From WikiChip
Nehalem - Microarchitectures - Intel
| Edit Values | |
| Nehalem µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel |
| Introduction | August, 2008 |
| Phase-out | March, 2010 |
| Process | 45 nm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-64 |
| Succession | |
Nehalem was the microarchitecture for Intel's 45 nm process for desktops and servers as a successor to Penryn. Nehalem is named after the Nehalem River. Nehalem was replaced by the Westmere microarchitecture in 2010.
Process Technology
| 45 nm Manufacturing Fabs | |
|---|---|
| Fab | Location |
| D1D | Hillsboro, Oregon |
| Fab 32 | Chandler, Arizona |
| Fab 28 | Kiryat Gat, Israel |
Penryn-based microprocessors were manufactured on a 45 nm process. Intel's 45 nm process is the is the first high-volume manufacturing process to introduce High-k + metal gate transistors.
Scaling:
| Core | Nehalem | Δ | 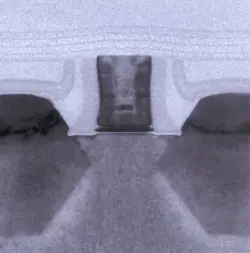
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 nm | 45 nm | |||
| Metal Layers | 8 | 9 | ||
| Gate Pitch | 220 nm | 180 nm | 0.82x | |
| Interconnect Pitch | 210 nm | 160 nm | 0.76x | |
| SRAM bit cell (HD) | 0.570 µm² | 0.346 um² | 0.61x | |
| SRAM bit cell (LP) | 0.680 µm² | 0.382 um² | 0.56x |
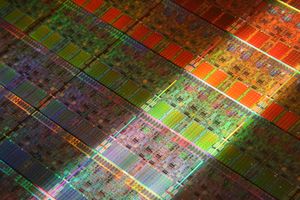
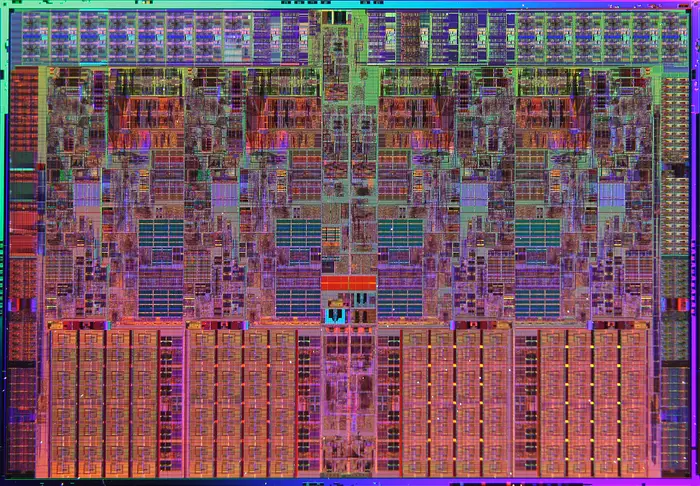
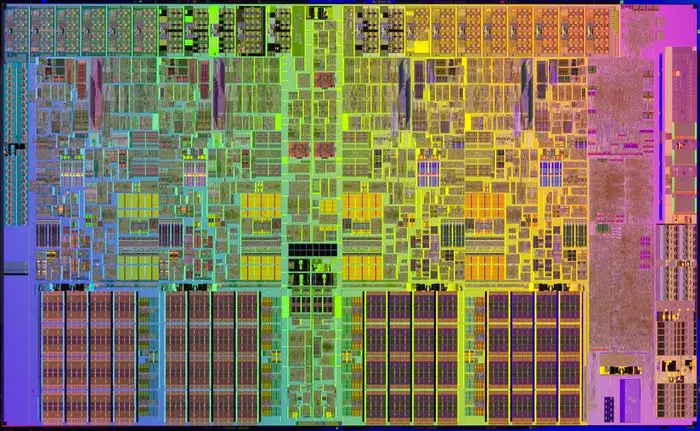
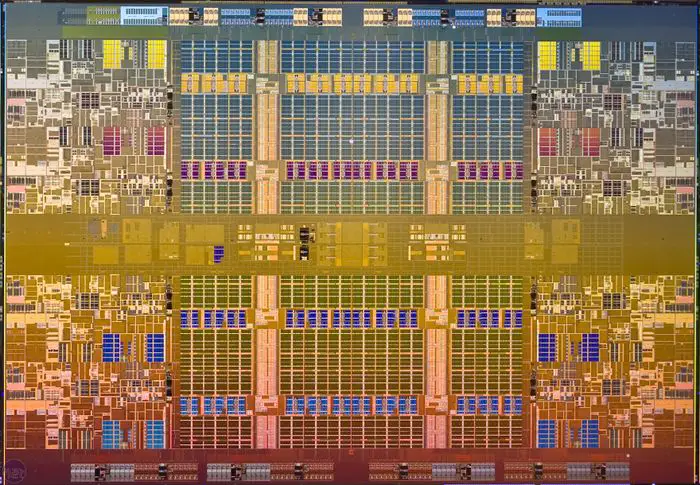
Die Shot
Bloomfield
- 263 mm²
- 713,000,000 transistors
- 45 nm process
- 4 cores
Lynnfield
- 296 mm²
- 774,000,000 transistors
- 45 nm process
- 4 cores
Nehalem-EX
- 648 mm²
- 2.300,000,000 transistors
- 45 nm process
- 8 cores
Facts about "Nehalem - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | Nehalem + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | August 2008 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/nehalem (client) + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-64 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Nehalem + |
| phase-out | March 2010 + |
| process | 45 nm (0.045 μm, 4.5e-5 mm) + |