(→Example: based on https://fuse.wikichip.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/intel-10nm-density.png - add some older processes mtr/mm2. What about other foundries and is there moore law) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{title|MTr/mm²}} | {{title|MTr/mm²}} | ||
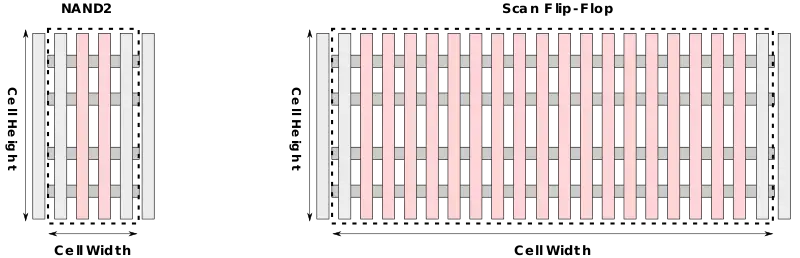
| − | '''MTr/mm²''' ('''mega-transistor per squared millimeter''') is a [[transistor density]] unit that | + | '''MTr/mm²''' ('''mega-transistor per squared millimeter''') is a [[transistor density]] unit that serves as a [[figure of merit]] in quantifying a [[process node]]. The metric makes use of a weighted system consisting of two typical [[standard cells]] found in most [[standard cell library|libraries]] - a very small [[NAND2]] cell and a very large [[scan flip flop|SFF]] cell. |
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | The metric was proposed by Mark Bohr, [[Intel]]'s director of process architecture and integration, in 2017. Bohr stated the metric is actually a resurrection of a similar metric that had been abandoned in the past. The metric attempts to take into account second order design rules that the simpler density metrics such as [[CPP x MMP]] and [[CPP x MMP x Tracks]] cannot capture because they do not represent a typical [[standard cell]]. It should be noted that the metric explicitly excludes [[SRAM]] cell sizes because of the large variance in SRAM-to-logic ratio between popular chips. Furthermore, the metal pitch does not play a role in limiting SRAM as it does with other standard cells. Therefore, SRAM cell sizes should be reported separately alongside the MTr/mm² unit. | + | The metric was proposed by Mark Bohr, [[Intel]]'s director of process architecture and integration, in 2017. Bohr stated the metric is actually a resurrection of a similar metric that had been abandoned in the past. The metric attempts to take into account second-order design rules that the simpler density metrics such as [[CPP x MMP]] and [[CPP x MMP x Tracks]] cannot capture because they do not represent a typical [[standard cell]]. It should be noted that the metric explicitly excludes [[SRAM]] cell sizes because of the large variance in SRAM-to-logic ratio between popular chips. Furthermore, the metal pitch does not play a role in limiting SRAM as it does with other standard cells. Therefore, SRAM cell sizes should be reported separately alongside the MTr/mm² unit. |
Two [[standard cell|cells]] that are found in every [[standard library]] are used: a very small 2-input [[NAND]] cell consisting of just four [[transistors]] and a very large [[scan flip-flop]] cell. The NAND2 is weighted as 0.6 while the SFF is weighted as 0.4. | Two [[standard cell|cells]] that are found in every [[standard library]] are used: a very small 2-input [[NAND]] cell consisting of just four [[transistors]] and a very large [[scan flip-flop]] cell. The NAND2 is weighted as 0.6 while the SFF is weighted as 0.4. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[Intel]]'s [[22 nm process]] (2012) had 16.5 MTr/mm², [[14 nm process]] (2014) had 44.67 MTr/mm², and [[14++ nm process]] had 37.22 MTr/mm². <!-- from https://fuse.wikichip.org/news/1371/a-look-at-intels-10nm-std-cell-as-techinsights-reports-on-the-i3-8121u-finds-ruthenium/--> | [[Intel]]'s [[22 nm process]] (2012) had 16.5 MTr/mm², [[14 nm process]] (2014) had 44.67 MTr/mm², and [[14++ nm process]] had 37.22 MTr/mm². <!-- from https://fuse.wikichip.org/news/1371/a-look-at-intels-10nm-std-cell-as-techinsights-reports-on-the-i3-8121u-finds-ruthenium/--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | * [[CPP x FP]] | ||
| + | * [[CPP x MMP]] | ||
| + | * [[CPP x MMP x Tracks]] | ||
Revision as of 21:10, 28 June 2018
MTr/mm² (mega-transistor per squared millimeter) is a transistor density unit that serves as a figure of merit in quantifying a process node. The metric makes use of a weighted system consisting of two typical standard cells found in most libraries - a very small NAND2 cell and a very large SFF cell.
Overview
The metric was proposed by Mark Bohr, Intel's director of process architecture and integration, in 2017. Bohr stated the metric is actually a resurrection of a similar metric that had been abandoned in the past. The metric attempts to take into account second-order design rules that the simpler density metrics such as CPP x MMP and CPP x MMP x Tracks cannot capture because they do not represent a typical standard cell. It should be noted that the metric explicitly excludes SRAM cell sizes because of the large variance in SRAM-to-logic ratio between popular chips. Furthermore, the metal pitch does not play a role in limiting SRAM as it does with other standard cells. Therefore, SRAM cell sizes should be reported separately alongside the MTr/mm² unit.
Two cells that are found in every standard library are used: a very small 2-input NAND cell consisting of just four transistors and a very large scan flip-flop cell. The NAND2 is weighted as 0.6 while the SFF is weighted as 0.4.
Example
Intel's 10 nm process consists of a minimum metal pitch of 36nm with 8 diffusion lines for a cell height of 272 nanometers. Additionally, the process has a poly pitch of 54 nm and cells on Intel's 10 nm use a single dummy gate. For 0.6 NAND2 + 0.4 SFF, Intel's 10nm has a density of 100.76 MTr/mm² along with a high-density 6T SRAM measuring 0.0312 µm². Note that Intel itself reported their 10nm at 100.8 MTr/mm².
Intel's 22 nm process (2012) had 16.5 MTr/mm², 14 nm process (2014) had 44.67 MTr/mm², and 14++ nm process had 37.22 MTr/mm².