(→All Raptor Lake Chips) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
'''Raptor Lake''' ('''RPL''') is [[Intel]]'s successor to {{\\|Alder Lake}}, an enhanced [[Intel 7]]-process based [[microarchitecture]] for mainstream workstations, desktops, and mobile devices. The microarchitecture was developed by Intel's R&D center (IDC) in [[wikipedia:Haifa, Israel|Haifa, Israel]]. | '''Raptor Lake''' ('''RPL''') is [[Intel]]'s successor to {{\\|Alder Lake}}, an enhanced [[Intel 7]]-process based [[microarchitecture]] for mainstream workstations, desktops, and mobile devices. The microarchitecture was developed by Intel's R&D center (IDC) in [[wikipedia:Haifa, Israel|Haifa, Israel]]. | ||
| − | For desktop and mobile, | + | For desktop and mobile, Raptor Lake is branded as 13th Generation Intel {{intel|Core i3}}, {{intel|Core i5}}, {{intel|Core i7}}, and {{intel|Core i9}} processors. |
== Codenames == | == Codenames == | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
== Brands == | == Brands == | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:13th gen announcement.png|thumb|Raptor Lake is branded 13th Generation Core processors.]] |
Intel released Raptor Lake under 3 main brand families for mainstream desktops and mobile. | Intel released Raptor Lake under 3 main brand families for mainstream desktops and mobile. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
! colspan="2" | Cores !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Hyper-Threading|HT}} !! rowspan="2" | {{x86|AVX}} !! rowspan="2" | {{x86|AVX2}} !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Turbo Boost|TBT}} !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Turbo Boost Max|TBMT}} !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Thermal Velocity Boost|TVB}} | ! colspan="2" | Cores !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Hyper-Threading|HT}} !! rowspan="2" | {{x86|AVX}} !! rowspan="2" | {{x86|AVX2}} !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Turbo Boost|TBT}} !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Turbo Boost Max|TBMT}} !! rowspan="2" | {{intel|Thermal Velocity Boost|TVB}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! P Cores !! E Cores |
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:core i3 logo (2020).png|50px|link=intel/core_i3]] || {{intel|Core i3}} || style="text-align: left;" | Low-end Performance | | [[File:core i3 logo (2020).png|50px|link=intel/core_i3]] || {{intel|Core i3}} || style="text-align: left;" | Low-end Performance | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
== Process Technology== | == Process Technology== | ||
| + | {{main|Intel 7 Process}} | ||
| + | [[File:pat gelsinger announces worlds first 6ghz processor.jpg|thumb|Raptor Lake features the world's first 6 GHz processor.]] | ||
Raptor Lake is fabricated on an enhanced version of the [[Intel 7 process]]. Internally it’s sometimes referred to as "[[Intel 7 Ultra]]", the company's 3rd generation SuperFin Transistor architecture. The enhanced node shifts the V-F curve enough to allow a significant reduction in voltage at ISO-frequency or, alternatively, a few 100 MHz improvement in frequency at ISO-voltage. | Raptor Lake is fabricated on an enhanced version of the [[Intel 7 process]]. Internally it’s sometimes referred to as "[[Intel 7 Ultra]]", the company's 3rd generation SuperFin Transistor architecture. The enhanced node shifts the V-F curve enough to allow a significant reduction in voltage at ISO-frequency or, alternatively, a few 100 MHz improvement in frequency at ISO-voltage. | ||
| Line 86: | Line 88: | ||
! Core !! Extended<br>Family !! Family !! Extended<br>Model !! Model | ! Core !! Extended<br>Family !! Family !! Extended<br>Model !! Model | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | rowspan="2" | {{intel|Raptor Lake S|S|l=core}} || 0 || 0x6 || || | + | | rowspan="2" | {{intel|Raptor Lake S|S|l=core}} || 0 || 0x6 || 0xB || 0x7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="4" | Family 6 Model | + | | colspan="4" | Family 6 Model 183 |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 97: | Line 99: | ||
=== Key changes from {{\\|Alder Lake}}=== | === Key changes from {{\\|Alder Lake}}=== | ||
* Core | * Core | ||
| − | ** {{\\| | + | ** {{\\|Golden Cove}} → {{\\|Raptor Cove}} P-cores |
| − | ** "Enhanced {{\\|Gracemont}}" cores | + | ** {{\\|Gracemont}} → "Enhanced {{\\|Gracemont}}" E-cores |
