From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/rock creek"
(rock creek) |
(some initial content, references, documents from Intel Labs) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|designer=Intel | |designer=Intel | ||
|manufacturer=Intel | |manufacturer=Intel | ||
| − | |introduction=2009 | + | |introduction=December 2009 |
|process=45 nm | |process=45 nm | ||
|cores=48 | |cores=48 | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|successor link=intel/microarchitectures/knights ferry | |successor link=intel/microarchitectures/knights ferry | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Rock Creek''' or the ''' Single-Chip Cloud Computer''' ('''SCC''') was the successor to {{\\|Polaris}}, a [[45 nm]] [[many-core]] microarchitecture designed by [[intel]] for high performance computing. | + | '''Rock Creek''' or the ''' Single-Chip Cloud Computer''' ('''SCC''') was the successor to {{\\|Polaris}}, a [[45 nm]] [[many-core]] microarchitecture designed by [[intel]] for high performance computing. The SCC, like {{\\|Polaris}}, was a research project from Intel's [[Tera-scale Computing Research Program]]. |
| + | |||
| + | == Architecture == | ||
| + | {{empty section}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Overview == | ||
| + | {{empty section}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Die == | ||
| + | * [[45 nm process]] | ||
| + | * 1 poly, 9 Metal (Cu) | ||
| + | * 1,300,000,000 transistors | ||
| + | * 26.5 mm x 21.4 mm | ||
| + | ** 567.1 mm² die size | ||
| + | * 1,567 pins LGA packages | ||
| + | ** 970 signal pins | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:rock creek die.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:rock creek die (annotated).png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Tile === | ||
| + | ** 48,000,000 transistors | ||
| + | * 3.6 mm x 5.2 mm | ||
| + | ** 18.7 mm² silicon area | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:rock creek tile (annotated).png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Additional Shots === | ||
| + | Additional die and wafer shots provided by Intel: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery mode=slideshow> | ||
| + | File:rock creek 1.jpg | ||
| + | File:rock creek 2.jpg | ||
| + | File:rock creek 3.jpg | ||
| + | File:rock creek 4.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Bibliography == | ||
| + | * [[:File:SCC Sympossium Feb212010 FINAL-A.pdf|“Single-chip Cloud Computer”. An experimental many-core processor from Intel Labs.]] Jim Held, Intel Fellow & Director. Tera-scale Computing Research. Symposium in Santa Clara. 2/12/10. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Documents === | ||
| + | * [[:File:SCC Sympossium Dec2010 CHN final.pptx]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:MARC-Symposium-Nov-2010-Stefan-Lankes.pdf|First Experiences with the SCC and a Comparison with Established Architectures]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:RockyLakeHW.pdf|Rocky Lake Hardware (defines LEDs)]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:SCC Platform Overview.pdf|The SCC Platform Overview]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:SCCProgrammersGuide.pdf|The SCC Programmer’s Guide Revision 1.0]] | ||
| + | * [[:File:SCC EAS.pdf|SCC External Architecture Specification (EAS) Revision 1.1]] | ||
Revision as of 03:50, 31 March 2019
| Edit Values | |
| Knights Ferry µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | December 2009 |
| Process | 45 nm |
| Core Configs | 48 |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86 |
| Extensions | L1OM |
| Succession | |
Rock Creek or the Single-Chip Cloud Computer (SCC) was the successor to Polaris, a 45 nm many-core microarchitecture designed by intel for high performance computing. The SCC, like Polaris, was a research project from Intel's Tera-scale Computing Research Program.
Architecture
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Overview
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
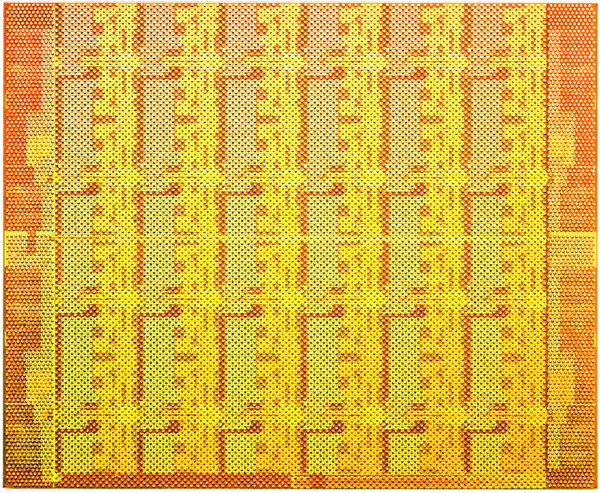
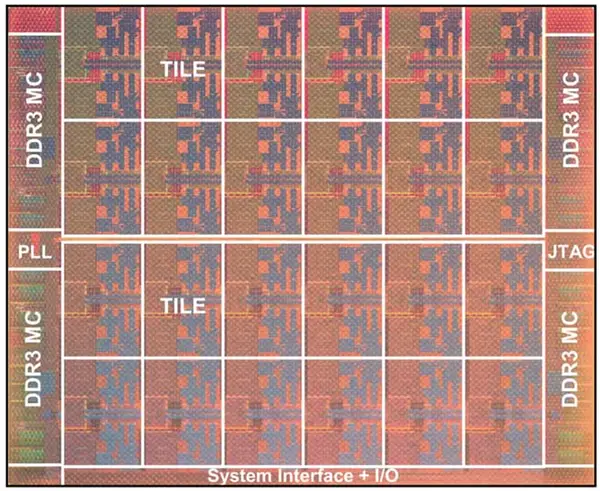
Die
- 45 nm process
- 1 poly, 9 Metal (Cu)
- 1,300,000,000 transistors
- 26.5 mm x 21.4 mm
- 567.1 mm² die size
- 1,567 pins LGA packages
- 970 signal pins
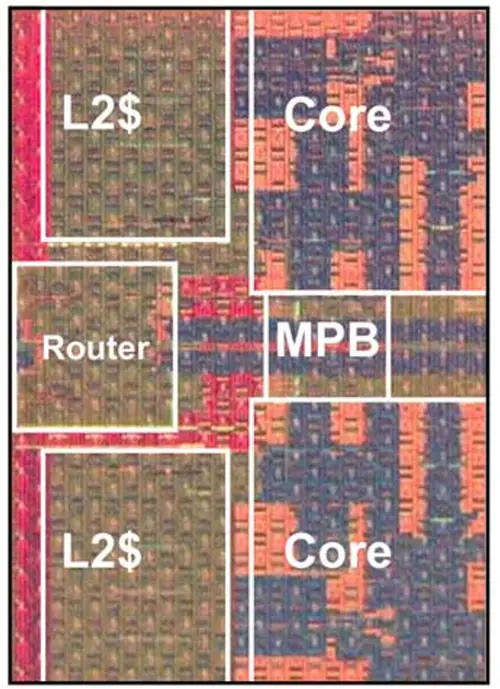
Tile
- 48,000,000 transistors
- 3.6 mm x 5.2 mm
- 18.7 mm² silicon area
Additional Shots
Additional die and wafer shots provided by Intel:
Bibliography
- “Single-chip Cloud Computer”. An experimental many-core processor from Intel Labs. Jim Held, Intel Fellow & Director. Tera-scale Computing Research. Symposium in Santa Clara. 2/12/10.
Documents
Facts about "Rock Creek - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | Knights Ferry + |
| core count | 48 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | December 2009 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/rock creek + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Knights Ferry + |
| process | 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) + |