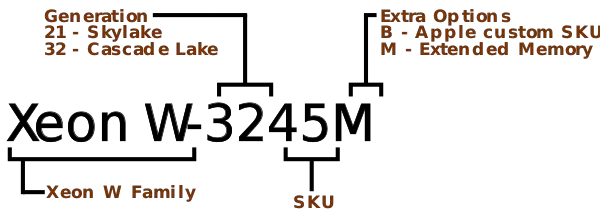| (33 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| isa = x86-64 | | isa = x86-64 | ||
| microarch = Skylake | | microarch = Skylake | ||
| + | | microarch 2 = Cascade Lake | ||
| word = 64 bit | | word = 64 bit | ||
| proc = 14 nm | | proc = 14 nm | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
| clock min = 2.3 GHz | | clock min = 2.3 GHz | ||
| clock max = 4.0 GHz | | clock max = 4.0 GHz | ||
| − | | package = FCLGA-2066 | + | | package = FCLGA-2066 or FCLGA3647 |
| − | | socket = Socket R4 | + | | socket = Socket R4 or Socket P |
| succession = Yes | | succession = Yes | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
| successor link = | | successor link = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Xeon W''' is a family of enterprise {{arch|64}} multi-core [[x86]] | + | '''Xeon W''' is a family of enterprise-class {{arch|64}} multi-core [[x86]] performance workstation microprocessors. |
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| + | [[File:intel xeon w intro.jpg|right|thumb]] | ||
The Xeon W family targets business and enterprise-class performance workstations, situated below the scalable Xeon family and above the {{intel|Xeon E3}}. Compared to the {{intel|Xeon E3}}, Xeon W come with more cores, more [[PCIe]] lanes, [[ECC]] memory, generally almost all available technologies offered by the chip, volume management and various RAS features. | The Xeon W family targets business and enterprise-class performance workstations, situated below the scalable Xeon family and above the {{intel|Xeon E3}}. Compared to the {{intel|Xeon E3}}, Xeon W come with more cores, more [[PCIe]] lanes, [[ECC]] memory, generally almost all available technologies offered by the chip, volume management and various RAS features. | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| − | + | Originally introduced in August [[2017]], the Xeon W family is [[Intel]]'s family of workstation-class processors. Prior to their introduction, this segment was served by {{intel|Xeon E5}} family 1600-series. Prior to {{intel|Skylake (server)|Skylake|l=arch}}, the server segment and high-HEDT as well as workstations shared the same socket. With Skylake, the server segment diverged with the workstations and [[HEDT]] parts having their own [[socket]]. The Xeon W family and the HEDT {{intel|Core i7}}/{{intel|Core i9}} parts share the same socket. | |
| + | |||
| + | The Xeon W family is split into two series - 2000 and 3000 - where the 3000 is positioned above the 2000-series lineup in the product stack. The major difference between the two is that the 3000-series uses the same platform and socket as the mainstream {{intel|Xeon Scalable}} lineup while the 2000-series processors use the enthusiasts platform. Because of that, the 3000 series can provide some additional features such as higher core-count and I/O compared to the 2000-series. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Naming scheme == | ||
| + | Xeon W SKUs follow the following naming scheme. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:xeon w naming scheme.svg|600px]] | ||
== Members == | == Members == | ||
| − | === Skylake === | + | === W-2000 === |
| + | The W-2000 series is the mainstream workstation series. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== W-2100-Series (Skylake) ==== | ||
| + | {{main|intel/microarchitectures/skylake (server)|l1=Skylake (server) Microarchitecture}} | ||
| + | Skylake-based Xeon W processors come with all the features enabled and only [[core count]] and {{intel|frequency behavior|frequency}} being the differentiating feature, with the exception of the two low-end models. For the most part, all models come with {{x86|AVX-512}} along with two full execution units, similar to the high-end {{intel|Skylake SP|l=core}} models. All models have 48 [[PCIe]] lanes and have all the following features in common: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Bus:''' DMI 3.0 | ||
| + | * '''Mem:''' 512 GiB of quad-channel DDR4-2666 ECC Memory | ||
| + | * '''I/O:''' 48 [[PCIe]] 3.0 Lanes | ||
| + | * '''TDP:''' 120 W / 140 W | ||
| + | * '''ISA:''' Everything up to AVX-512 (SMM, FPU, NX, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, AVX, FMA3, AVX2, {{x86|AVX-512}}-{{x86|AVX512F|F}}/{{x86|AVX512CD|CD}}/{{x86|AVX512BW|BW}}/{{x86|AVX512DQ|DQ}}/{{x86|AVX512VL|VL}} with 2 FMA units) | ||