** 2x {{\\|Gracemont}} cores (16 E cores, up from 8) | ** 2x {{\\|Gracemont}} cores (16 E cores, up from 8) | ||
** Considerably higher frequency (Up to 800 MHz higher) | ** Considerably higher frequency (Up to 800 MHz higher) | ||
*** First commercial processor to break the 6 GHz barrier | *** First commercial processor to break the 6 GHz barrier | ||
* Technology | * Technology | ||
| − | ** | + | ** [[Enhanced Intel 7 Process]] ("[[Intel 7 Ultra]]") |
* Memory | * Memory | ||
** DDR5 | ** DDR5 | ||
*** 1.17x Higher data rate (5,600 MT/s, up from 4,800 MT/s) | *** 1.17x Higher data rate (5,600 MT/s, up from 4,800 MT/s) | ||
| + | * Chipset | ||
| + | ** Z690 → Z790 | ||
| + | *** Dropped Optane memory support | ||
| + | *** 1.66x more PCIe 4.0 lanes (x20, up from x14) | ||
| + | *** 0.5x PCIe 3.0 lanes (x8, down from x16) | ||
| + | *** 1 more USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 (5, up from 4) | ||
{{expand list}} | {{expand list}} | ||
| Line 150: | Line 158: | ||
* Enhanced Intel 7 | * Enhanced Intel 7 | ||
| − | |||
| − | == All Raptor Lake | + | :[[File:intel raptor lake die (8+16).jpg|class=wikichip_ogimage|700px]] |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:intel raptor lake die (8+16) (annotated).png|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === System Agent === | ||
| + | :{| | ||
| + | | [[File:raptor lake (system agent).png|200px]] | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | | [[File:raptor lake (system agent) (annotated).png|200px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Integrated Graphics === | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:raptor lake (gpu).png|200px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == All Raptor Lake processors == | ||
<!-- NOTE: | <!-- NOTE: | ||
This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| Line 161: | Line 184: | ||
--> | --> | ||
{{comp table start}} | {{comp table start}} | ||
| − | <table class="comptable sortable | + | <table class="comptable sortable"> |
| − | {{comp table header|main| | + | {{comp table header|main|13:List of Raptor Lake-based Processors}} |
| − | {{comp table header|main|10:Main processor | + | {{comp table header|main|10:Main processor|3:GPU}} |
| − | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Price|Family | + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Price|Family|Core|Cores|Threads|L3$|Power|Base|Max Turbo|Name|Base|Burst}} |
{{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[microarchitecture::Raptor Lake]] | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[microarchitecture::Raptor Lake]] | ||
|?full page name | |?full page name | ||
| Line 171: | Line 194: | ||
|?release price | |?release price | ||
|?microprocessor family | |?microprocessor family | ||
| − | |||
|?core name | |?core name | ||
|?core count | |?core count | ||
| Line 178: | Line 200: | ||
|?tdp | |?tdp | ||
|?base frequency#GHz | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
| − | |?turbo frequency | + | |?turbo frequency#GHz |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|?integrated gpu | |?integrated gpu | ||
|?integrated gpu base frequency | |?integrated gpu base frequency | ||
| Line 187: | Line 206: | ||
|format=template | |format=template | ||
|template=proc table 3 | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| − | |userparam= | + | |userparam=15 |
|mainlabel=- | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | |valuesep=, | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[microarchitecture::Raptor Lake]]}} | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[microarchitecture::Raptor Lake]]}} | ||
| Line 195: | Line 215: | ||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
| − | * Intel. personal communication. | + | * Intel Innovation 2022. |
| + | * Intel. personal communication. 2022. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:06, 5 September 2024
| Edit Values | |
| Raptor Lake µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | September 27, 2022 |
| Process | Intel 7 |
| Core Configs | 24, 16, 8 |
| Pipeline | |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Extensions | MMX, AVX, AVX2 |
| Cache | |
| L3 Cache | 3 MiB/Cluster |
| Succession | |
Raptor Lake (RPL) is Intel's successor to Alder Lake, an enhanced Intel 7-process based microarchitecture for mainstream workstations, desktops, and mobile devices. The microarchitecture was developed by Intel's R&D center (IDC) in Haifa, Israel.
