generation AMD Ryzen Threadripper processors |
| LGA 4189 | 2020 | Intel Cooper Lake Intel Ice Lake-SP |
Desktop Server |
LGA | 4189[9] | 0.99[9] | ||
| LGA 1200 | 2020 | Intel Comet Lake (10th gen) Intel Rocket Lake (11th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1200 | |||
| LGA 1700 | 2021 | Intel Alder Lake (12th gen) Intel Raptor Lake (13th gen) Intel Raptor Lake (14th gen) |
Desktop | LGA | 1700 | |||
| Socket sWRX8 | 2022 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper Pro (5000 series) | Desktop | LGA | 4094 | |||
| Socket AM5 | 2022 | AMD Ryzen 7000 series AMD Ryzen 8000 series (APU) AMD Ryzen 9000 series |
Desktop | LGA | 1718 | Zen 4 Ryzen CPUs | ||
| Socket SP5 | 2022 | AMD Epyc Genoa | Server | LGA | 6096 | Used for EPYC Genoa and Milan | ||
| LGA 4677 | 2022 | Intel Sapphire Rapids |
Server | LGA | 4677 | |||
| Socket SP6 | 2023 | AMD EPYC Siena | Server | LGA | 4844 | |||
| Socket sTR5 | 2023 | AMD Ryzen Threadripper AMD Ryzen Threadripper Pro Storm Peak (7000 series, Zen 4) |
Desktop | LGA | 4844 | |||
| LGA 1851 | 2024 | Intel Meteor Lake-PS (Core Ultra Series 1) Intel Arrow Lake (Core Ultra 200S Series) TBA |
Desktop | LGA | 1851 | |||
| LGA 7529 | 2024 | Intel Sierra Forest | Server | LGA | 7529 | |||
| Socket name | Year of introduction | CPU families | Computer type | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch (mm) |
Bus clock & transfers |
Notes |
Intel CPU Packages[edit]
| This article is still a stub and needs your attention. You can help improve this article by editing this page and adding the missing information. |
- ↑ Intel 815 Chipset Family.
- ↑ CPU only has 478 pins, but the socket has 479.
- ↑ Template:cite web
- ↑ Template:cite web
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Template:cite web
- ↑ Template:cite web
- ↑ CPU only has 938 pins, but the socket has 941.
- ↑ AMD Documentation Template:cite web
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Template:Cite web
Facts about "Socket LGA-1567 - Intel"
| Has subobject "Has subobject" is a predefined property representing a container construct and is provided by Semantic MediaWiki. | Socket LGA-1567 - Intel#package + |
| package | FCLGA-8 +, FCLGA-1151 +, rPGA-988A + and BGA-1288 + |
| socket | LGA-1151 + |