From WikiChip
Piledriver - Microarchitectures - AMD
| Edit Values | |
| Piledriver µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | AMD |
| Manufacturer | AMD |
| Introduction | May 15, 2012 |
| Phase-out | 2014 |
| Process | 32 nm |
| Core Configs | 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Succession | |
Piledriver was the microarchitecture developed by AMD as a successor to Bulldozer.
- In 2014, Steamroller superseded Piledriver.
Architecture[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
All Piledriver Chips[edit]
| Piledriver Chips | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Family | Core | Launched | Power Dissipation | Freq | Max Mem |
| Count: 0 | ||||||
Buldozer (Piledriver) Family[edit]
| Architecture | Process (nm) |
Family | Release date |
Code name | Model group | Cores | Clock rate (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bulldozer (x86-64) |
32 nm | Bulldozer | Oct 2011 | Zambezi | FX-4100 series (4100, 4120, 4130, 4150, 4170) |
4 | 3600–4200 (3700–4300 boost) |
| FX-6100 series (6100, 6120, 6130, 6200) |
6 | 3300–3800 (3600–4200 boost) | |||||
| FX-8100 series (8100, 8120, 8140, 8150, 8170) |
8 | 2800–3900 (3100–4500 boost) | |||||
| Mar 2012 | Zurich | Opteron 3200 series (3250HE, 3260HE, 3280) |
4/8 | 2400–2700 (2700–3700 boost) | |||
| Nov 2011 | Valencia | Opteron 4200 series (42DX, 42MX, 4226, 4228HE, 4230HE, 4234, 4238, 4240, 4256EE, 4274HE, 4276HE, 4280, 4284) |
4/6/8 | 1600–3400 (1900–3800 boost) | |||
| Interlagos | Opteron 6200 series (6204, 6212, 6220, 6230HE, 6234, 6238, 6262HE, 6272, 6274, 6276, 6278, 6282SE, 6284SE) |
4/8/12/16 | 1600–3300 (2100–3600 boost) | ||||
| Piledriver | Trinity | Sempron X2 240, Athlon X2 340, Athlon X4 740, Athlon X4 750K, FirePro A300, FirePro A320 |
