(M55) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|type 2=Pipelined | |type 2=Pipelined | ||
|oooe=No | |oooe=No | ||
| − | |speculative= | + | |speculative=No |
|renaming=No | |renaming=No | ||
|stages=4 | |stages=4 | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Cortex-M55''' is an ultra-low-power [[ARM]] [[microarchitecture]] designed by [[ARM Holdings]] for microcontrollers and embedded subsystems. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable [[IP core]] and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-M55, which implemented the {{arm|ARMv8.1-M}} ISA, is an ultra-low-power core which is often found in microcontrllers, low-power chips, and in the embedded subsystems of more powerful chips. | '''Cortex-M55''' is an ultra-low-power [[ARM]] [[microarchitecture]] designed by [[ARM Holdings]] for microcontrollers and embedded subsystems. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable [[IP core]] and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-M55, which implemented the {{arm|ARMv8.1-M}} ISA, is an ultra-low-power core which is often found in microcontrllers, low-power chips, and in the embedded subsystems of more powerful chips. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == History == | ||
| + | The Cortex-M55 was officially launched on February 10, 2020. Support for {{arm|custom instructions}} will be added in 2021. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Process Technology == | ||
| + | Though the Cortex-M55 is designed to be fabricated on various different [[process nodes]] ranging from very mature nodes such as the [[130 nm]] to leading-edge [[7 nm]] and [[5 nm]] nodes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Compiler support == | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Compiler !! Arch-Specific || Arch-Favorable | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Arm Compiler]] || <code>-mcpu=cortex-m55</code> || <code>-mtune=cortex-m55</code> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[GCC]] || <code>-mcpu=cortex-m55</code> || <code>-mtune=cortex-m55</code> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[LLVM]] || <code>-march=cortex-m55</code> || <code>-mtune=cortex-m55</code> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Architecture == | ||
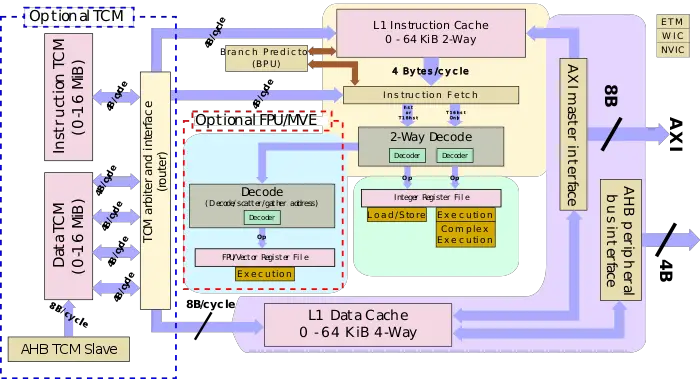
| + | == Block Diagram === | ||
| + | :[[File:cortex-m55 block diagram.svg|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Memory Hierarchy === | ||
| + | The Cortex-M55 has a private L1I, L1D, I-TCM, and D-TCM. All four are configurable in size. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Cache | ||
| + | ** L1I Cache | ||
| + | *** 0 - 64 KiB | ||
| + | *** 2-way set associative | ||
| + | *** Optional ECC support | ||
| + | ** L1D Cache | ||
| + | *** 0 - 64 KiB | ||
| + | *** 4-way set associative | ||
| + | *** Supports both [[write-back]] (WB) and [[write-through]] (WT) | ||
| + | *** Optional ECC support | ||
| + | * [[tightly-coupled memory|TCM]] | ||
| + | ** I-TCM | ||
| + | *** 0 - 16 MiB | ||
| + | *** Supports wait-states | ||
| + | *** Optional ECC support | ||
| + | ** D-TCM | ||
| + | *** 0 - 16 MiB | ||
| + | *** Supports wait-states | ||
| + | *** Optional ECC support | ||
Revision as of 00:42, 16 February 2020
| Edit Values | |
| Cortex-M55 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | February 10, 2020 |
| Process | 55 nm, 45 nm, 32 nm, 28 nm, 22 nm, 16 nm, 10 nm, 7 nm, 5 nm |
| Core Configs | 1, 2, 4 |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Scalar, Pipelined |
| OoOE | No |
| Speculative | No |
| Reg Renaming | No |
| Stages | 4 |
| Decode | 1-2-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv8.1-M |
| Extensions | FPU, Helium |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 0-64 KiB/core 2-way set associative |
| L1D Cache | 0-64 KiB/core 4-way set associative |
Cortex-M55 is an ultra-low-power ARM microarchitecture designed by ARM Holdings for microcontrollers and embedded subsystems. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable IP core and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-M55, which implemented the ARMv8.1-M ISA, is an ultra-low-power core which is often found in microcontrllers, low-power chips, and in the embedded subsystems of more powerful chips.
Contents
History
The Cortex-M55 was officially launched on February 10, 2020. Support for custom instructions will be added in 2021.
Process Technology
Though the Cortex-M55 is designed to be fabricated on various different process nodes ranging from very mature nodes such as the 130 nm to leading-edge 7 nm and 5 nm nodes.
Compiler support
| Compiler | Arch-Specific | Arch-Favorable |
|---|---|---|
| Arm Compiler | -mcpu=cortex-m55 |
-mtune=cortex-m55
|
| GCC | -mcpu=cortex-m55 |
-mtune=cortex-m55
|
| LLVM | -march=cortex-m55 |
-mtune=cortex-m55
|
Architecture
Block Diagram =
Memory Hierarchy
The Cortex-M55 has a private L1I, L1D, I-TCM, and D-TCM. All four are configurable in size.
- Cache
- L1I Cache
- 0 - 64 KiB
- 2-way set associative
- Optional ECC support
- L1D Cache
- 0 - 64 KiB
- 4-way set associative
- Supports both write-back (WB) and write-through (WT)
- Optional ECC support
- L1I Cache
- TCM
- I-TCM
- 0 - 16 MiB
- Supports wait-states
- Optional ECC support
- D-TCM
- 0 - 16 MiB
- Supports wait-states
- Optional ECC support
- I-TCM
| codename | Cortex-M55 + |
| core count | 1 +, 2 + and 4 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | February 10, 2020 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/cortex-m55 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv8.1-M + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Cortex-M55 + |
| pipeline stages | 4 + |
| process | 55 nm (0.055 μm, 5.5e-5 mm) +, 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) +, 32 nm (0.032 μm, 3.2e-5 mm) +, 28 nm (0.028 μm, 2.8e-5 mm) +, 22 nm (0.022 μm, 2.2e-5 mm) +, 16 nm (0.016 μm, 1.6e-5 mm) +, 10 nm (0.01 μm, 1.0e-5 mm) +, 7 nm (0.007 μm, 7.0e-6 mm) + and 5 nm (0.005 μm, 5.0e-6 mm) + |