-
WikiChip
WikiChip
-
Architectures
Popular x86
-
Intel
- Client
- Server
- Big Cores
- Small Cores
-
AMD
Popular ARM
-
ARM
- Server
- Big
- Little
-
Cavium
-
Samsung
-
-
Chips
Popular Families
-
Ampere
-
Apple
-
Cavium
-
HiSilicon
-
MediaTek
-
NXP
-
Qualcomm
-
Renesas
-
Samsung
-
From WikiChip
Oak Trail - Platforms - Intel
< intel
(diff) ← Older revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| Oak Trail Platform | |
| Developer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel, TSMC |
| Process | 45 nm 0.045 μm
4.5e-5 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Platform | |
| Cores | Lincroft |
| Chipset | Langwell, Briertown, Whitney Point |
| Succession | |
| ← | → |
| Moorestown | Medfield |
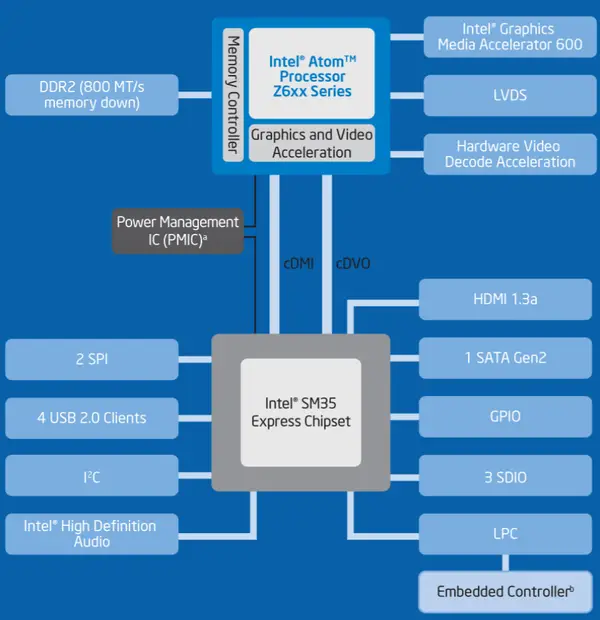
Oak Trail is the platform name for Intel's low-power platform Bonnell-based processors and chipsets designed for Mobile Internet Devices (MID) and Ultra Mobile PCs (UMPCs) serving as a successor to Menlow. Moorestown consists of a Lincroft-based processor, the Langwell chipset, and the Briertown Mixed Signal IC (MSIC). Additionally, Oak Trail introduced Whitney Point chip which introduced SATA, HD Audio, USB, HDMI, and various legacy I/O allowing it to run full-fledged Windows OS.