(integer ALU throuthput) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|cores 3=6P+0E | |cores 3=6P+0E | ||
|cores 4=2P+8E | |cores 4=2P+8E | ||
| − | |processing elements=32 | + | |processing elements=32 EU igpu |
| − | |processing elements 2=96 | + | |processing elements 2=96 EU igpu |
| + | |oooe=Yes | ||
|speculative=Yes | |speculative=Yes | ||
| + | |renaming=Yes | ||
|isa=x86-64 | |isa=x86-64 | ||
| + | |extension=MMX | ||
| + | |extension 2=AVX | ||
| + | |extension 3=AVX2 | ||
| + | |extension 4=AVX-512 (needs BIOS support and no E core) | ||
|l1i=32 KB | |l1i=32 KB | ||
|l1i per=core | |l1i per=core | ||
| Line 31: | Line 37: | ||
|predecessor 2 link=intel/microarchitectures/rocket lake | |predecessor 2 link=intel/microarchitectures/rocket lake | ||
|predecessor 3=Lakefield | |predecessor 3=Lakefield | ||
| + | |predecessor 3 link=intel/microarchitectures/lakefield | ||
|successor=Raptor Lake | |successor=Raptor Lake | ||
|successor link=intel/microarchitectures/raptor lake | |successor link=intel/microarchitectures/raptor lake | ||
|successor 2=Meteor Lake | |successor 2=Meteor Lake | ||
| + | |successor 2 link=intel/microarchitectures/meteor lake | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Alder Lake''' ('''ADL''') is [[Intel]]'s successor to both {{\\|Tiger Lake}} and {{\\|Rocket Lake}}, an [[Intel 7]]-process based [[microarchitecture]] for mainstream workstations, desktops, and mobile devices. Alder Lake is Intel's first [[10-nanometer]]-class proper successor to all prior generation of processors - spanning from ultra-low power to desktop and workstations. The microarchitecture was developed by Intel's R&D center in [[wikipedia:Haifa, Israel|Haifa, Israel]]. | '''Alder Lake''' ('''ADL''') is [[Intel]]'s successor to both {{\\|Tiger Lake}} and {{\\|Rocket Lake}}, an [[Intel 7]]-process based [[microarchitecture]] for mainstream workstations, desktops, and mobile devices. Alder Lake is Intel's first [[10-nanometer]]-class proper successor to all prior generation of processors - spanning from ultra-low power to desktop and workstations. The microarchitecture was developed by Intel's R&D center in [[wikipedia:Haifa, Israel|Haifa, Israel]]. | ||
| Line 60: | Line 68: | ||
! Cores !! {{intel|Hyper-Threading|HT}} !! {{x86|AVX}} !! {{x86|AVX2}} !! {{intel|Turbo Boost|TBT}} !! {{intel|Turbo Boost Max|TBMT}} | ! Cores !! {{intel|Hyper-Threading|HT}} !! {{x86|AVX}} !! {{x86|AVX2}} !! {{intel|Turbo Boost|TBT}} !! {{intel|Turbo Boost Max|TBMT}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[File:core i5 logo (2020).png|50px|link=intel/core_i5]] || {{intel|Core i5}} || style="text-align: left;" | Mid-range Performance || [[10 cores|10]] (6+4) || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|no}} | + | | [[File:core i3 logo (2020).png|50px|link=intel/core_i3]] || {{intel|Core i3}} || style="text-align: left;" | Low-end Performance || [[4 cores|4]] (4+0) || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|no}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:core i5 logo (2020).png|50px|link=intel/core_i5]] || {{intel|Core i5}} || style="text-align: left;" | Mid-range Performance || [[10 cores|10]] (6+4)<br> [[6 cores|6]] (6+0) || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|no}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:core i7 logo (2020).png|50px|link=intel/core_i7]] || {{intel|Core i7}} || style="text-align: left;" | High-end Performance || [[12 cores|12]] (8+4) || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} | | [[File:core i7 logo (2020).png|50px|link=intel/core_i7]] || {{intel|Core i7}} || style="text-align: left;" | High-end Performance || [[12 cores|12]] (8+4) || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} || {{tchk|yes}} | ||
| Line 88: | Line 98: | ||
! Core !! Extended<br>Family !! Family !! Extended<br>Model !! Model | ! Core !! Extended<br>Family !! Family !! Extended<br>Model !! Model | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="2" | {{intel|Alder Lake | + | | rowspan="2" | {{intel|Alder Lake S|S|l=core}} || 0 || 0x6 || 0x9 || 0x7 |
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="4" | Family 6 Model 151 | | colspan="4" | Family 6 Model 151 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="2" | {{intel|Alder Lake | + | | rowspan="2" | {{intel|Alder Lake P|P|l=core}} || 0 || 0x6 || 0x9 || 0xA |
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="4" | Family 6 Model 154 | | colspan="4" | Family 6 Model 154 | ||
| Line 104: | Line 114: | ||
=== Key changes from {{\\|Tiger Lake}}=== | === Key changes from {{\\|Tiger Lake}}=== | ||
* Core | * Core | ||
| − | ** Hybrid Golden Cove ( | + | ** Hybrid Golden Cove (performance core) & Gracemont (efficiency core) microarchitecture |
