| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
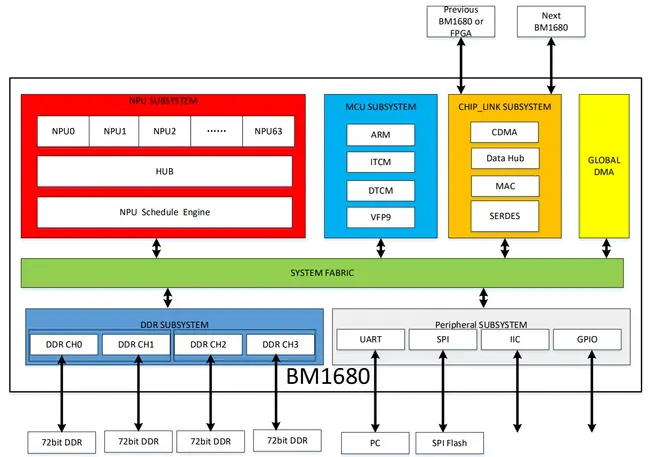
The chip consists of five subsystems: [[NPU]], [[MCU]], Chip Link, Memory, and Peripherals. The MCU Subsystem is a low-power embedded [[ARM]] microcontroller. The NPU Subsystem consists of 64 [[NPUs]], the hub, and an NPU Schedule Engine. The scheduling engine is in charge of controlling the data flow to the individual NPUs. Bitmain has not many intimate details of the NPU cores but each core is known to have 512 KiB of program-visible [[SRAM]] and supports 64 single-precision operations. With a total of 64 NPUs, the chip has a total of 32 [[MiB]] of [[cache]] and a peak performance of 2 [[TFLOPS]] (single-precision). | The chip consists of five subsystems: [[NPU]], [[MCU]], Chip Link, Memory, and Peripherals. The MCU Subsystem is a low-power embedded [[ARM]] microcontroller. The NPU Subsystem consists of 64 [[NPUs]], the hub, and an NPU Schedule Engine. The scheduling engine is in charge of controlling the data flow to the individual NPUs. Bitmain has not many intimate details of the NPU cores but each core is known to have 512 KiB of program-visible [[SRAM]] and supports 64 single-precision operations. With a total of 64 NPUs, the chip has a total of 32 [[MiB]] of [[cache]] and a peak performance of 2 [[TFLOPS]] (single-precision). | ||
| − | :[[File:BM1680 block diagram.png| | + | :[[File:BM1680 block diagram.png|650px]] |
Revision as of 17:29, 18 November 2017
Template:mpu Sophon BM1680 is a neural processor designed by Bitmain and introduced in 2017. The BM1680 is capable of performing both network inference and network training.
Manufactured on TSMC's 28HPC+ process, the BM1680 is capable of 80 billion algorithmic operations per second. Bitmain claims the chip is designed not only for inference, but also for training of neural networks, suitable for working with the common ANNs such as CNN, RNN, and DNN.
Overview
The chip consists of five subsystems: NPU, MCU, Chip Link, Memory, and Peripherals. The MCU Subsystem is a low-power embedded ARM microcontroller. The NPU Subsystem consists of 64 NPUs, the hub, and an NPU Schedule Engine. The scheduling engine is in charge of controlling the data flow to the individual NPUs. Bitmain has not many intimate details of the NPU cores but each core is known to have 512 KiB of program-visible SRAM and supports 64 single-precision operations. With a total of 64 NPUs, the chip has a total of 32 MiB of cache and a peak performance of 2 TFLOPS (single-precision).
| Has subobject "Has subobject" is a predefined property representing a container construct and is provided by Semantic MediaWiki. | Sophon BM1680 - Bitmain#package + |
| core voltage | 0.9 V (9 dV, 90 cV, 900 mV) + |
| core voltage tolerance | 5% + |
| designer | Bitmain + |
| family | Sophon + |
| first announced | October 25, 2017 + |
| first launched | November 8, 2017 + |
| full page name | bitmain/sophon/bm1680 + |
| has ecc memory support | true + |
| instance of | microprocessor + |
| io voltage | 1.8 V (18 dV, 180 cV, 1,800 mV) + |
| io voltage tolerance | 5% + |
| ldate | November 8, 2017 + |
| main image |  + + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| market segment | Artificial Intelligence + |
| max memory | 16,384 MiB (16,777,216 KiB, 17,179,869,184 B, 16 GiB, 0.0156 TiB) + |
| max memory bandwidth | 79.47 GiB/s (81,377.28 MiB/s, 85.33 GB/s, 85,330.263 MB/s, 0.0776 TiB/s, 0.0853 TB/s) + |
| max memory channels | 4 + |
| max operating temperature | 125 °C + |
| min operating temperature | 0 °C + |
| model number | BM1680 + |
| name | Sophon BM1680 + |
| package | FCBGA-1599 + |
| peak flops (single-precision) | 2,000,000,000,000 FLOPS (2,000,000,000 KFLOPS, 2,000,000 MFLOPS, 2,000 GFLOPS, 2 TFLOPS, 0.002 PFLOPS, 2.0e-6 EFLOPS, 2.0e-9 ZFLOPS) + |
| process | 28 nm (0.028 μm, 2.8e-5 mm) + |
| supported memory type | DDR4-2666 + |
| tdp | 41 W (41,000 mW, 0.055 hp, 0.041 kW) + |
| tdp (typical) | 25 W (25,000 mW, 0.0335 hp, 0.025 kW) + |
| technology | CMOS + |