| + | * '''Features:''' {{intel|Speed Shift}}, {{intel|vPro}}, {{intel|VT-x}}/{{intel|EPT}}, {{intel|VT-d}}, {{intel|TBT 2.0}}, {{intel|TSX}}, {{intel|TXT}}, {{intel|SpeedStep}}, {{intel|Identity Protection}}, {{intel|Secure Key}}, {{intel|MPX}}, {{intel|OS Guard}}, and {{intel|Volume Management Device}} (VMD). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that ''B'' models appear to be a special variant for [[Apple]]'s iMac Pros. | ||
| + | |||
<!-- NOTE: | <!-- NOTE: | ||
This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 67: | ||
--> | --> | ||
{{comp table start}} | {{comp table start}} | ||
| − | <table class="comptable sortable tc4 tc5"> | + | <table class="comptable sortable tc4 tc5 tc11"> |
| − | {{comp table header|main| | + | {{comp table header|main|11:List of Skylake W-based Processors}} |
| − | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Price|Cores|Threads|TDP|L2|L3|%Frequency|%Turbo}} | + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Price|Cores|Threads|TDP|L2|L3|%Frequency|%Turbo|Mem Type|%Max Mem}} |
{{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Skylake W]] | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Skylake W]] | ||
|?full page name | |?full page name | ||
| Line 58: | Line 82: | ||
|?base frequency#GHz | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
|?turbo frequency (1 core)#GHz | |?turbo frequency (1 core)#GHz | ||
| + | |?supported memory type | ||
| + | |?max memory#GiB | ||
|format=template | |format=template | ||
|template=proc table 3 | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| − | |userparam= | + | |userparam=13 |
| + | |sort=model number | ||
|mainlabel=- | |mainlabel=- | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Skylake W]]}} | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Skylake W]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== W-2200-Series (Cascade Lake) ==== | ||
| + | === W-3000 === | ||
| + | Xeon W 3000 series was derived from the SP line of server processors, because those had dies with more than 18 cores. As such this line of processors uses Socket 3647 like the Xeon SP series. Since they are limited to single socket they possess no UPI-Links or Intel Omni-Path. | ||
| + | ==== W-3100-Series (Skylake) ==== | ||
| + | {{main|intel/microarchitectures/skylake|l1=Skylake Microarchitecture}} | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc4 tc5 tc11"> | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|12:List of Skylake W-based Processors}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Price|Cores|Threads|TDP|L2|L3|%Frequency|%{{intel|turbo boost|Turbo}}|%{{intel|turbo boost max|Turbo Max}}|Mem Type|%Max Mem}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Skylake SP]] [[family::Xeon W]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?release price | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?thread count | ||
| + | |?tdp | ||
| + | |?l2$ size | ||
| + | |?l3$ size | ||
| + | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?turbo frequency (1 core)#GHz | ||
| + | |?intel turbo boost max technology 3 0 frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?supported memory type | ||
| + | |?max memory#TiB | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=14 | ||
| + | |sort=model number | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Skylake SP]] [[family::Xeon W]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
| + | ==== W-3200-Series (Cascade Lake) ==== | ||
| + | {{main|intel/microarchitectures/cascade lake|l1=Cascade Lake Microarchitecture}} | ||
| + | In early 2019 Intel launched their W-3200 series processors based on the {{intel|Cascade Lake|l=arch}} microarchitecture. Those processors are fabricated on an enhanced [[14 nm process]] which allows for higher clock speeds and introduced a {{intel|Cascade Lake#Key changes from Skylake|l=arch|number of}} hardware changes against the various [[speculative execution]] [[side channel analysis|vulnerabilities]]. Those processors also introduced new {{x86|AVX-512 VNNI|new instructions}} for the [[acceleration]] of machine learning (inference), {{intel|Turbo Boost Max}}, and increased the PCIe lanes to 64. All processors also have the following features in common: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Proc:''' [[14 nm process]] | ||
| + | * '''Bus:''' DMI 3.0 | ||
| + | * '''Mem:''' 1 TiB of hexa-channel DDR4-2933 ECC Memory | ||
