-
WikiChip
WikiChip
-
Architectures
Popular x86
-
Intel
- Client
- Server
- Big Cores
- Small Cores
-
AMD
Popular ARM
-
ARM
- Server
- Big
- Little
-
Cavium
-
Samsung
-
-
Chips
Popular Families
-
Ampere
-
Apple
-
Cavium
-
HiSilicon
-
MediaTek
-
NXP
-
Qualcomm
-
Renesas
-
Samsung
-
From WikiChip
ARM250 - Microarchitectures - ARM
| Edit Values | |
| ARM250 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | VLSI Technology |
| Introduction | 1992 |
| Process | 1 µm |
| Core Configs | 1 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Scalar, Pipelined |
| Stages | 3 |
| Decode | 1-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv2a |
| Cores | |
| Core Names | ARM250 |
| Succession | |
ARM250 was a system on a chip microarchitecture that was introduced by ARM Holdings around the same time the ARM6 was introduced.
Overview
Architecture
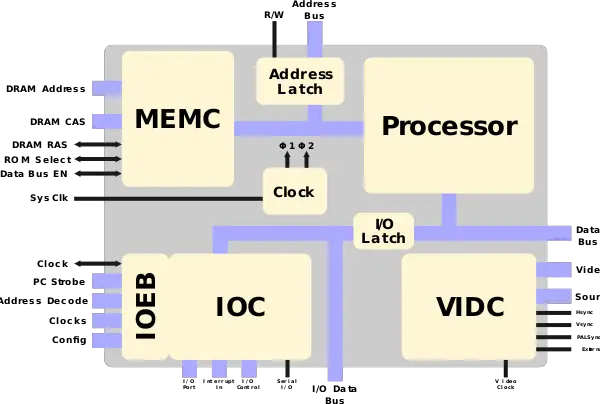
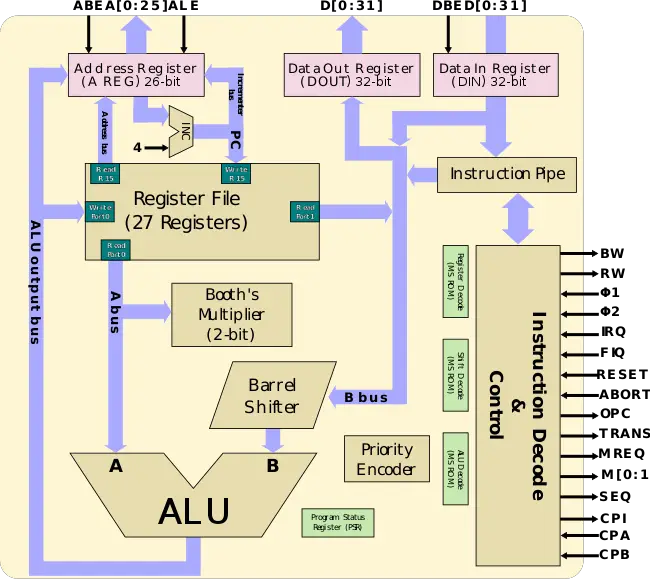
Block Diagram
Entire Chip
Core
Die
Documents
- ARM250 Datasheet, August 11, 1992
Retrieved from "https://en.wikichip.org/w/index.php?title=arm_holdings/microarchitectures/arm250&oldid=53728"
Facts about "ARM250 - Microarchitectures - ARM"
| codename | ARM250 + |
| core count | 1 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | 1992 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/arm250 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv2a + |
| manufacturer | VLSI Technology + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | ARM250 + |
| pipeline stages | 3 + |
| process | 1,000 nm (1 μm, 0.001 mm) + |