| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|technology=CMOS | |technology=CMOS | ||
|power=1 mW | |power=1 mW | ||
| − | |v core=3 V | + | |v core min=0.54 V |
| + | |v core max=3 V | ||
|package name 1=eta_compute,bga81 | |package name 1=eta_compute,bga81 | ||
|predecessor=ECM3531 | |predecessor=ECM3531 | ||
|predecessor link=eta_compute/ecm353x/ecm3531 | |predecessor link=eta_compute/ecm353x/ecm3531 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''ECM3532''' is an extreme-low-power microcontroller designed by [[Eta Compute]] and introduced in [[2020]]. Fabricated on [[55ULP|55 nm (55ULP) process]], this chip is designed for the processing of AI at the edge. When launched, in early 2020, the ECM3532 was the lowest-power [[neural processor|AI edge processor]] in the world with typical AI workloads running at well under 1 | + | '''ECM3532''' is an extreme-low-power microcontroller designed by [[Eta Compute]] and introduced in [[2020]]. Fabricated on [[55ULP|55 nm (55ULP) process]], this chip is designed for the processing of AI at the edge for long-term battery-powered and energy-harvesting IoT applications. When launched, in early 2020, the ECM3532 was the lowest-power commercial [[neural processor|AI edge processor]] in the world with typical AI workloads running at well under 1 mA for total power consumption of less than a single [[milliwatt]]. |
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
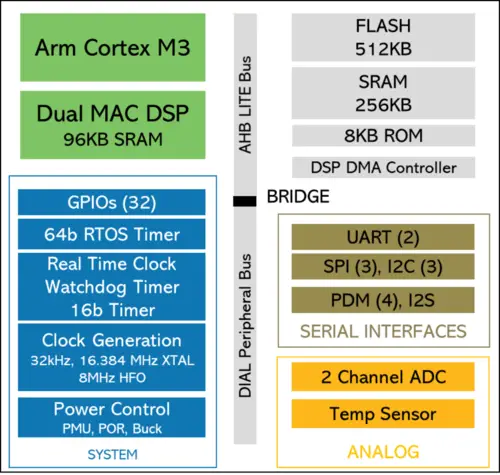
| − | {{ | + | The ECM3532 is a multi-core [[neural processor]] which incorporates an [[Arm]] {{armh|Cortex-M3|l=arch}} along with a dual-MAC NXP CoolFlux DSP16. Additionally, the chip incorporates 512 KiB of Flash and a total of 352 KiB of [[SRAM]]. The chip started sampling in early January 2020 and entered production in the second quarter of 2020. The ECM3532 is designed for extreme-low-power applications which can last years on battery or solar. The chip is designed to have 7 uA stall current, 500 nA sleep current with RTC on and 750 nA for sleep current with RTC on and 32 KiB of memory. Under typical operations, the chip can operate at under 5 uA/MHz (or up to 13 uA/MHz for intense applications such as Coremark). At a peak frequency of 100 MHz, this translate to around 400 uA and at around 3V, this yields around 1.2 mW of power. This makes this chip the, when introduced in early 2020, the world's lowest-power [[neural processor|AI chip]]. |
| + | |||
| + | Under normal operation, the chip executes on the {{armh|Cortex-M3|M3|l=arch}} which then offloads the more intensive repreated neural-network computations to the DSP. The CoolFlux DSP16 features a dual MAC architecture, allowing for up to two 16-bit MACs per cycle (4 OPS/cycle) or up to four 8-bit MACs per cycle (8 OPS/cycle). The DSP16 has its own 96 KiB of [[SRAM]] in addition to the 256 KiB shared by the entire SoC. With 8-bit weights, 64 KiB of memory is enough for 65,536 weights. Operating at up to 100 MHz, this chip had a peak raw ML performance of up to 800 [[MOPS]]. | ||
== Block diagram == | == Block diagram == | ||
| − | :[[File:ecm3532 block.png| | + | :[[File:ecm3532 block.png|500px]] |
Revision as of 02:12, 12 February 2020
| Edit Values | |
| ECM3532 | |
| General Info | |
| Designer | Eta Compute |
| Model Number | ECM3532 |
| Market | Embedded |
| Introduction | February 12, 2020 (announced) April, 2020 (launched) |
| General Specs | |
| Family | ECM353x |
| Frequency | 100 MHz |
| Microarchitecture | |
| ISA | ARMv7-M (ARM) |
| Microarchitecture | Cortex-M3, CoolFlux DSP16 |
| Technology | CMOS |
| Electrical | |
| Power dissipation | 1 mW |
| Vcore | 0.54 V-3 V |
| Packaging | |
| Package | BGA-81 (BGA) |
| Dimension | 5 mm × 5 mm |
| Contacts | 81 |
| Succession | |
ECM3532 is an extreme-low-power microcontroller designed by Eta Compute and introduced in 2020. Fabricated on 55 nm (55ULP) process, this chip is designed for the processing of AI at the edge for long-term battery-powered and energy-harvesting IoT applications. When launched, in early 2020, the ECM3532 was the lowest-power commercial AI edge processor in the world with typical AI workloads running at well under 1 mA for total power consumption of less than a single milliwatt.
Overview
The ECM3532 is a multi-core neural processor which incorporates an Arm Cortex-M3 along with a dual-MAC NXP CoolFlux DSP16. Additionally, the chip incorporates 512 KiB of Flash and a total of 352 KiB of SRAM. The chip started sampling in early January 2020 and entered production in the second quarter of 2020. The ECM3532 is designed for extreme-low-power applications which can last years on battery or solar. The chip is designed to have 7 uA stall current, 500 nA sleep current with RTC on and 750 nA for sleep current with RTC on and 32 KiB of memory. Under typical operations, the chip can operate at under 5 uA/MHz (or up to 13 uA/MHz for intense applications such as Coremark). At a peak frequency of 100 MHz, this translate to around 400 uA and at around 3V, this yields around 1.2 mW of power. This makes this chip the, when introduced in early 2020, the world's lowest-power AI chip.
Under normal operation, the chip executes on the M3 which then offloads the more intensive repreated neural-network computations to the DSP. The CoolFlux DSP16 features a dual MAC architecture, allowing for up to two 16-bit MACs per cycle (4 OPS/cycle) or up to four 8-bit MACs per cycle (8 OPS/cycle). The DSP16 has its own 96 KiB of SRAM in addition to the 256 KiB shared by the entire SoC. With 8-bit weights, 64 KiB of memory is enough for 65,536 weights. Operating at up to 100 MHz, this chip had a peak raw ML performance of up to 800 MOPS.
Block diagram
| base frequency | 100 MHz (0.1 GHz, 100,000 kHz) + |
| core voltage (max) | 3 V (30 dV, 300 cV, 3,000 mV) + |
| core voltage (min) | 0.54 V (5.4 dV, 54 cV, 540 mV) + |
| designer | Eta Compute + |
| family | ECM353x + |
| first announced | February 12, 2020 + |
| first launched | April 2020 + |
| full page name | eta compute/ecm353x/ecm3532 + |
| instance of | microprocessor + |
| isa | ARMv7-M + |
| isa family | ARM + |
| ldate | April 2020 + |
| market segment | Embedded + |
| microarchitecture | Cortex-M3 + and CoolFlux DSP16 + |
| model number | ECM3532 + |
| name | ECM3532 + |
| package | BGA-81 + |
| power dissipation | 0.001 W (1 mW, 1.341e-6 hp, 1.0e-6 kW) + |
| technology | CMOS + |