| + | ** "''M''" models have 2 TiB extended memory support | ||
| + | * '''I/O:''' 64 [[PCIe]] 3.0 Lanes | ||
| + | * '''TDP:''' 160 W, 180 W, 205 W | ||
| + | * '''ISA:''' Everything up to AVX-512 (SMM, FPU, NX, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, AVX, FMA3, AVX2, {{x86|AVX-512}}-{{x86|AVX512F|F}}/{{x86|AVX512CD|CD}}/{{x86|AVX512BW|BW}}/{{x86|AVX512DQ|DQ}}/{{x86|AVX512VL|VL}}/{{x86|AVX512VNNI|VNNI}} with 2 FMA units) | ||
| + | * '''Features:''' {{intel|Speed Shift}}, {{intel|vPro}}, {{intel|VT-x}}/{{intel|EPT}}, {{intel|VT-d}}, {{intel|TBT 2.0}}, {{intel|TSX}}, {{intel|TXT}}, {{intel|SpeedStep}}, {{intel|Identity Protection}}, {{intel|Secure Key}}, {{intel|MPX}}, {{intel|OS Guard}}, and {{intel|Volume Management Device}} (VMD). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- NOTE: | ||
| + | This table is generated automatically from the data in the actual articles. | ||
| + | If a microprocessor is missing from the list, an appropriate article for it needs to be | ||
| + | created and tagged accordingly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Missing a chip? please dump its name here: https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/WikiChip:wanted_chips | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc4 tc5 tc11"> | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|12:List of Cascade Lake W-based Processors}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Price|Cores|Threads|TDP|L2|L3|%Frequency|%{{intel|turbo boost|Turbo}}|%{{intel|turbo boost max|Turbo Max}}|Mem Type|%Max Mem}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Cascade Lake SP]] [[family::Xeon W]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?release price | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?thread count | ||
| + | |?tdp | ||
| + | |?l2$ size | ||
| + | |?l3$ size | ||
| + | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?turbo frequency (1 core)#GHz | ||
| + | |?intel turbo boost max technology 3 0 frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?supported memory type | ||
| + | |?max memory#TiB | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=14 | ||
| + | |sort=model number | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Cascade Lake SP]] [[family::Xeon W]]}} | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | {{comp table end}} | ||
| + | ==== W-3300-Series (Ice Lake) ==== | ||
| + | {{main|intel/microarchitectures/ice lake|l1=Ice Lake Microarchitecture}} | ||
| + | {{comp table start}} | ||
| + | <table class="comptable sortable tc4 tc5 tc11"> | ||
| + | {{comp table header|main|12:List of Ice Lake W-based Processors}} | ||
| + | {{comp table header|cols|Launched|Price|Cores|Threads|TDP|L2|L3|%Frequency|%{{intel|turbo boost|Turbo}}|%{{intel|turbo boost max|Turbo Max}}|Mem Type|%Max Mem}} | ||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Ice Lake SP]] [[family::Xeon W]] | ||
| + | |?full page name | ||
| + | |?model number | ||
| + | |?first launched | ||
| + | |?release price | ||
| + | |?core count | ||
| + | |?thread count | ||
| + | |?tdp | ||
| + | |?l2$ size | ||
| + | |?l3$ size | ||
| + | |?base frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?turbo frequency (1 core)#GHz | ||
| + | |?intel turbo boost max technology 3 0 frequency#GHz | ||
| + | |?supported memory type | ||
| + | |?max memory#TiB | ||
| + | |format=template | ||
| + | |template=proc table 3 | ||
| + | |userparam=14 | ||
| + | |sort=model number | ||
| + | |mainlabel=- | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{comp table count|ask=[[Category:microprocessor models by intel]] [[core name::Ice Lake SP]] [[family::Xeon W]]}} | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
{{comp table end}} | {{comp table end}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:17, 11 September 2021
| Xeon W | |
| Developer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Type | microprocessors |
| Introduction | August 29, 2017 (announced) August 29, 2017 (launch) |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| µarch | Skylake, Cascade Lake |
| Word size | 64 bit 8 octets
16 nibbles |
| Process | 14 nm 0.014 μm
1.4e-5 mm |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Clock | 2.3 GHz-4.0 GHz |
| Package | FCLGA-2066 or FCLGA3647 |
| Socket | Socket R4 or Socket P |
| Succession | |
| ← | |
| Xeon E5 | |
Xeon W is a family of enterprise-class 64-bit multi-core x86 performance workstation microprocessors.