For desktop and mobile, Raptor Lake is branded as 13th Generation Intel Core i3, Core i5, Core i7, and Core i9 processors.
Contents
Codenames[edit]
| Core | Abbrev | Description | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raptor Lake S | RPL-S | Mainstream performance | Desktop performance to value, AiOs, and minis |
| Raptor Lake U | RPL-U | Ultra-low Power | Light notebooks, portable All-in-Ones (AiOs), Minis, and conference room |
| Raptor Lake P | RPL-P | Ultimate mobile performance, mobile workstations, portable All-in-Ones (AiOs), Minis | |
| Raptor Lake H | RPL-H | High-performance graphics | Ultimate mobile performance, mobile workstations |
| Raptor Lake HS | RPL-HS | High-performance graphics |
Brands[edit]
Intel released Raptor Lake under 3 main brand families for mainstream desktops and mobile.
| Logo | Family | General Description | Differentiating Features | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cores | HT | AVX | AVX2 | TBT | TBMT | TVB | ||||
| P Cores | E Cores | |||||||||
 |
Core i3 | Low-end Performance | ||||||||
 |
Core i5 | Mid-range Performance | 6 | 8 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | ✘ |
 |
Core i7 | High-end Performance | 8 | 8 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
 |
Core i9 | Extreme Performance | 8 | 16 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
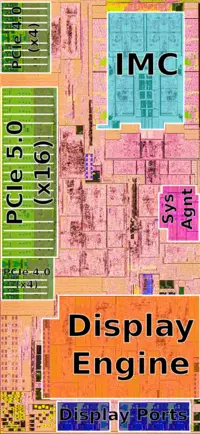
Process Technology[edit]
- Main article: Intel 7 Process
Raptor Lake is fabricated on an enhanced version of the Intel 7 process. Internally it’s sometimes referred to as "Intel 7 Ultra", the company's 3rd generation SuperFin Transistor architecture. The enhanced node shifts the V-F curve enough to allow a significant reduction in voltage at ISO-frequency or, alternatively, a few 100 MHz improvement in frequency at ISO-voltage.
Compiler support[edit]
| Compiler | Arch-Specific | Arch-Favorable |
|---|---|---|
| ICC | -march=alderlake |
-mtune=alderlake
|
| GCC | -march=alderlake |
-mtune=alderlake
|
| LLVM | -march=alderlake |
-mtune=alderlake
|
| Visual Studio | /arch:AVX2 |
/tune:alderlake
|
CPUID[edit]
| Core | Extended Family |
Family | Extended Model |
Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0 | 0x6 | 0xB | 0x7 |
| Family 6 Model 183 | ||||
History[edit]
Intel teased Raptor Lake for the first time during their Investor Meeting in early 2022. At the Intel Innovation 2022 conference, the company officially announced Raptor Lake. Enthusiasts desktop processors started shipping on October 20. Mobile and the rest of the Raptor Lake lineup is expected to be announced at CES 2023.
