(→History) |
(→Process Technology) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
== Process Technology == | == Process Technology == | ||
| + | {{see also|3 µm process}} | ||
ARM1-based chips were manufactured by [[VLSI Technology]] on a [[3 µm]] double-level metal [[CMOS]] process. | ARM1-based chips were manufactured by [[VLSI Technology]] on a [[3 µm]] double-level metal [[CMOS]] process. | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 24 June 2017
| Edit Values | |
| ARM1 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | VLSI Technology |
| Introduction | 1985 |
| Process | 3 µm |
| Core Configs | 1 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv1 |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 0 KiB/Core |
| L1D Cache | 0 KiB/Core |
| Succession | |
ARM1 was the first ARM microarchitecture implemented by ARM Holdings (then Acorn Computers) as a research and development project for the BBC Computer Literacy Project. ARM1 was introduced in 1985 and was extended to be used as a coprocessor in the Acorn's BBC Micro microcomputers. ARM1 was distributed as an evaluation system and was never commercialized.
History
- Main article: ARM's History
The ARM1 (Acorn RISC Machine 1) is Acorn Computers' first microprocessor design. The ARM1 was the initial result of the Advanced Research and Development division Acorn Computers formed in order to advance the development of their own RISC processor. The ARM instruction set design started in 1983. A reference model was written in BBC BASIC by Sophie Wilson and Steve Furber in just 808 lines of code. On April 26 1985, after 6 man-years of design effort, the first ARM processor prototype was delivered. The first batch of prototypes were functional and were shipped to customers in the form of evaluation systems. At that time the ARM1 was the simplest RISC processor produced.
The first prototype tested worked on the first try, this was despite the ammeter reading no power. The prototype test board designed was faulty with a short. The chip was entirely running off the leakage from the I/Os. Designed to run at 1 W, the chip averaged under 100 mW typical power.
Process Technology
- See also: 3 µm process
ARM1-based chips were manufactured by VLSI Technology on a 3 µm double-level metal CMOS process.
Architecture
Overview
- Goal 1.5x performance of the VAX 11/780
- 3 µm process
- 26-bit address space
- Pipeline
- Very simple
- 3-stage
- No hardware multiplication
- 25 32-bit registers
- 16 For user
- 9 For supervisor
- 4 Modes
- User, Supervisor, IRQ, FIQ
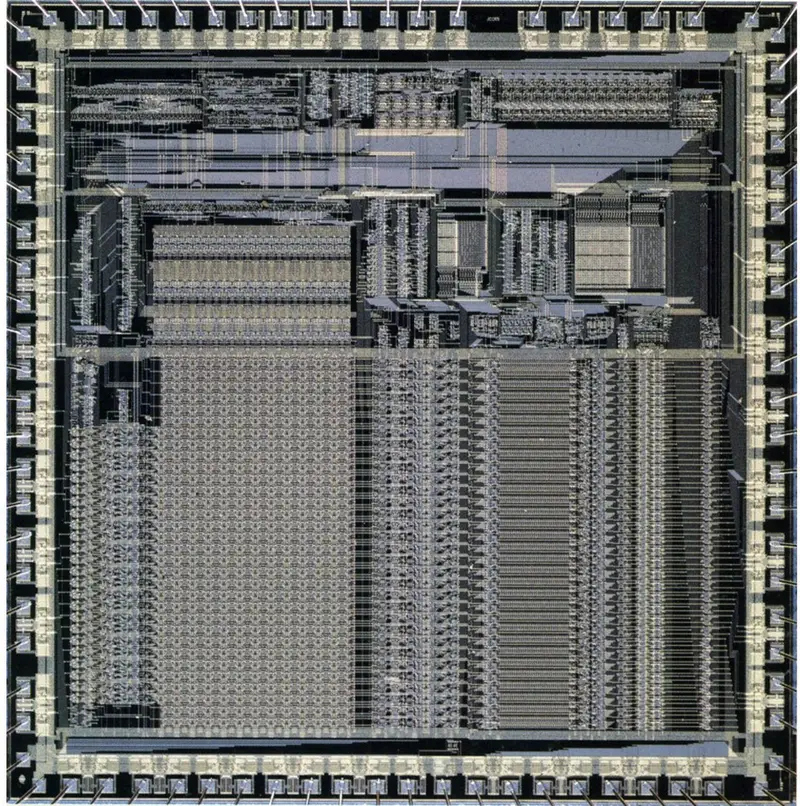
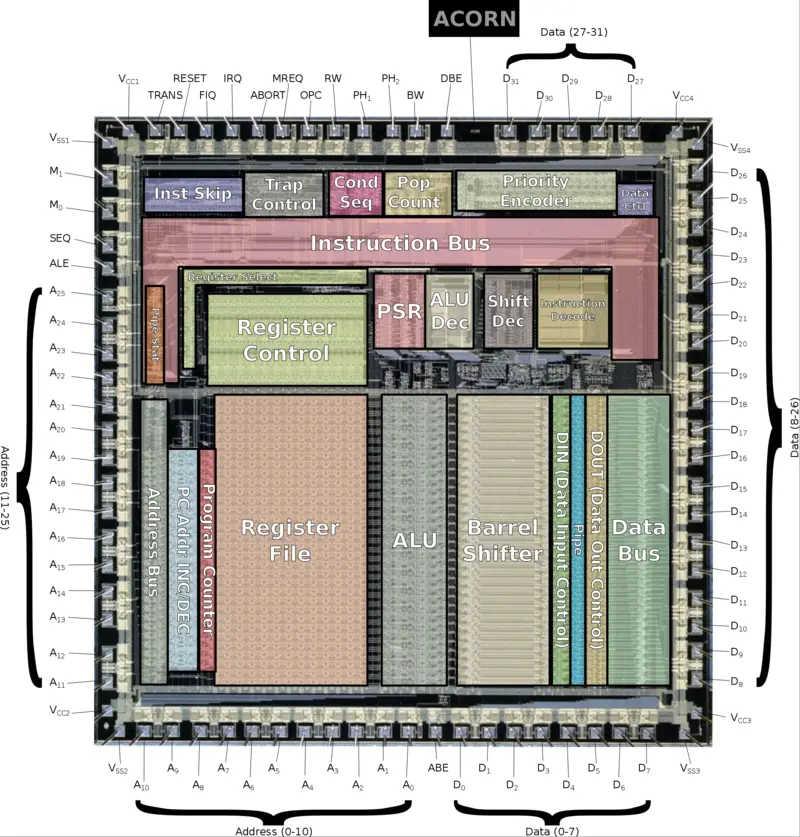
Die Shot
- 3 µm process
- 24,800 transistors
- ~6,000 gates
- ~7 mm x 7mm
- 50 mm² die size
- PLCC-82
- 74 signal pins
- 8 power/ground pins
| codename | ARM1 + |
| core count | 1 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | 1985 + |
| full page name | acorn/microarchitectures/arm1 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv1 + |
| manufacturer | VLSI Technology + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | ARM1 + |
| process | 3,000 nm (3 μm, 0.003 mm) + |