| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|manufacturer=TSMC | |manufacturer=TSMC | ||
|introduction=May 31, 2018 | |introduction=May 31, 2018 | ||
| − | |process | + | |process=7 nm |
| − | |||
|cores=1 | |cores=1 | ||
|cores 2=2 | |cores 2=2 | ||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Cortex-A76''' (codename '''Enyo''') is the successor to the {{armh|Cortex-A75|l=arch}}, a low-power high-performance [[ARM]] [[microarchitecture]] designed by [[ARM Holdings]] for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable [[IP core]] and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-A76, which implemented the {{arm|ARMv8.2}} ISA, is the a performant core which is often combined with a number of lower power cores (e.g. {{\\|Cortex-A55}}) in a {{armh|DynamIQ big.LITTLE}} configuration to achieve better energy/performance. | '''Cortex-A76''' (codename '''Enyo''') is the successor to the {{armh|Cortex-A75|l=arch}}, a low-power high-performance [[ARM]] [[microarchitecture]] designed by [[ARM Holdings]] for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable [[IP core]] and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-A76, which implemented the {{arm|ARMv8.2}} ISA, is the a performant core which is often combined with a number of lower power cores (e.g. {{\\|Cortex-A55}}) in a {{armh|DynamIQ big.LITTLE}} configuration to achieve better energy/performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Process Technology == | ||
| + | Though the Cortex-A76 may be fabricated on various different [[process nodes]], it has been primarily designed for the [[12 nm]], [[7 nm]], and [[5 nm]] process nodes. | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| Line 51: | Line 53: | ||
{{empty section}} | {{empty section}} | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | {{ | + | The Cortex-A76 is a high-performance synthesizable core designed by [[Arm]] as the successor to the {{\\|Cortex-A75}}. It is delievered as Register Transfer Level (RTL) description in Verilog and is designed. This core supports the {{arm|ARMv8.2}} extension as well as a number of other partial extensions. The A76 is a 4-way superscalar out-of-order processor with a private level 1 and level 2 caches. It is designed to be implemented inside the [[DynamIQ Shared Unit]] (DSU) cluster along with other cores (e.g., with [[little cores]] such as the {{\\|Cortex-A55}}) |
| + | |||
== Core == | == Core == | ||
{{empty section}} | {{empty section}} | ||
Revision as of 01:58, 27 December 2018
| Edit Values | |
| Cortex-A76 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | May 31, 2018 |
| Process | 7 nm |
| Core Configs | 1, 2, 4 |
| Pipeline | |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Stages | 11-13 |
| Decode | 4-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv8.2 |
| Extensions | FPU, NEON |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 64 KiB/core 4-way set associative |
| L1D Cache | 64 KiB/core 4-way set associative |
| L2 Cache | 256-512 KiB/core 8-way set associative |
| L3 Cache | 0-4 MiB/Cluster |
| Succession | |
| Contemporary | |
| Ares | |
Cortex-A76 (codename Enyo) is the successor to the Cortex-A75, a low-power high-performance ARM microarchitecture designed by ARM Holdings for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable IP core and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-A76, which implemented the ARMv8.2 ISA, is the a performant core which is often combined with a number of lower power cores (e.g. Cortex-A55) in a DynamIQ big.LITTLE configuration to achieve better energy/performance.
Contents
Process Technology
Though the Cortex-A76 may be fabricated on various different process nodes, it has been primarily designed for the 12 nm, 7 nm, and 5 nm process nodes.