Contents
Overview[edit]
The Xeon W family targets business and enterprise-class performance workstations, situated below the scalable Xeon family and above the Xeon E3. Compared to the Xeon E3, Xeon W come with more cores, more PCIe lanes, ECC memory, generally almost all available technologies offered by the chip, volume management and various RAS features.
Originally introduced in August 2017, the Xeon W family is Intel's family of workstation-class processors. Prior to their introduction, this segment was served by Xeon E5 family 1600-series. Prior to Skylake, the server segment and high-HEDT as well as workstations shared the same socket. With Skylake, the server segment diverged with the workstations and HEDT parts having their own socket. The Xeon W family and the HEDT Core i7/Core i9 parts share the same socket.
The Xeon W family is split into two series - 2000 and 3000 - where the 3000 is positioned above the 2000-series lineup in the product stack. The major difference between the two is that the 3000-series uses the same platform and socket as the mainstream Xeon Scalable lineup while the 2000-series processors use the enthusiasts platform. Because of that, the 3000 series can provide some additional features such as higher core-count and I/O compared to the 2000-series.
Naming scheme[edit]
Xeon W SKUs follow the following naming scheme.
Members[edit]
W-2000[edit]
The W-2000 series is the mainstream workstation series.
W-2100-Series (Skylake)[edit]
- Main article: Skylake (server) Microarchitecture
Skylake-based Xeon W processors come with all the features enabled and only core count and frequency being the differentiating feature, with the exception of the two low-end models. For the most part, all models come with AVX-512 along with two full execution units, similar to the high-end Skylake SP models. All models have 48 PCIe lanes and have all the following features in common:
- Bus: DMI 3.0
- Mem: 512 GiB of quad-channel DDR4-2666 ECC Memory
- I/O: 48 PCIe 3.0 Lanes
- TDP: 120 W / 140 W
- ISA: Everything up to AVX-512 (SMM, FPU, NX, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, AVX, FMA3, AVX2, AVX-512-F/CD/BW/DQ/VL with 2 FMA units)
- Features: Speed Shift, vPro, VT-x/EPT, VT-d, TBT 2.0, TSX, TXT, SpeedStep, Identity Protection, Secure Key, MPX, OS Guard, and Volume Management Device (VMD).
Note that B models appear to be a special variant for Apple's iMac Pros.
| List of Skylake W-based Processors | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Price | Cores | Threads | TDP | L2 | L3 | Frequency | Turbo | Mem Type | Max Mem |
| W-2102 | 29 August 2017 | $ 202.00 € 181.80 £ 163.62 ¥ 20,872.66 | 4 | 4 | 120 W 120,000 mW 0.161 hp 0.12 kW | 4 MiB 4,096 KiB 4,194,304 B 0.00391 GiB | 8.25 MiB 8,448 KiB 8,650,752 B 0.00806 GiB | 2.9 GHz 2,900 MHz 2,900,000 kHz | DDR4-2400 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB | |
| W-2104 | 29 August 2017 | $ 255.00 € 229.50 £ 206.55 ¥ 26,349.15 | 4 | 4 | 120 W 120,000 mW 0.161 hp 0.12 kW | 4 MiB 4,096 KiB 4,194,304 B 0.00391 GiB | 8.25 MiB 8,448 KiB 8,650,752 B 0.00806 GiB | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | DDR4-2400 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB | |
