From WikiChip
Difference between revisions of "intel/microarchitectures/tremont"
(→Architecture) |
|||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
== Architecture == | == Architecture == | ||
| − | + | Tremont is designed with significant single-thread performance in mind while focusing on low-power small silicon area cores. | |
=== Key changes from {{\\|Goldmont Plus}} === | === Key changes from {{\\|Goldmont Plus}} === | ||
| − | * | + | * Significant [[IPC]] uplift ([[Intel]] self-reported average 32% IPC accross proxy benchmarks such as [[SPEC CPU2006]]/[[SPEC CPU2017]]) |
| − | ** | + | * Front-end |
| + | ** Redesigned front-end | ||
| + | *** New dual symmetric decode cluster | ||
| + | **** Out-of-order decode | ||
| + | **** 6-wide decode | ||
| + | ***** 3-way decode per cluster | ||
| + | ** Smarter [[prefetchers]] | ||
| + | ** Improved [[branch predictor]] | ||
| + | *** Big-core level of performance | ||
| + | * Back-end | ||
| + | ** larger ROB | ||
| + | ** wide issue (10-wide) | ||
| + | * Execution Engine | ||
| + | ** 2x store data ports (up from 1) | ||
| + | |||
====New instructions ==== | ====New instructions ==== | ||
| Line 104: | Line 118: | ||
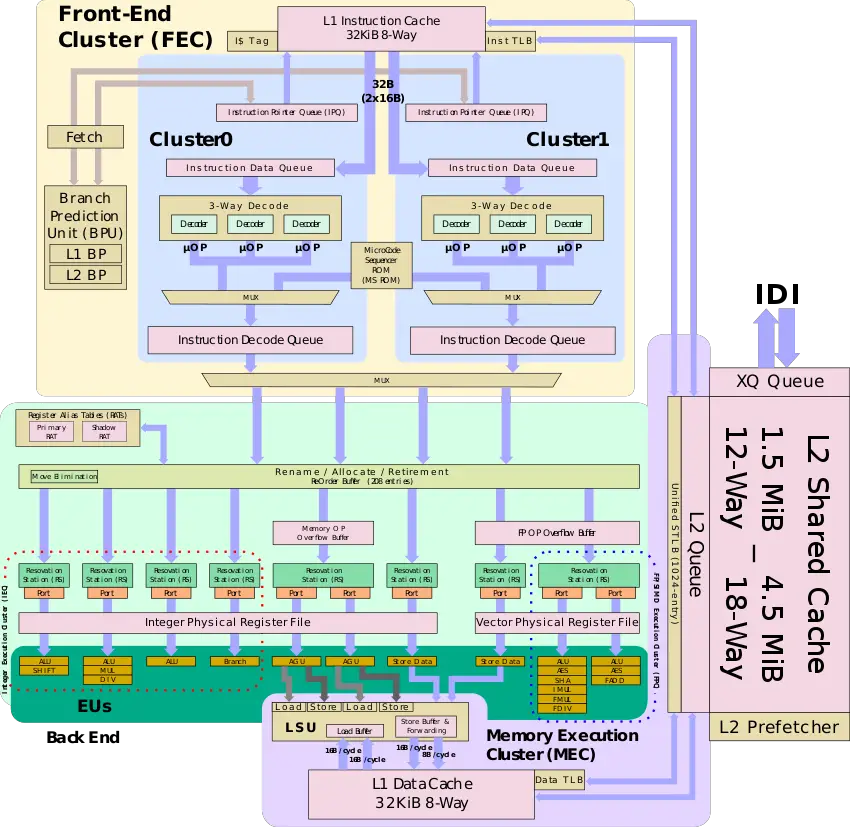
=== Block Diagram === | === Block Diagram === | ||
==== Individual Core ==== | ==== Individual Core ==== | ||
| + | :[[File:tremont block diagram.svg|850px]] | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 24 October 2019
| Edit Values | |
| Tremont µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | 2019 |
| Process | 10 nm |
| Pipeline | |
| Type | Superscalar |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Extensions | MOVBE, MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, POPCNT, AES, PCLMUL, RDRND, XSAVE, XSAVEOPT, FSGSBASE, PTWRITE, RDPID, SGX, UMIP, GFNI-SSE, CLWB, ENCLV, SHA |
| Cores | |
| Core Names | Elkhart Lake, Skyhawk Lake |
| Succession | |
Tremont is Intel's successor to Goldmont Plus, a 10 nm microarchitecture for ultra-low power devices and microservers.
Contents
Codenames
| Platform | Core Name | PCH |
|---|---|---|
| Skyhawk Lake | ||
| Jacobsville | Elkhart Lake | Mule Creek Canyon |
Brands
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Release Dates
Tremont was released in a number of products in late 2019.
Technology
Tremont uses Intel's 10 nm process.
Compiler support
| Compiler | Arch-Specific | Arch-Favorable |
|---|---|---|
| ICC | -march=tremont |
-mtune=tremont
|
| GCC | -march=tremont |
-mtune=tremont
|
| LLVM | -march=tremont |
-mtune=tremont
|
| Visual Studio | /arch:? |
/tune:?
|
CPUID
| Core | Extended Family |
Family | Extended Model |
Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ? | 0 | 0x6 | 0x8 | 0x6 |
| Family 6 Model 134 | ||||
Architecture
Tremont is designed with significant single-thread performance in mind while focusing on low-power small silicon area cores.
Key changes from Goldmont Plus
- Significant IPC uplift (Intel self-reported average 32% IPC accross proxy benchmarks such as SPEC CPU2006/SPEC CPU2017)
- Front-end
- Redesigned front-end
- New dual symmetric decode cluster
- Out-of-order decode
- 6-wide decode
- 3-way decode per cluster
- New dual symmetric decode cluster
- Smarter prefetchers
- Improved branch predictor
- Big-core level of performance
- Redesigned front-end
- Back-end
- larger ROB
- wide issue (10-wide)
- Execution Engine
- 2x store data ports (up from 1)
New instructions
Tremont introduced a number of new instructions:
-
CLWB- Force cache line write-back without flush -
ENCLV- SGX oversubscription instructions -
CLDEMOTE- Cache line demote instruction -
SSE_GFNI- SSE-based Galois Field New Instructions - Direct store instructions: MOVDIRI, MOVDIR64B
- User wait instructions: TPAUSE, UMONITOR, UMWAIT
- Split Lock Detection - detection and cause an exception for split locks
Block Diagram
Individual Core
Facts about "Tremont - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | Tremont + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | 2019 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/tremont + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Tremont + |
| process | 10 nm (0.01 μm, 1.0e-5 mm) + |