| − | ** | + | ** Higher IPC(Intel self-reported 19% IPC) |
| + | *** Some common integer ALU ops (CMP,TEST,AND,OR,XOR,LEA) increased throughput by 1 insn/cycle | ||
| + | *** Vector floating point addition/subtraction latency decreased from 4 to 2 cycles | ||
| + | *** [V]PCLMULQDQ latency decreased from 8/6 to 3 cycles | ||
** Intel 7 node | ** Intel 7 node | ||
* Memory | * Memory | ||
| Line 113: | Line 126: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| − | Alder Lake departs from all prior Intel SoCs by featuring the company's first mainstream implementation of a single-ISA heterogeneous multi-core microarchitecture. While not the first ({{\\|Lakefield}} was), Alder Lake is the first to target all market segments from mobile to desktop and workstation. The overall microarchitecture builds on | + | Alder Lake departs from all prior Intel SoCs by featuring the company's first mainstream implementation of a single-ISA heterogeneous multi-core microarchitecture. While not the first ({{\\|Lakefield}} was), Alder Lake is the first to target all market segments from mobile to desktop and workstation. The overall microarchitecture builds on its predecessor, {{\\|Tigerlake}} but expends on its by integrating two vastly different types of cores - up to eight [[big cores]] based on the {{\\|Golden Cove}} microarchitecture and up to eight [[small cores]] based on the {{\\|Gracemont}} microarchitecture. The big cores are designed to push single-thread performance while the small cores are designed to push multi-thread power efficiency. By finely orchestrating thread scheduling based on performance demand, Alder Lake is able to provide both higher multi-threading performance-efficiency and better single-thread performance. |
=== SoC design === | === SoC design === | ||
| Line 122: | Line 135: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| − | ! colspan=" | + | ! colspan="5" | Die |
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! Name !! Configuration !! Dimensions !! Area | + | ! Name !! CPU Configuration !! GPU !! Dimensions !! Area |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="2" | ADL-S || 8P + 8E || 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm || 215.25 mm² | + | | rowspan="2" | ADL-S || 8P + 8E || rowspan="2" | 32 EU || 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm || 215.25 mm² |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 6P + | + | | 6P + 0E || 10.5 mm x 15.5 mm || 162.75 mm² |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | ADL-P || 6P + 8E | + | | ADL-P || 6P + 8E || rowspan="2" | 96 EU |
|- | |- | ||
| ADL-M || 2P + 8E | | ADL-M || 2P + 8E | ||
| Line 137: | Line 150: | ||
=== ADL-S (8P+8E) === | === ADL-S (8P+8E) === | ||
* 8 performance cores + 8 efficiency cores | * 8 performance cores + 8 efficiency cores | ||
| + | * 32 EU gpu (256 shaders) | ||
* [[Intel 7]] process | * [[Intel 7]] process | ||
* 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm | * 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm | ||
| Line 149: | Line 163: | ||
=== ADL-S (6P+0E) === | === ADL-S (6P+0E) === | ||
* 6 performance cores, no efficiency cores | * 6 performance cores, no efficiency cores | ||
| + | * 32 EU gpu (256 shaders) | ||
* [[Intel 7]] process | * [[Intel 7]] process | ||
* 10.5 mm x 15.5 mm | * 10.5 mm x 15.5 mm | ||
Latest revision as of 09:38, 3 August 2023
| Edit Values | |
| Alder Lake µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | 2021 |
| Process | intel 7 (10nm ESF) |
| Core Configs | "P+8E" can not be assigned to a declared number type with value 8. 8P+8E, "P+8E" can not be assigned to a declared number type with value 6. 6P+8E, "P+0E" can not be assigned to a declared number type with value 6. 6P+0E, "P+8E" can not be assigned to a declared number type with value 2. 2P+8E |
| PE Configs | 32 EU igpu, 96 EU igpu |
| Pipeline | |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Extensions | MMX, AVX, AVX2, AVX-512 (needs BIOS support and no E core) |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 32 KB/core |
| L1D Cache | 48 KB (P) / 64 KB (E)/core |
| L1 Cache | 80 KB (P) / 96 KB (E)/core |
| L2 Cache | 1.25 MB (P) / 2MB (4E)/core |
| L3 Cache | up to 30 MB |
| Cores | |
| Core Names | Golden Cove, Gracemont |
| Succession | |
Alder Lake (ADL) is Intel's successor to both Tiger Lake and Rocket Lake, an Intel 7-process based microarchitecture for mainstream workstations, desktops, and mobile devices. Alder Lake is Intel's first 10-nanometer-class proper successor to all prior generation of processors - spanning from ultra-low power to desktop and workstations. The microarchitecture was developed by Intel's R&D center in Haifa, Israel.