| W-2123 | 29 August 2017 | $ 294.00 € 264.60 £ 238.14 ¥ 30,379.02 | 4 | 8 | 120 W 120,000 mW 0.161 hp 0.12 kW | 4 MiB 4,096 KiB 4,194,304 B 0.00391 GiB | 8.25 MiB 8,448 KiB 8,650,752 B 0.00806 GiB | 3.6 GHz 3,600 MHz 3,600,000 kHz | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| W-2125 | 29 August 2017 | $ 444.00 € 399.60 £ 359.64 ¥ 45,878.52 | 4 | 8 | 120 W 120,000 mW 0.161 hp 0.12 kW | 4 MiB 4,096 KiB 4,194,304 B 0.00391 GiB | 8.25 MiB 8,448 KiB 8,650,752 B 0.00806 GiB | 4 GHz 4,000 MHz 4,000,000 kHz | 4.5 GHz 4,500 MHz 4,500,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| W-2133 | 29 August 2017 | $ 617.00 € 555.30 £ 499.77 ¥ 63,754.61 | 6 | 12 | 140 W 140,000 mW 0.188 hp 0.14 kW | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB 6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB | 8.25 MiB 8,448 KiB 8,650,752 B 0.00806 GiB | 3.6 GHz 3,600 MHz 3,600,000 kHz | 3.9 GHz 3,900 MHz 3,900,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| W-2135 | 29 August 2017 | $ 835.00 € 751.50 £ 676.35 ¥ 86,280.55 | 6 | 12 | 140 W 140,000 mW 0.188 hp 0.14 kW | 6 MiB 6,144 KiB 6,291,456 B 0.00586 GiB | 8.25 MiB 8,448 KiB 8,650,752 B 0.00806 GiB | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 4.5 GHz 4,500 MHz 4,500,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| W-2140B | 21 December 2017 | 8 | 16 | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 11 MiB 11,264 KiB 11,534,336 B 0.0107 GiB | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | 4.2 GHz 4,200 MHz 4,200,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB | ||
| W-2145 | 29 August 2017 | $ 1,113.00 € 1,001.70 £ 901.53 ¥ 115,006.29 | 8 | 16 | 140 W 140,000 mW 0.188 hp 0.14 kW | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 11 MiB 11,264 KiB 11,534,336 B 0.0107 GiB | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 4.5 GHz 4,500 MHz 4,500,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| W-2150B | 21 December 2017 | 10 | 20 | 10 MiB 10,240 KiB 10,485,760 B 0.00977 GiB | 13.75 MiB 14,080 KiB 14,417,920 B 0.0134 GiB | 3 GHz 3,000 MHz 3,000,000 kHz | 4.5 GHz 4,500 MHz 4,500,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB | ||
| W-2155 | 29 August 2017 | $ 1,440.00 € 1,296.00 £ 1,166.40 ¥ 148,795.20 | 10 | 20 | 140 W 140,000 mW 0.188 hp 0.14 kW | 10 MiB 10,240 KiB 10,485,760 B 0.00977 GiB | 13.75 MiB 14,080 KiB 14,417,920 B 0.0134 GiB | 3.3 GHz 3,300 MHz 3,300,000 kHz | 4.5 GHz 4,500 MHz 4,500,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| W-2170B | 21 December 2017 | 14 | 28 | 14 MiB 14,336 KiB 14,680,064 B 0.0137 GiB | 19.25 MiB 19,712 KiB 20,185,088 B 0.0188 GiB | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz 2,500,000 kHz | 4.3 GHz 4,300 MHz 4,300,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB | ||
| W-2175 | 29 August 2017 | $ 1,947.00 € 1,752.30 £ 1,577.07 ¥ 201,183.51 | 14 | 28 | 140 W 140,000 mW 0.188 hp 0.14 kW | 14 MiB 14,336 KiB 14,680,064 B 0.0137 GiB | 19.25 MiB 19,712 KiB 20,185,088 B 0.0188 GiB | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz 2,500,000 kHz | 4.3 GHz 4,300 MHz 4,300,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| W-2191B | 21 December 2017 | 18 | 36 | 18 MiB 18,432 KiB 18,874,368 B 0.0176 GiB | 24.75 MiB 25,344 KiB 25,952,256 B 0.0242 GiB | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 4.3 GHz 4,300 MHz 4,300,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB | ||
| W-2195 | 29 August 2017 | $ 2,553.00 € 2,297.70 £ 2,067.93 ¥ 263,801.49 | 18 | 36 | 140 W 140,000 mW 0.188 hp 0.14 kW | 18 MiB 18,432 KiB 18,874,368 B 0.0176 GiB | 24.75 MiB 25,344 KiB 25,952,256 B 0.0242 GiB | 2.3 GHz 2,300 MHz 2,300,000 kHz | 4.3 GHz 4,300 MHz 4,300,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 512 GiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 0.5 TiB |
| Count: 14 | |||||||||||
W-2200-Series (Cascade Lake)[edit]
W-3000[edit]
Xeon W 3000 series was derived from the SP line of server processors, because those had dies with more than 18 cores. As such this line of processors uses Socket 3647 like the Xeon SP series. Since they are limited to single socket they possess no UPI-Links or Intel Omni-Path.
