-
WikiChip
WikiChip
-
Architectures
Popular x86
-
Intel
- Client
- Server
- Big Cores
- Small Cores
-
AMD
Popular ARM
-
ARM
- Server
- Big
- Little
-
Cavium
-
Samsung
-
-
Chips
Popular Families
-
Ampere
-
Apple
-
Cavium
-
HiSilicon
-
MediaTek
-
NXP
-
Qualcomm
-
Renesas
-
Samsung
-
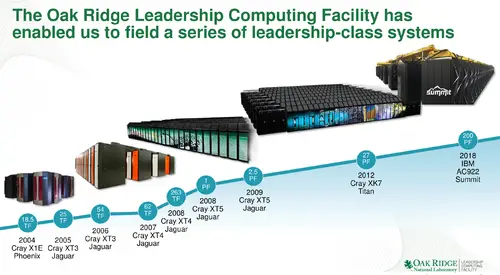
Summit (OLCF-4) is a 200-petaFLOP supercomputer operating by the DoE Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Summit was officially unveiled on June 8, 2018 as the fastest supercomputer in the world, overtaking Sunway TaihuLight.
History
Summit is one of three systems as part of the Collaboration of Oak Ridge, Argonne, and Lawrence Livermore Labs (CORAL) procurement program. Research and planning started in 2012 with initial system delivery arriving in late 2017. The full system arrived in early 2018 and the system was officially unveiled on June 8, 2018. Summit is estimated to have cost around $200 million as part of the CORAL procurement program.
Overview
Summit was designed to deliver 5-10x improvement in performance for real big science workload performance over Titan. Compared to Titan which had 18,688 nodes (AMD Opteron + Nvidia Kepler) with a 9 MW power consumption, Summit slightly increased the power consumption to 13 MW, reduced the number of nodes to only 4,608, but tenfold the peak theoretical performance from 27 petaFLOPS to around 225 PF.