For desktop and mobile, Alder Lake is branded as 12th Generation Intel Core i3, Core i5, Core i7, and Core i9 processors.
Contents
Codenames[edit]
| Core | Abbrev | Platform | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alder Lake M | ADL-M | Light notebooks, 2-in-1s detachable, tablets, conference room, computer sticks, etc. | |
| Alder Lake P | ADL-P | Ultimate mobile performance, mobile workstations, portable All-in-Ones (AiOs), Minis | |
| Alder Lake S | ADL-S | Desktop performance to value, AiOs, and minis |
Brands[edit]
Intel released Alder Lake under 3 main brand families for mainstream workstations, desktops, and mobile.
| Logo | Family | General Description | Differentiating Features | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cores | HT | AVX | AVX2 | TBT | TBMT | ||||
 |
Core i3 | Low-end Performance | 4 (4+0) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | |
 |
Core i5 | Mid-range Performance | 10 (6+4) 6 (6+0) |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | |
 |
Core i7 | High-end Performance | 12 (8+4) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
 |
Core i9 | Extreme Performance | 16 (8+8) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
Process Technology[edit]
Intel is planning Alder Lake to be built on an improved Intel 7 node (previously 10nm Enhanced SuperFin (ESF)). This will be the case for both the powerful Golden Cove cores, and Gracemont cores.
Compiler support[edit]
| Compiler | Arch-Specific | Arch-Favorable |
|---|---|---|
| ICC | -march=alderlake |
-mtune=alderlake
|
| GCC | -march=alderlake |
-mtune=alderlake
|
| LLVM | -march=alderlake |
-mtune=alderlake
|
| Visual Studio | /arch:AVX2 |
/tune:alderlake
|
CPUID[edit]
| Core | Extended Family |
Family | Extended Model |
Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0 | 0x6 | 0x9 | 0x7 |
| Family 6 Model 151 | ||||
| P | 0 | 0x6 | 0x9 | 0xA |
| Family 6 Model 154 | ||||
History[edit]
In January 2021 Intel teased Alder Lake in their CES 2021 speech. On the July 26th's Intel Accelerated webcast, CEO Pat Gelsinger hinted at the Alder Lake lineup being released at a future event called "Intel Innovation" which aired between October 27-28th.
Architecture[edit]
Key changes from Tiger Lake[edit]
- Core
- Hybrid Golden Cove (performance core) & Gracemont (efficiency core) microarchitecture
- Higher IPC(Intel self-reported 19% IPC)
- Some common integer ALU ops (CMP,TEST,AND,OR,XOR,LEA) increased throughput by 1 insn/cycle
- Vector floating point addition/subtraction latency decreased from 4 to 2 cycles
- [V]PCLMULQDQ latency decreased from 8/6 to 3 cycles
- Intel 7 node
- Memory
- Support for DDR5
- Speeds of at least 4800MHz, up to 5600MHz
- Improved power delivery system
Overview[edit]
Alder Lake departs from all prior Intel SoCs by featuring the company's first mainstream implementation of a single-ISA heterogeneous multi-core microarchitecture. While not the first (Lakefield was), Alder Lake is the first to target all market segments from mobile to desktop and workstation. The overall microarchitecture builds on its predecessor, Tigerlake but expends on its by integrating two vastly different types of cores - up to eight big cores based on the Golden Cove microarchitecture and up to eight small cores based on the Gracemont microarchitecture. The big cores are designed to push single-thread performance while the small cores are designed to push multi-thread power efficiency. By finely orchestrating thread scheduling based on performance demand, Alder Lake is able to provide both higher multi-threading performance-efficiency and better single-thread performance.
