| Edit Values | |
| Sunny Cove µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | 2019 |
| Process | 10 nm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Succession | |
Sunny Cove is the successor to Palm Cove, a high-performance 10 nm x86 core microarchitecture designed by Intel for an array of server and client products.
Contents
History
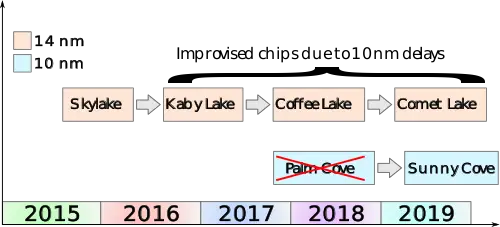
Sunny Cove was originally unveiled by Intel at their 2018 architecture day. Intel originally intended for Sunny Cove to succeed Palm Cove in late 2017 which was it was intended to be the first 10 nm-based core and the proper successor to Skylake. Prolong delays and problems with their 10 nm process and resulted in a number of improvised derivatives of Skylake including Kaby Lake, Coffee Lake, and Comet Lake. For all practical purposes, Palm Cove has been skipped and Intel has gone directly to Sunny Cove. Sunny Cove is expected to debut in mid-2019.
Process Technology
Sunny Cove is designed to take advantage of Intel's 10 nm process.
Architecture
Key changes from Palm Cove
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Overview
Sunny Cove is Intel's core microarchitecture for a series of client and server chips that succeed Palm Cove (and effectively the Skylake series of derivative). Sunny cove introduces a very large set of enhancements and improvements of its predecessor including a wider and deeper pipeline. Sunny Cove is implemented in a number of chips including Lakefield, Ice Lake (Client), and Ice Lake (Server).
Bibliography
- Intel Architecture Day 2018, December 11, 2018
| codename | Sunny Cove + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | 2019 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/sunny cove + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Sunny Cove + |
| process | 10 nm (0.01 μm, 1.0e-5 mm) + |