Architecture[edit]
Key changes from Alder Lake[edit]
- Core
- Golden Cove → Raptor Cove P-cores
- Gracemont → "Enhanced Gracemont" E-cores
- 2x Gracemont cores (16 E cores, up from 8)
- Considerably higher frequency (Up to 800 MHz higher)
- First commercial processor to break the 6 GHz barrier
- Technology
- Memory
- DDR5
- 1.17x Higher data rate (5,600 MT/s, up from 4,800 MT/s)
- DDR5
- Chipset
- Z690 → Z790
- Dropped Optane memory support
- 1.66x more PCIe 4.0 lanes (x20, up from x14)
- 0.5x PCIe 3.0 lanes (x8, down from x16)
- 1 more USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 (5, up from 4)
- Z690 → Z790
This list is incomplete; you can help by expanding it.
Overview[edit]
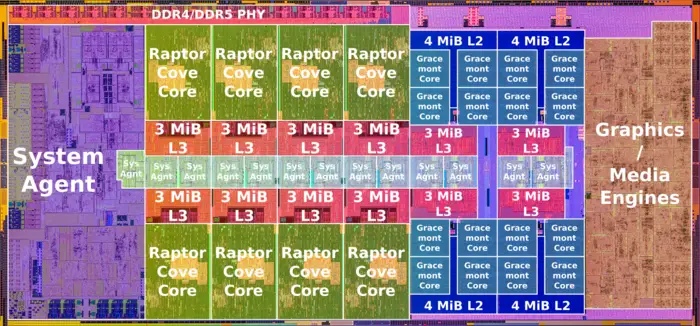
Raptor Lake is an enhanced refresh of Alder Lake, a single-ISA heterogeneous multi-core microarchitecture. This SoC targets all client market segments from ultra-mobile devices to desktops and workstations. As with Alder Lake, Raptor Lake integrate two vastly different types of cores - up to eight big performance cores ("P-Cores") along with up to sixteen small efficiency cores ("E-Cores") onto a single monolithic integrated circuit. The big cores are designed to push single-thread performance while the small cores are designed to push multi-thread power efficiency. By finely orchestrating thread scheduling based on performance demand, Raptor Lake is designed to provide both higher multi-threading performance efficiency and better single-thread performance.
The Raptor Lake SoC integrate up to eight Raptor Cove big cores. Those cores are an enhanced version of the Golden Cove cores found in Alder Lake. Additionally, Raptor Lake also doubled the number of Gracemont cores to 16 cores comprising 4 quad-core clusters.
SoC design[edit]
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Packaging[edit]
Raptor Lake comes in 4 different packagings.
| Package | LGA-1700 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core | Raptor Lake S | Raptor Lake H | Raptor Lake U | Raptor Lake P |
| TDP | 125 W | 45 W | 15 W | 9 W |
| Dimensions | 37.5 mm x 45.0 mm | |||
| Balls | ||||
| Ball Pitch | ||||
| Package (Front) |  |
 |
 |

|
| Package (Back) | 
|
Die[edit]
Raptor Lake comes in four die variants depending on the market segment.
Raptor Lake S (8P+16E)[edit]
Raptor Lake S comprises 8 P-Cores + 16 E-Cores.