2/4 | 1600–3800 (2400–4200 boost) | |||
| Richland | Sempron X2 250, Athlon X2 350, Athlon X2 370K, Athlon X2 750, Athlon X2 760K |
2/4 | 1700–4100 (2600–4400 boost) | ||||
| Oct 2012 | Vishera | FX-4300 series (4300, 4320, 4350) |
4 | 3800–4200 (4000–4300 boost) | |||
| FX-6300 series (6300, 6350) |
6 | 3500–3900 (4100–4200 boost) | |||||
| FX-8300 series (8300, 8310, 8320, 8320E, 8350, 8370, 8370E, 9370, 9590) |
8 | 3300–4700 (4000–5000 boost) | |||||
| Dec 2012 | Delhi | Opteron 3300 series (3320EE, 3350HE, 3365, 3380) |
4/8 | 1900–2800 (2100–3800 boost) | |||
| Seoul | Opteron 4300 series (43CXEE, 43GKHE, 4310EE, 4332HE, 4334, 4340, 4365EE, 4376HE, 4386) |
4/6/8 | 2000–3500 (2300–3800 boost) | ||||
| Nov 2012 | Abu Dhabi | Opteron 6300 series (6308, 6320, 6328, 6338P, 6344, 6348, 6366HE, 6370P, 6376, 6378, 6380, 6386SE) |
4/8/12/16 | 1800–3500 (2300–3800 boost) | |||
| 28 nm | Steamroller | Jan 2014 | Kaveri | Athlon X2 450, Athlon X4 840, Athlon X4 860K, Athlon X4 870K, Athlon X4 880K |
2/4 | 1800–4100 (3000–4300 boost) | |
| Excavator | Jan 2015 | Carrizo | Athlon X4 835, Athlon X4 845, FX-8800P, A6-8500P, A6Pro-8500B |
2/4 | 1600–3500 (3000–3800 boost) | ||
| Jan 2016 | Bristol Ridge | Athlon X4 940, Athlon X4 950, Athlon X4 970 |
2/4 | 2300–3800 (3200–4200 boost) |
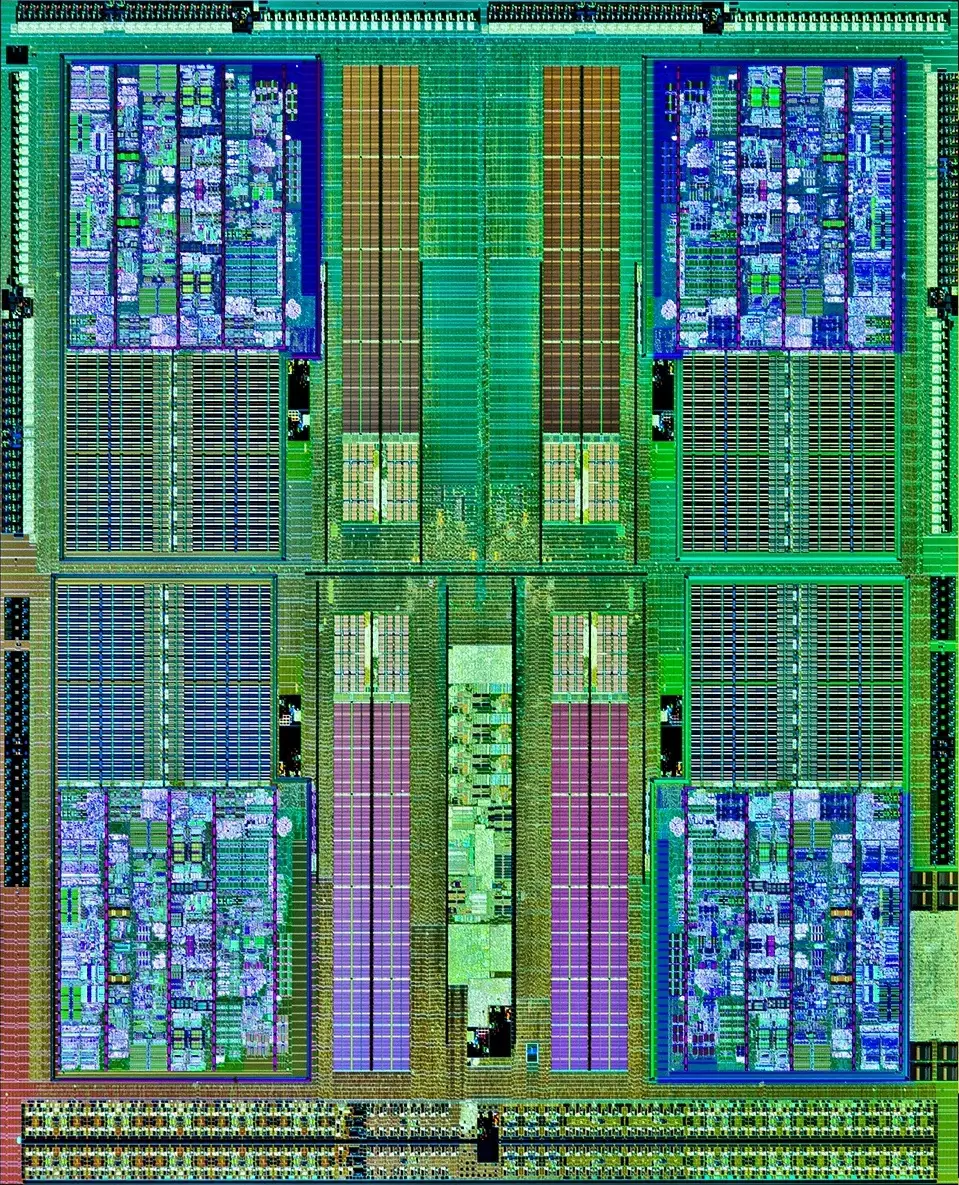
Die Shot[edit]
See also[edit]
Facts about "Piledriver - Microarchitectures - AMD"
| codename | Piledriver + |
| core count | 2 +, 4 +, 6 +, 8 +, 12 + and 16 + |
| designer | AMD + |
| first launched | May 15, 2012 + |
| full page name | amd/microarchitectures/piledriver + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | AMD + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Piledriver + |
| phase-out | 2014 + |
| process | 32 nm (0.032 μm, 3.2e-5 mm) + |