Architecture
Key changes from Cortex-A75
Block Diagram
Typical SoC
Individual Core
Memory Hierarchy
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
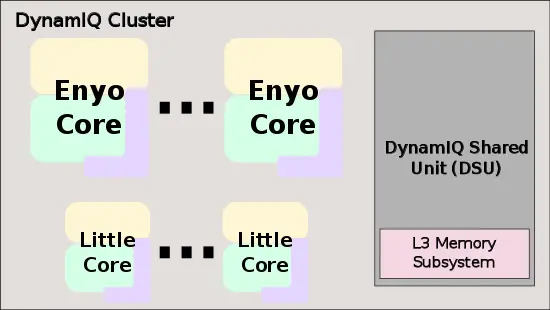
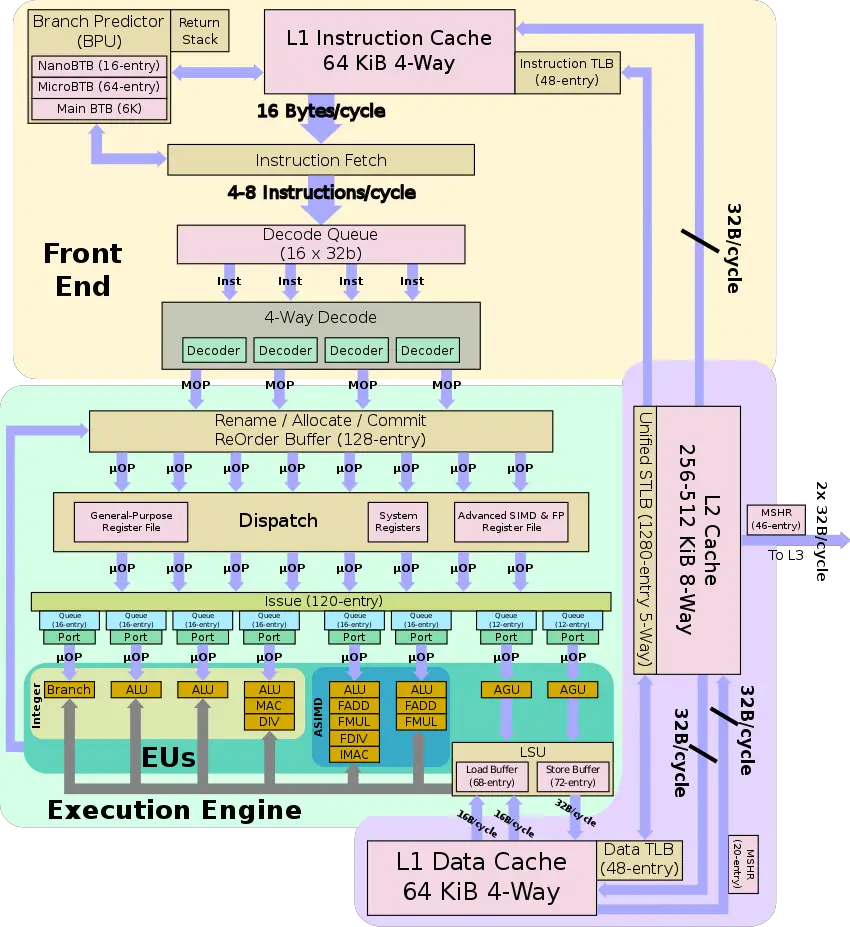
Overview
The Cortex-A76 is a high-performance synthesizable core designed by Arm as the successor to the Cortex-A75. It is delievered as Register Transfer Level (RTL) description in Verilog and is designed. This core supports the ARMv8.2 extension as well as a number of other partial extensions. The A76 is a 4-way superscalar out-of-order processor with a private level 1 and level 2 caches. It is designed to be implemented inside the DynamIQ Shared Unit (DSU) cluster along with other cores (e.g., with little cores such as the Cortex-A55)
Core
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Overview
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Pipeline
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Bibliography
- Arm Tech Day, 2018
| codename | Cortex-A76 + |
| core count | 1 +, 2 + and 4 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | May 31, 2018 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/cortex-a76 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv8.2 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Cortex-A76 + |
| pipeline stages (max) | 13 + |
| pipeline stages (min) | 11 + |
| process | 7 nm (0.007 μm, 7.0e-6 mm) + |