SoC design[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Die[edit]
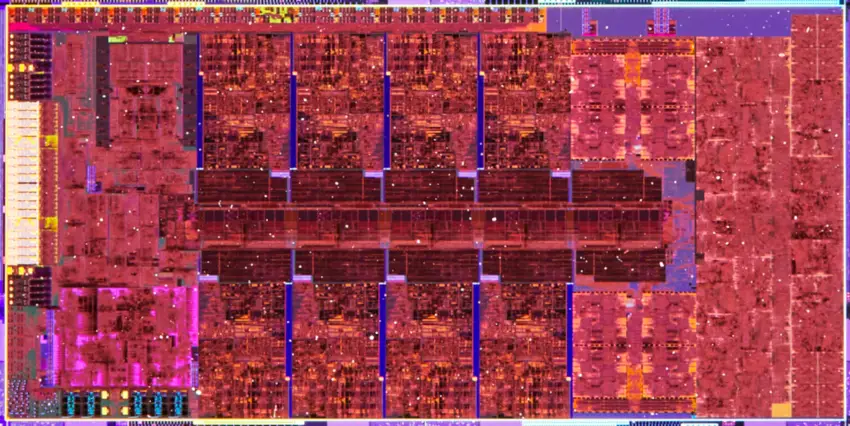
Alder Lake comes in four die variants depending on the market segment.
| Die | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | CPU Configuration | GPU | Dimensions | Area |
| ADL-S | 8P + 8E | 32 EU | 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm | 215.25 mm² |
| 6P + 0E | 10.5 mm x 15.5 mm | 162.75 mm² | ||
| ADL-P | 6P + 8E | 96 EU | ||
| ADL-M | 2P + 8E | |||
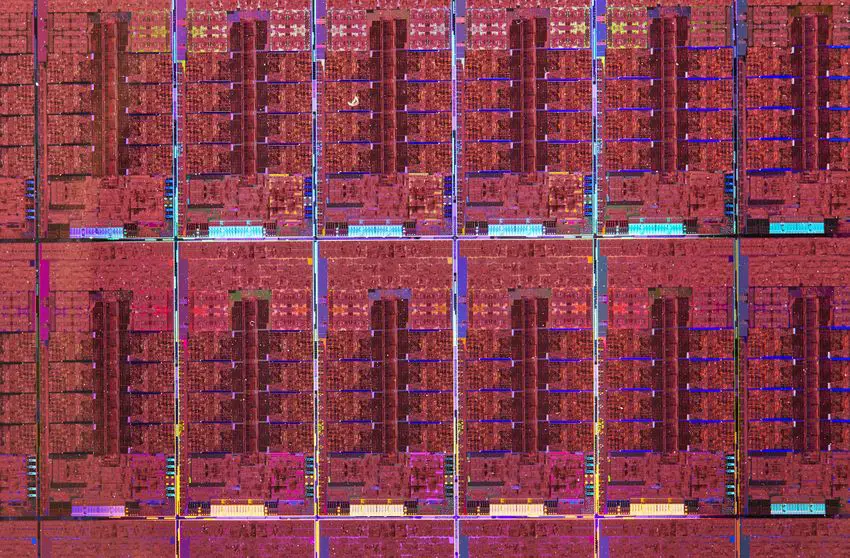
ADL-S (8P+8E)[edit]
- 8 performance cores + 8 efficiency cores
- 32 EU gpu (256 shaders)
- Intel 7 process
- 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm
- 215.25 mm² die size
ADL-S (6P+0E)[edit]
- 6 performance cores, no efficiency cores
- 32 EU gpu (256 shaders)
- Intel 7 process
- 10.5 mm x 15.5 mm
- 162.75 mm² die size
Additional Shots[edit]
| codename | Alder Lake + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | 2021 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/alder lake + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Alder Lake + |