(Rumor update.) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{core | {{core | ||
|name=Genoa | |name=Genoa | ||
| − | |no image= | + | |no image=Yes |
|developer=AMD | |developer=AMD | ||
|manufacturer=TSMC | |manufacturer=TSMC | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|predecessor link=amd/cores/milan | |predecessor link=amd/cores/milan | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Genoa''' is codename | + | [[File:amd epyc roadmap 2021-01.png|thumb|right]] |
| + | '''Genoa''' is the codename of [[AMD]]'s high-performance enterprise-level server microprocessors based on the {{amd|Zen 4|l=arch}} microarchitecture which will succeed the {{amd|EPYC#7003 Series (Zen 3)|EPYC 7003}} "{{\\|Milan}}" series. | ||
| + | AMD roadmaps show the CPU cores of these processors will be fabricated on a TSMC [[5 nm process]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Genoa" processors will power the exaflop supercomputer El Capitan with delivery anticipated in early 2023. They will support next generation memory and I/O subsystems and utilize the third generation of AMD's [[Infinity Fabric|Infinity Architecture]].<ref>[https://www.amd.com/en/products/exascale-era "Powering the Exascale Era"], AMD.com, retrieved April 2021.</ref><ref>[https://www.hpe.com/us/en/newsroom/press-release/2020/03/hpe-and-amd-power-complex-scientific-discovery-in-worlds-fastest-supercomputer-for-us-department-of-energys-doe-national-nuclear-security-administration-nnsa.html "HPE and AMD power complex scientific discovery in world’s fastest supercomputer for U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)"], HPE.com, retrieved April 2021.</ref> | ||
{{future information}} | {{future information}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Leaked information suggests "Genoa" processors, branded EPYC 7004 series, will be available in a 6096-contact [[land grid array]] package for Socket SP5 with [[TDP]] up to 320 Watt and a configurable TDP-up reaching 400 Watt. They will support 12 channels of [[DDR5]]-5200 memory and 128 [[PCIe]] Gen 5 lanes per socket, up to 160 lanes total on 2P systems as prior generations. "Genoa" processors are expected to implement up to 96 cores with 2-way SMT i.e. 192 threads per socket.<ref>@ExecuFix (February 28, 2021), [https://twitter.com/ExecuFix/status/1365981401808580614 "Genoa"] (Tweet) - via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Twitter Twitter].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 20:23, 16 May 2021
| Edit Values | |
| Genoa | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | AMD |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Microarchitecture | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Microarchitecture | Zen 4 |
| Word Size | 8 octets 64 bit16 nibbles |
| Process | 5 nm 0.005 μm 5.0e-6 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Succession | |
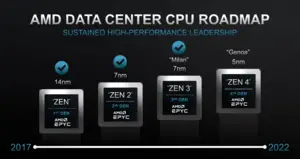
Genoa is the codename of AMD's high-performance enterprise-level server microprocessors based on the Zen 4 microarchitecture which will succeed the EPYC 7003 "Milan" series.
AMD roadmaps show the CPU cores of these processors will be fabricated on a TSMC 5 nm process.
"Genoa" processors will power the exaflop supercomputer El Capitan with delivery anticipated in early 2023. They will support next generation memory and I/O subsystems and utilize the third generation of AMD's Infinity Architecture.[1][2]
Leaked information suggests "Genoa" processors, branded EPYC 7004 series, will be available in a 6096-contact land grid array package for Socket SP5 with TDP up to 320 Watt and a configurable TDP-up reaching 400 Watt. They will support 12 channels of DDR5-5200 memory and 128 PCIe Gen 5 lanes per socket, up to 160 lanes total on 2P systems as prior generations. "Genoa" processors are expected to implement up to 96 cores with 2-way SMT i.e. 192 threads per socket.[3]
References
- ↑ "Powering the Exascale Era", AMD.com, retrieved April 2021.
- ↑ "HPE and AMD power complex scientific discovery in world’s fastest supercomputer for U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)", HPE.com, retrieved April 2021.
- ↑ @ExecuFix (February 28, 2021), "Genoa" (Tweet) - via Twitter.
| designer | AMD + |
| first launched | November 10, 2022 + |
| instance of | core + |
| isa | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture | Zen 4 + |
| name | Genoa + |
| package | SP5 + and FCLGA-6096 + |
| process | 5 nm (0.005 μm, 5.0e-6 mm) + and 6 nm (0.006 μm, 6.0e-6 mm) + |
| socket | Socket SP5 + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 64 bit (8 octets, 16 nibbles) + |