(→Die) |
(→Core) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| + | The ARM250 doesn't introduce anything new in itself. The core is an {{acorn|ARM3|l=arch}} with the MMU logic taken from the {{\\|ARM6}} which was also released around the same time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Key changes from {{\\|ARM3}} === | ||
| + | * Integrates support chips on-die | ||
| + | ** Integrated MEMC | ||
| + | ** Integrated VIDC | ||
| + | ** Integrated IOEB/IOC | ||
| + | * Virtual memory | ||
| + | ** Integrated [[MMU]] ({{\\|ARM6}}'s) | ||
| + | |||
=== Block Diagram === | === Block Diagram === | ||
==== Entire Chip ==== | ==== Entire Chip ==== | ||
| − | : [[File:arm250 block diagram.svg| | + | : [[File:arm250 block diagram.svg|650px]] |
==== Core ==== | ==== Core ==== | ||
| + | :''({{acorn|ARM3|l=arch}} core)'' | ||
: [[File:arm2 block diagram.svg|650px]] | : [[File:arm2 block diagram.svg|650px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:35, 10 July 2017
| Edit Values | |
| ARM250 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | VLSI Technology |
| Introduction | 1992 |
| Process | 1 µm |
| Core Configs | 1 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Scalar, Pipelined |
| Stages | 3 |
| Decode | 1-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv2a |
| Cores | |
| Core Names | ARM250 |
| Succession | |
ARM250 was a system on a chip microarchitecture that was introduced by ARM Holdings around the same time the ARM6 was introduced.
Contents
History[edit]
- See also: ARM's History
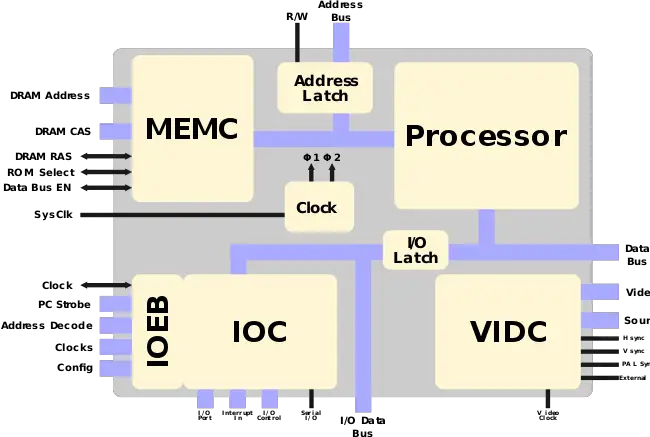
With the development of the ARM6 and a process shrink by VTI, ARM took the opportunity to introduce the ARM250. The ARM250 is a very high integration chip - incorporating the ARM3 core along with most of the new MMU logic that was developed for the ARM6 along with all the support chips that were previously needed for the ARM3/2 - the MEMC chip (Memory Controller), VIDC chip (Video Controller), IOC/IOEB (I/O Controller).
Note that the added L1 cache found on the ARM3 is not found on the ARM250.
Process Technology[edit]
- See also: 1 µm process
The ARM250 was implemented on a 1 µm double-level metal (DLM) CMOS process.
Architecture[edit]
The ARM250 doesn't introduce anything new in itself. The core is an ARM3 with the MMU logic taken from the ARM6 which was also released around the same time.
Key changes from ARM3[edit]
- Integrates support chips on-die
- Integrated MEMC
- Integrated VIDC
- Integrated IOEB/IOC
- Virtual memory
Block Diagram[edit]
Entire Chip[edit]
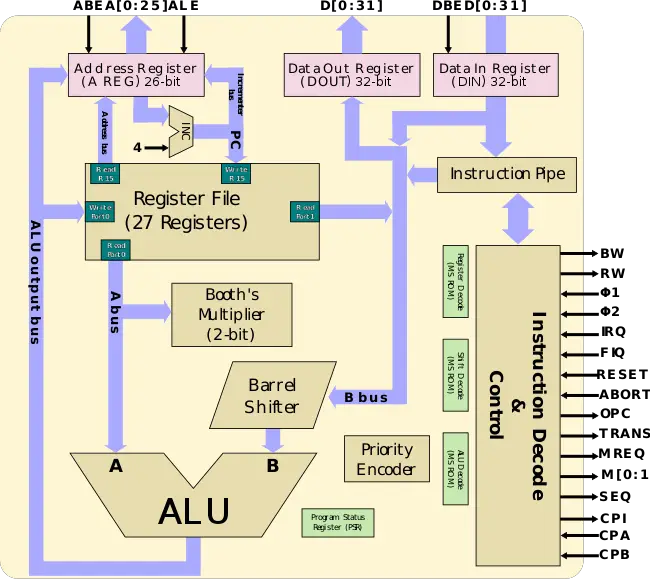
Core[edit]
- (ARM3 core)
-
Die[edit]
- 1-micron process CMOS
- 2 metal layers
- 58 mm² die size
- 98,019 transistors
- $25 (for 100K quantities)
- PJQFP-160
References[edit]
- Muller, Mike. "ARM6: a high performance low power consumption macrocell." Compcon Spring'93, Digest of Papers.. IEEE, 1993.
Documents[edit]
- ARM250 Datasheet, August 11, 1992
| codename | ARM250 + |
| core count | 1 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | 1992 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/arm250 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv2a + |
| manufacturer | VLSI Technology + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | ARM250 + |
| pipeline stages | 3 + |
| process | 1,000 nm (1 μm, 0.001 mm) + |