(→Architecture) |
|||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| − | {{ | + | Ambric's Am2000 models are all made of small homogeneous units called '''Brics'''. The exact number of brics depends on the model. |
| + | |||
| + | === communication === | ||
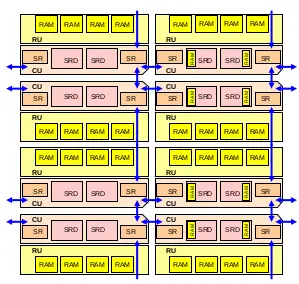
| + | [[File:ambric neighbor channels.png|thumb|right|350px|'''Neighbor Channels''']] | ||
| + | Ambric's architecture makes heavy use of channels - synchronized interconnects that carry both data and instructions in a [[FIFO]]. Channels are a strong point of this architecture as all data goes through channels including [[memory]] and [[registers]]. Channel interconnects can be loosely divided into three categories: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Intra-Bric Channels''': internal channels that span no loner than a single bric. All basic communication utilizes these channels. They are dynamically configured by the instructions themselves. Typical ALU [[register]]/[[memory]] utilizes these channels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Neighbor Channels''': channels spanning between two CU units. These channels only go to an adjacent control unit (i.e. directly North, South, East, or West). Only one channel is aviable in each direction. Channels are {{arch|32}} wide operating at up to 9.6 GT/s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Inter-Bric Channels''': also known as distanced bric channels, are communication channels that operate globally between any two brics. | ||
== Programming == | == Programming == | ||
Revision as of 21:26, 24 June 2016
| Ambric Am2000 | |

| |
| Am2045 | |
| Developer | Ambric |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Type | Microprocessors |
| Introduction | October 10, 2006 (announced) December, 2006 (launch) |
| Architecture | Many-core 32-bit microprocessor |
| Word size | 32 bit 4 octets
8 nibbles |
| Process | 130 nm 0.13 μm
1.3e-4 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 1 MHz-333 Mhz |
| Package | FCBGA-868, FCBGA-896 |
Am2000 was a family of 32-bit MPPAs designed by Ambric. The series was introduced at the 2006 Fall Microprocessor Forum. The two flagship models the Am2045 (A) and later Am2045B had over 300 cores with maximum theoretical performance of over one trillion operations per second. Due to the economic downturn of 2008 Ambric failed to secure additional funding and was forced to sell its assets to Nethra Imaging which continued to manufacture the chips until 2013. Prior to the acquisition Ambric also announced a 600 cores, 600 MHz model. It's unknown if the model ever made it to market. Designs, software, and related patents are now held by Imagination Technologies.
Ambric, unlike many of its competitors, managed to develop a sound programming model that proved itself to be simple enough and intuitive enough to allow easy programming. Am2000 found their way to various military applications, medical instruments, and high-end multimedia hardware.
Contents
Overview
Introduced in the fall of 2006, the Am2000 is a series of many-core processors implemented as a massively parallel processor array designed to replace high-end embedded processors, DSPs, and FPGAs in applications where fast general-purpose integer arithmetic and digital-signal processing is required. Such tasks usually land themselves fairly well in highly parallel environments.
Ambric's AM2000 series is an example of one of the few massively parallel processors that succeeded in independently developing a solid programming model and tools that worked extremely well with the underlying processor that relatively easy to code. A complete set of development tools were also offered with the product including extensions to Eclipse IDE. Code for the AM2000 used a language called aJava which was a strict subset of Java that compiled directly into machine code.
Members
,,,,,,,| Am2000 Models | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Process | Freq | Core Count |
| Am2012 | January 2007 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 333 MHz 0.333 GHz 333,000 kHz | 96 |
| Am2016 | 15 November 2007 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 kHz | 120 |
| Am2024 | January 2007 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 333 MHz 0.333 GHz 333,000 kHz | 192 |
| Am2029 | 15 November 2007 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 kHz | 216 |
| Am2035 | January 2007 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 333 MHz 0.333 GHz 333,000 kHz | 280 |
| Am2045 | January 2007 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 333 MHz 0.333 GHz 333,000 kHz | 344 |
| Am2045B | 15 November 2007 | 130 nm 0.13 μm 1.3e-4 mm | 350 MHz 0.35 GHz 350,000 kHz | 344 |
| Am2070 | 90 nm 0.09 μm 9.0e-5 mm | 600 MHz 0.6 GHz 600,000 kHz | 560 | |
| Count: 8 | ||||
Architecture
Ambric's Am2000 models are all made of small homogeneous units called Brics. The exact number of brics depends on the model.
communication
Ambric's architecture makes heavy use of channels - synchronized interconnects that carry both data and instructions in a FIFO. Channels are a strong point of this architecture as all data goes through channels including memory and registers. Channel interconnects can be loosely divided into three categories:
- Intra-Bric Channels: internal channels that span no loner than a single bric. All basic communication utilizes these channels. They are dynamically configured by the instructions themselves. Typical ALU register/memory utilizes these channels.
- Neighbor Channels: channels spanning between two CU units. These channels only go to an adjacent control unit (i.e. directly North, South, East, or West). Only one channel is aviable in each direction. Channels are 32-bit wide operating at up to 9.6 GT/s.
- Inter-Bric Channels: also known as distanced bric channels, are communication channels that operate globally between any two brics.
Programming
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Applications
The Am2000 has been used for high-definition video processing, medical imaging devices, high performance network processing, image recognition, and various military applications such as drones.
See also
| designer | Ambric + |
| first announced | October 10, 2006 + |
| first launched | December 2006 + |
| full page name | ambric/am2000 + |
| instance of | microprocessor family + |
| main designer | Ambric + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| name | Ambric Am2000 + |
| package | FCBGA-868 + and FCBGA-896 + |
| process | 130 nm (0.13 μm, 1.3e-4 mm) + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 32 bit (4 octets, 8 nibbles) + |