From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "arm holdings/microarchitectures/cortex-a57"
(→Die) |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
== Die == | == Die == | ||
| − | === Samsung [[Exynos 5433]] === | + | === 20 nm === |
| + | ==== Samsung [[Exynos 5433]] ==== | ||
* Samsung [[20 nm process]] | * Samsung [[20 nm process]] | ||
* 113 mm² die size | * 113 mm² die size | ||
| Line 39: | Line 40: | ||
:[[File:exynos 5433 die.png|600px]] | :[[File:exynos 5433 die.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 16 nm === | ||
| + | ==== Renesas [[R-Car H3]] ==== | ||
| + | * TSMC [[16 nm process]] | ||
| + | * 12.94 mm × 8.61 mm | ||
| + | * 111.36 mm² die size | ||
| + | * Quad-core {{\\|Cortex-A53}} | ||
| + | ** ~3.27 mm² cluster | ||
| + | ** ~0.60 mm² core | ||
| + | ** ~0.7`mm² L2 cache | ||
| + | * Quad-core Cortex-A57 | ||
| + | ** ~10.21 mm² cluster | ||
| + | ** ~1.66 mm² core | ||
| + | ** ~3.28 mm² L2 cache | ||
| + | * {{\\|Cortex-R7}} (dual-core [[lock-step]]) | ||
| + | ** ~1.04 mm² cluster | ||
| + | * GX6650 GPU | ||
| + | ** ~28.12 mm² | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | : [[File:r-car h3 die shot.png|650px]] | ||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
* Pyo, Jungyul, et al. "23.1 20nm high-K metal-gate heterogeneous 64b quad-core CPUs and hexa-core GPU for high-performance and energy-efficient mobile application processor." Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2015 IEEE International. IEEE, 2015 | * Pyo, Jungyul, et al. "23.1 20nm high-K metal-gate heterogeneous 64b quad-core CPUs and hexa-core GPU for high-performance and energy-efficient mobile application processor." Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2015 IEEE International. IEEE, 2015 | ||
Revision as of 14:28, 29 December 2018
| Edit Values | |
| Cortex-A57 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | ARM Holdings |
| Manufacturer | TSMC |
| Introduction | Oct 30, 2012 |
| Succession | |
Cortex-A57 (codename Atlas) is the successor to the Cortex-A15, a low-power high-performance ARM microarchitecture designed by ARM Holdings for the mobile market. This microarchitecture is designed as a synthesizable IP core and is sold to other semiconductor companies to be implemented in their own chips. The Cortex-A57, which implemented the ARMv8 ISA, is the a performant core which is often combined with a number of lower power cores (e.g. Cortex-A53) in a big.LITTLE configuration to achieve better energy/performance.
Contents
Architecture
Key changes from Cortex-A15
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Block Diagram
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Memory Hierarchy
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Die
20 nm
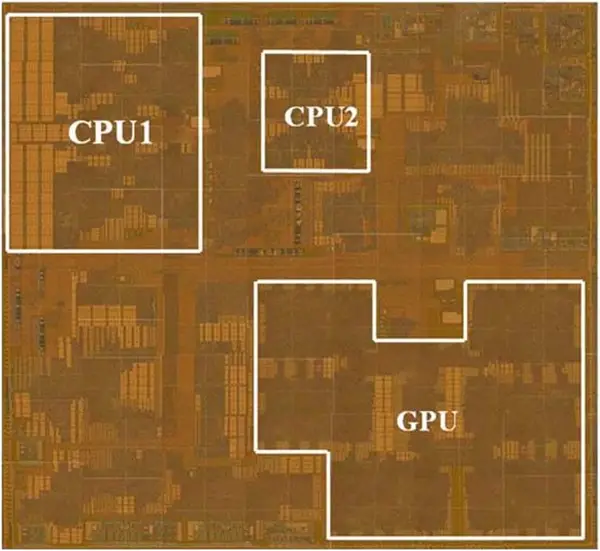
Samsung Exynos 5433
- Samsung 20 nm process
- 113 mm² die size
- Mali-T760 (6 EU)
- Quad-core Cortex-A53 (small cores)
- 32 KiB L1I$ and 32 KiB L1D$ per core, and a shared 256 KiB L2
- 4.4 mm² per cluster
- ~1 mm² per core
- ~0.55 mm² for 256 KiB L2 cache
- Quad-core Cortex-A57 (big cores)
- 48KB L1I$ and 32KB L1D$ per core, and a shared 2 MiB L2
- 15.85 mm² per cluster
- ~3 mm² per core
- ~3.87 mm² for 2 MiB L2 cache
16 nm
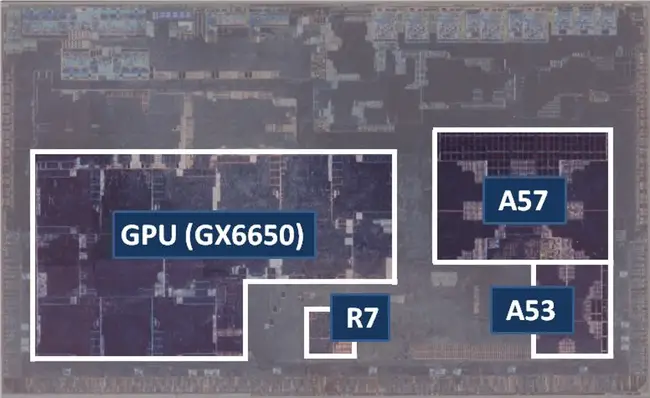
Renesas R-Car H3
- TSMC 16 nm process
- 12.94 mm × 8.61 mm
- 111.36 mm² die size
- Quad-core Cortex-A53
- ~3.27 mm² cluster
- ~0.60 mm² core
- ~0.7`mm² L2 cache
- Quad-core Cortex-A57
- ~10.21 mm² cluster
- ~1.66 mm² core
- ~3.28 mm² L2 cache
- Cortex-R7 (dual-core lock-step)
- ~1.04 mm² cluster
- GX6650 GPU
- ~28.12 mm²
Bibliography
- Pyo, Jungyul, et al. "23.1 20nm high-K metal-gate heterogeneous 64b quad-core CPUs and hexa-core GPU for high-performance and energy-efficient mobile application processor." Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2015 IEEE International. IEEE, 2015
Facts about "Cortex-A57 - Microarchitectures - ARM"
| codename | Cortex-A57 + |
| designer | ARM Holdings + |
| first launched | October 30, 2012 + |
| full page name | arm holdings/microarchitectures/cortex-a57 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| manufacturer | TSMC + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Cortex-A57 + |