System Agent[edit]
Integrated Graphics[edit]
All Raptor Lake processors[edit]
| List of Raptor Lake-based Processors | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main processor | GPU | ||||||||||||
| Model | Launched | Price | Family | Core | Cores | Threads | L3$ | Power | Base | Max Turbo | Name | Base | Burst |
| i5-13600K | 20 October 2022 | $ 319.00 € 287.10 , $ 329.00£ 258.39 ¥ 32,962.27 € 296.10 £ 266.49 ¥ 33,995.57 | Core i5 | Raptor Lake S | 14 | 20 | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB , 18 MiB6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB 18,432 KiB 18,874,368 B 0.0176 GiB | 125 W 125,000 mW , 181 W0.168 hp 0.125 kW 181,000 mW 0.243 hp 0.181 kW | 2.6 GHz 2,600 MHz , 3.5 GHz2,600,000 kHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | 5.1 GHz 5,100 MHz 5,100,000 kHz | UHD Graphics 770 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,500 MHz 1.5 GHz 1,500,000 KHz |
| i5-13600KF | 20 October 2022 | $ 294.00 € 264.60 , $ 304.00£ 238.14 ¥ 30,379.02 € 273.60 £ 246.24 ¥ 31,412.32 | Core i5 | Raptor Lake S | 14 | 20 | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB , 18 MiB6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB 18,432 KiB 18,874,368 B 0.0176 GiB | 125 W 125,000 mW , 181 W0.168 hp 0.125 kW 181,000 mW 0.243 hp 0.181 kW | 2.6 GHz 2,600 MHz , 3.5 GHz2,600,000 kHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | 5.1 GHz 5,100 MHz 5,100,000 kHz | |||
| i7-13700K | 20 October 2022 | $ 409.00 € 368.10 , $ 419.00£ 331.29 ¥ 42,261.97 € 377.10 £ 339.39 ¥ 43,295.27 | Core i7 | Raptor Lake S | 16 | 24 | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB , 24 MiB6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB 24,576 KiB 25,165,824 B 0.0234 GiB | 125 W 125,000 mW , 253 W0.168 hp 0.125 kW 253,000 mW 0.339 hp 0.253 kW | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz , 3.4 GHz2,500,000 kHz 3,400 MHz 3,400,000 kHz | 5.4 GHz 5,400 MHz 5,400,000 kHz | UHD Graphics 770 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,600 MHz 1.6 GHz 1,600,000 KHz |
| i7-13700KF | 20 October 2022 | $ 384.00 € 345.60 , $ 394.00£ 311.04 ¥ 39,678.72 € 354.60 £ 319.14 ¥ 40,712.02 | Core i7 | Raptor Lake S | 16 | 24 | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB , 24 MiB6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB 24,576 KiB 25,165,824 B 0.0234 GiB | 125 W 125,000 mW , 253 W0.168 hp 0.125 kW 253,000 mW 0.339 hp 0.253 kW | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz , 3.4 GHz2,500,000 kHz 3,400 MHz 3,400,000 kHz | 5.4 GHz 5,400 MHz 5,400,000 kHz | |||
| i9-13900K | 20 October 2022 | $ 589.00 € 530.10 , $ 599.00£ 477.09 ¥ 60,861.37 € 539.10 £ 485.19 ¥ 61,894.67 | Core i9 | Raptor Lake S | 24 | 32 | 12 MiB 12,288 KiB , 24 MiB12,582,912 B 0.0117 GiB 24,576 KiB 25,165,824 B 0.0234 GiB | 125 W 125,000 mW , 253 W0.168 hp 0.125 kW 253,000 mW 0.339 hp 0.253 kW | 2.2 GHz 2,200 MHz , 3 GHz2,200,000 kHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 5.8 GHz 5,800 MHz 5,800,000 kHz | UHD Graphics 770 | 300 MHz 0.3 GHz 300,000 KHz | 1,650 MHz 1.65 GHz 1,650,000 KHz |
| i9-13900KF | 20 October 2022 | $ 564.00 € 507.60 , $ 574.00£ 456.84 ¥ 58,278.12 € 516.60 £ 464.94 ¥ 59,311.42 | Core i9 | Raptor Lake S | 24 | 32 | 12 MiB 12,288 KiB , 24 MiB12,582,912 B 0.0117 GiB 24,576 KiB 25,165,824 B 0.0234 GiB | 125 W 125,000 mW , 253 W0.168 hp 0.125 kW 253,000 mW 0.339 hp 0.253 kW | 2.2 GHz 2,200 MHz , 3 GHz2,200,000 kHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 5.8 GHz 5,800 MHz 5,800,000 kHz | |||
| Count: 6 | |||||||||||||
Bibliography[edit]
- Intel Innovation 2022.
- Intel. personal communication. 2022.
| codename | Raptor Lake + |
| core count | 24 +, 16 + and 8 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | September 27, 2022 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/raptor lake + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Raptor Lake + |