W-3100-Series (Skylake)[edit]
- Main article: Skylake Microarchitecture
| List of Skylake W-based Processors | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Price | Cores | Threads | TDP | L2 | L3 | Frequency | Turbo | Turbo Max | Mem Type | Max Mem |
| W-3175X | 30 January 2019 | $ 3,000.00 € 2,700.00 £ 2,430.00 ¥ 309,990.00 | 28 | 56 | 255 W 255,000 mW 0.342 hp 0.255 kW | 28 MiB 28,672 KiB 29,360,128 B 0.0273 GiB | 38.5 MiB 39,424 KiB 40,370,176 B 0.0376 GiB | 3.1 GHz 3,100 MHz 3,100,000 kHz | 4.3 GHz 4,300 MHz 4,300,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 0.5 TiB 524,288 MiB 536,870,912 KiB 549,755,813,888 B 512 GiB | |
| Count: 1 | ||||||||||||
W-3200-Series (Cascade Lake)[edit]
- Main article: Cascade Lake Microarchitecture
In early 2019 Intel launched their W-3200 series processors based on the Cascade Lake microarchitecture. Those processors are fabricated on an enhanced 14 nm process which allows for higher clock speeds and introduced a number of hardware changes against the various speculative execution vulnerabilities. Those processors also introduced new new instructions for the acceleration of machine learning (inference), Turbo Boost Max, and increased the PCIe lanes to 64. All processors also have the following features in common:
- Proc: 14 nm process
- Bus: DMI 3.0
- Mem: 1 TiB of hexa-channel DDR4-2933 ECC Memory
- "M" models have 2 TiB extended memory support
- I/O: 64 PCIe 3.0 Lanes
- TDP: 160 W, 180 W, 205 W
- ISA: Everything up to AVX-512 (SMM, FPU, NX, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, AVX, FMA3, AVX2, AVX-512-F/CD/BW/DQ/VL/VNNI with 2 FMA units)
- Features: Speed Shift, vPro, VT-x/EPT, VT-d, TBT 2.0, TSX, TXT, SpeedStep, Identity Protection, Secure Key, MPX, OS Guard, and Volume Management Device (VMD).
| List of Cascade Lake W-based Processors | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Launched | Price | Cores | Threads | TDP | L2 | L3 | Frequency | Turbo | Turbo Max | Mem Type | Max Mem |
| W-3223 | 3 June 2019 | $ 749.00 € 674.10 £ 606.69 ¥ 77,394.17 | 8 | 16 | 160 W 160,000 mW 0.215 hp 0.16 kW | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 16.5 MiB 16,896 KiB 17,301,504 B 0.0161 GiB | 3.5 GHz 3,500 MHz 3,500,000 kHz | 4 GHz 4,000 MHz 4,000,000 kHz | 4.2 GHz 4,200 MHz 4,200,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 1 TiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1,024 GiB |
| W-3225 | 3 June 2019 | $ 1,199.00 € 1,079.10 £ 971.19 ¥ 123,892.67 | 8 | 16 | 160 W 160,000 mW 0.215 hp 0.16 kW | 8 MiB 8,192 KiB 8,388,608 B 0.00781 GiB | 16.5 MiB 16,896 KiB 17,301,504 B 0.0161 GiB | 3.7 GHz 3,700 MHz 3,700,000 kHz | 4.3 GHz 4,300 MHz 4,300,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | DDR4-2666 | 1 TiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1,024 GiB |
| W-3235 | 3 June 2019 | $ 1,398.00 € 1,258.20 £ 1,132.38 ¥ 144,455.34 | 12 | 24 | 180 W 180,000 mW 0.241 hp 0.18 kW | 12 MiB 12,288 KiB 12,582,912 B 0.0117 GiB | 19.25 MiB 19,712 KiB 20,185,088 B 0.0188 GiB | 3.3 GHz 3,300 MHz 3,300,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | 4.5 GHz 4,500 MHz 4,500,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 1 TiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1,024 GiB |
