| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| manufacturer = Intel | | manufacturer = Intel | ||
| first announced = April 18, 2007 | | first announced = April 18, 2007 | ||
| − | | first launched = | + | | first launched = June 3, 2008 |
| isa = x86-32 | | isa = x86-32 | ||
| isa 2 = x86-64 | | isa 2 = x86-64 | ||
Revision as of 11:59, 15 April 2017
| Edit Values | |
| Diamondville | |
 | |
| Atom N270, a Diamondville chip | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | April 18, 2007 (announced) June 3, 2008 (launched) |
| Microarchitecture | |
| ISA | x86-32, x86-64 |
| Microarchitecture | Bonnell |
| Word Size | 64 bit 648 octets 16 nibbles |
| Process | 45 nm 0.045 μm 4.5e-5 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 1,600 MHz - 1,666.66 MHz |
| Succession | |
Diamondville is the core name for Intel's first generation of Atom processors based on the Bonnell microarchitecture. Those ultra-low power chips were manufactured on Intel's 45 nm process and were specifically aimed for nettops, netbooks, and entry/value desktops. Diamondville effectively replaced Stealey in the netbooks and entry-level desktops segment.
Diamondville-SC refers to all the single-core Diamondville-based microprocessors. In late 2008 Intel introduced a single dual-core variant (the Atom 330) which went under the Diamondville-DC codename. The dual-core version is simple two identical Diamondville-SC dies packaged together.
Overview
All models are based on Bonnell manufactured on a 45 nm process and implement x86-32. Both Diamondville and Silverthorne use the same die. A number of Diamondville models do have additional features not enabled on Silverthorne models such as full support for x86-64. Diamondville generally targets the 4-8 W thermal envelope typically fan-less designs.
Common Features
- TDP: 2.5 W to 8 W
- ISA: Everything up to SSSE3 (SMM, FPU, NX, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3)
- Bus: 533.33-666.66 MT/s FSB
- Poulsbo Chipset
- 47,212,207 transistors
- 3.1 mm x 7.8 mm die size
- 24.18 mm² die area
Members
| List of Diamondville-based Atom Processors | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | Bus | Features | ||||||||||||||||||
| Model | Family | Price | Process | Launched | C | T | Freq | TDP | SDP | Speed | Rate | Package | HT | VT-x | ||||||
| 230 | Atom | $ 29.00 € 26.10 £ 23.49 ¥ 2,996.57 | 45 nm 0.045 μm 4.5e-5 mm | 3 June 2008 | 1 | 2 | 1.6 GHz 1,599.99 MHz 1,599,990 kHz | 4,000 mW 4 W 0.00536 hp 0.004 kW | 133.33 MHz 0.133 GHz 133,330 kHz | 533.33 MT/s 0.533 GT/s 533,330 kT/s | FCBGA-437 | ✔ | ✘ | |||||||
| 330 | Atom | $ 43.00 € 38.70 £ 34.83 ¥ 4,443.19 | 45 nm 0.045 μm 4.5e-5 mm | 21 September 2008 | 2 | 4 | 1.6 GHz 1,599.99 MHz 1,599,990 kHz | 8,000 mW 8 W 0.0107 hp 0.008 kW | 133.33 MHz 0.133 GHz 133,330 kHz | 533.33 MT/s 0.533 GT/s 533,330 kT/s | FCBGA-437 | ✔ | ✘ | |||||||
| N270 | Atom | $ 44.00 € 39.60 £ 35.64 ¥ 4,546.52 | 45 nm 0.045 μm 4.5e-5 mm | 3 June 2008 | 1 | 2 | 1.6 GHz 1,599.99 MHz 1,599,990 kHz | 2,500 mW 2.5 W 0.00335 hp 0.0025 kW | 133.33 MHz 0.133 GHz 133,330 kHz | 533.33 MT/s 0.533 GT/s 533,330 kT/s | FCBGA-437 | ✔ | ✘ | |||||||
| N280 | Atom | 45 nm 0.045 μm 4.5e-5 mm | 7 February 2009 | 1 | 2 | 1.667 GHz 1,666.66 MHz 1,666,660 kHz | 2,500 mW 2.5 W 0.00335 hp 0.0025 kW | 166.66 MHz 0.167 GHz 166,660 kHz | 666.66 MT/s 0.667 GT/s 666,660 kT/s | FCBGA-437 | ✔ | ✘ | ||||||||
| Count: 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
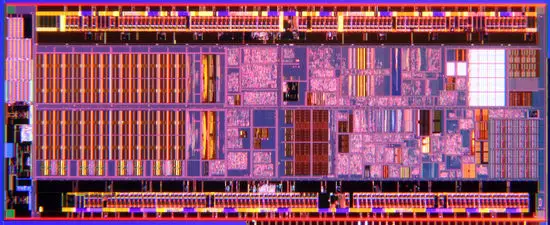
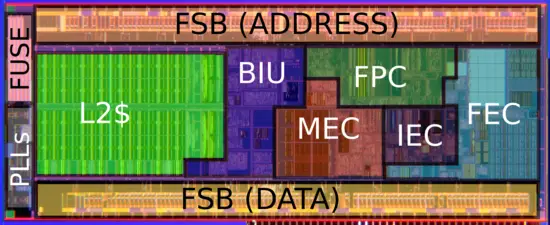
Die Shot
- See also: Bonnell § Silverthorne Die
- 45 nm process
- 9 metal layers
- 47,212,207 transistors
- 3.1 mm x 7.8 mm
- 24.18 mm² die size
See Also
- Bonnell
- Silverthorne
- Diamondville
- Geode NX
| designer | Intel + |
| first announced | April 18, 2007 + |
| first launched | June 3, 2008 + |
| instance of | core + |
| isa | x86-32 + and x86-64 + |
| main image |  + + |
| main image caption | Atom N270, a Diamondville chip + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture | Bonnell + |
| name | Diamondville + |
| process | 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 64 bit (8 octets, 16 nibbles) + |