From WikiChip
Rock Creek - Microarchitectures - Intel
| Edit Values | |
| Knights Ferry µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | December 2009 |
| Process | 45 nm |
| Core Configs | 48 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86 |
| Extensions | L1OM |
| Succession | |
Rock Creek or the Single-Chip Cloud Computer (SCC) was the successor to Polaris, a 45 nm many-core microarchitecture designed by intel for high performance computing. The SCC, like Polaris, was a research project from Intel's Tera-scale Computing Research Program.
Architecture
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Overview
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
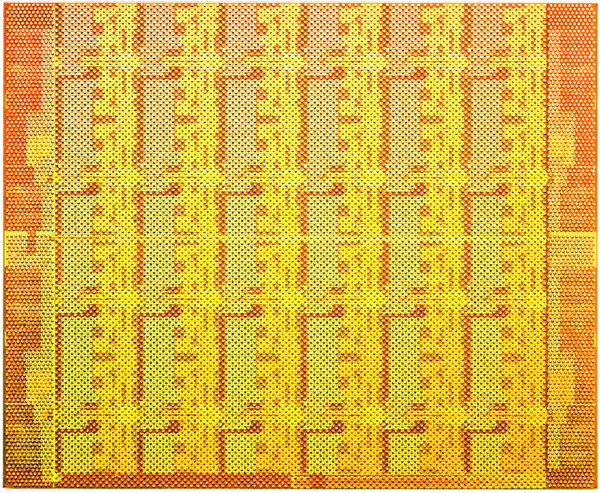
Die
- 45 nm process
- 1 poly, 9 Metal (Cu)
- 1,300,000,000 transistors
- 26.5 mm x 21.4 mm
- 567.1 mm² die size
- 1,567 pins LGA packages
- 970 signal pins
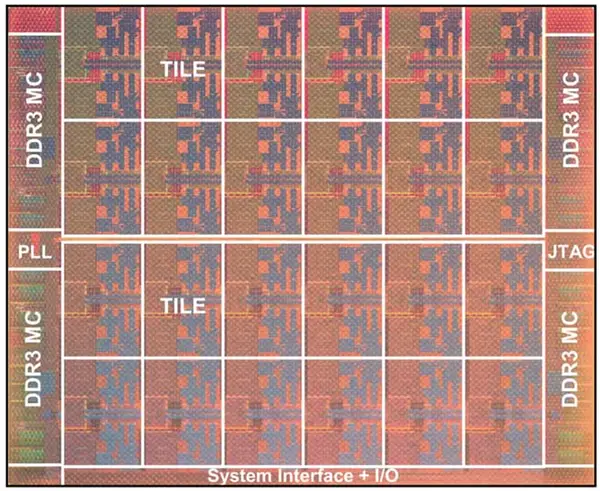
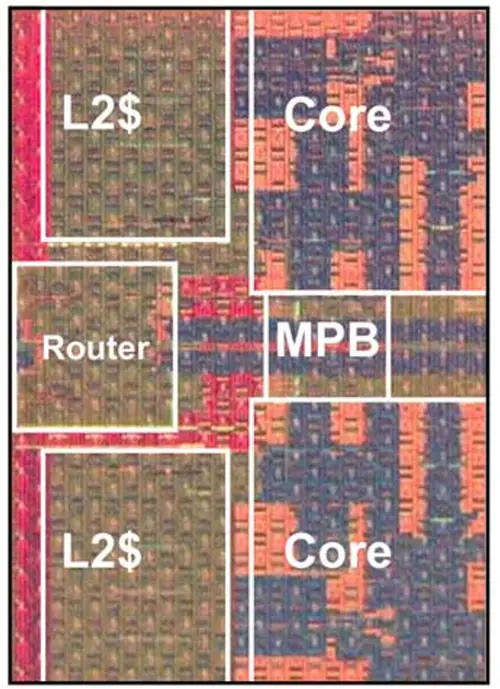
Tile
- 48,000,000 transistors
- 3.6 mm x 5.2 mm
- 18.7 mm² silicon area
Additional Shots
Additional die and wafer shots provided by Intel:
Bibliography
- “Single-chip Cloud Computer”. An experimental many-core processor from Intel Labs. Jim Held, Intel Fellow & Director. Tera-scale Computing Research. Symposium in Santa Clara. 2/12/10.
Documents
Facts about "Rock Creek - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | Knights Ferry + |
| core count | 48 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | December 2009 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/rock creek + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Knights Ferry + |
| process | 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) + |