| W-3245 | 3 June 2019 | $ 1,999.00 € 1,799.10 £ 1,619.19 ¥ 206,556.67 | 16 | 32 | 205 W 205,000 mW 0.275 hp 0.205 kW | 16 MiB 16,384 KiB 16,777,216 B 0.0156 GiB | 22 MiB 22,528 KiB 23,068,672 B 0.0215 GiB | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | 4.6 GHz 4,600 MHz 4,600,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 1 TiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1,024 GiB |
| W-3245M | 3 June 2019 | $ 5,002.00 € 4,501.80 £ 4,051.62 ¥ 516,856.66 | 16 | 32 | 205 W 205,000 mW 0.275 hp 0.205 kW | 16 MiB 16,384 KiB 16,777,216 B 0.0156 GiB | 22 MiB 22,528 KiB 23,068,672 B 0.0215 GiB | 3.2 GHz 3,200 MHz 3,200,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | 4.6 GHz 4,600 MHz 4,600,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 2 TiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2,048 GiB |
| W-3265 | 3 June 2019 | $ 3,349.00 € 3,014.10 £ 2,712.69 ¥ 346,052.17 | 24 | 48 | 205 W 205,000 mW 0.275 hp 0.205 kW | 24 MiB 24,576 KiB 25,165,824 B 0.0234 GiB | 33 MiB 33,792 KiB 34,603,008 B 0.0322 GiB | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | 4.6 GHz 4,600 MHz 4,600,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 1 TiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1,024 GiB |
| W-3265M | 3 June 2019 | $ 6,353.00 € 5,717.70 £ 5,145.93 ¥ 656,455.49 | 24 | 48 | 205 W 205,000 mW 0.275 hp 0.205 kW | 24 MiB 24,576 KiB 25,165,824 B 0.0234 GiB | 33 MiB 33,792 KiB 34,603,008 B 0.0322 GiB | 2.7 GHz 2,700 MHz 2,700,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | 4.6 GHz 4,600 MHz 4,600,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 2 TiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2,048 GiB |
| W-3275 | 3 June 2019 | $ 4,449.00 € 4,004.10 £ 3,603.69 ¥ 459,715.17 | 28 | 56 | 205 W 205,000 mW 0.275 hp 0.205 kW | 28 MiB 28,672 KiB 29,360,128 B 0.0273 GiB | 38.5 MiB 39,424 KiB 40,370,176 B 0.0376 GiB | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz 2,500,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | 4.6 GHz 4,600 MHz 4,600,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 1 TiB 1,048,576 MiB 1,073,741,824 KiB 1,099,511,627,776 B 1,024 GiB |
| W-3275M | 3 June 2019 | $ 7,453.00 € 6,707.70 £ 6,036.93 ¥ 770,118.49 | 28 | 56 | 205 W 205,000 mW 0.275 hp 0.205 kW | 28 MiB 28,672 KiB 29,360,128 B 0.0273 GiB | 38.5 MiB 39,424 KiB 40,370,176 B 0.0376 GiB | 2.5 GHz 2,500 MHz 2,500,000 kHz | 4.4 GHz 4,400 MHz 4,400,000 kHz | 4.6 GHz 4,600 MHz 4,600,000 kHz | DDR4-2933 | 2 TiB 2,097,152 MiB 2,147,483,648 KiB 2,199,023,255,552 B 2,048 GiB |
| Count: 9 | ||||||||||||
W-3300-Series (Ice Lake)[edit]
- Main article: Ice Lake Microarchitecture
See also[edit]
| designer | Intel + |
| first announced | August 29, 2017 + |
| first launched | August 29, 2017 + |
| full page name | intel/xeon w + |
| instance of | microprocessor family + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| main designer | Intel + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture | Skylake + and Cascade Lake + |
| name | Xeon W + |
| package | FCLGA-2066 or FCLGA3647 + |
| process | 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) + |
| socket | Socket R4 or Socket P + |
| technology | CMOS + |
| word size | 64 bit (8 octets, 16 nibbles) + |