| Edit Values | |
| Mongoose 1 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Samsung |
| Manufacturer | Samsung |
| Process | 14 nm |
| Pipeline | |
| OoOE | Yes |
| Speculative | Yes |
| Reg Renaming | Yes |
| Decode | 4-way |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | ARMv8 |
| Cache | |
| L1I Cache | 64 KiB/core 4-way set associative |
| L1D Cache | 32 KiB/core 8-way set associative |
| L2 Cache | 2 MiB/cluster 16-way set associative |
| Succession | |
Mongoose 1 (M1) is an ARM microarchitecture designed by Samsung for their consumer electronics. This was Samsung's first in-house developed high-performance low-power ARM microarchitecture.
History
The Mongoose 1 (M1) microarchitecture was Samsung's first in-house design which was done entirely from scratch. A design team was assembled and in roughly 3 years, they've gone from requirements to tape-out. The design was done at Samsung's Austin R&D Center (SARC) which was founded in 2010 for the sole purpose of developing high-performance, low-power, complex CPU and System IPs. A large portion of the design team consists of many ex-AMD Austin engineers as well as ex-IBMers.
Process Technology
M1 was fabricated on Samsung's 14 nm process.
Architecture
The M1 is Samsung's first in-house design from scratch.
- ARM v8.0
- 2.6 GHz clock frequency
- 2.3 GHz for multi-core workloads
- Sub 3-watt/core
- 14 nm process (FinFET)
- Core
- Advanced branch predictor
- 4-way instruction decode
- Most instructions map to a single µOP, with a few exceptions
- 4-way µOP dispatch and retire
- Out-of-order execution
- Out-of-order load and stores
- Multistride/multistream prefetcher
- Low-latency and low-power caches
Block Diagram
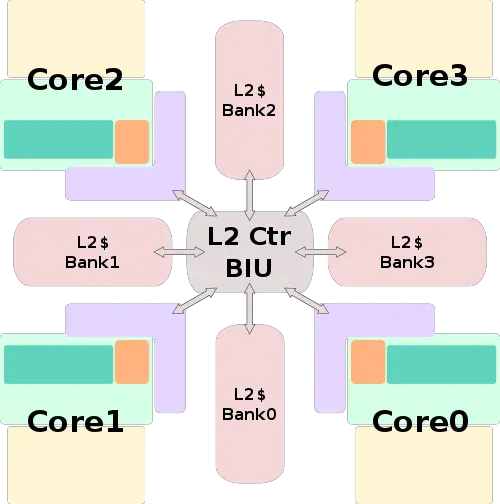
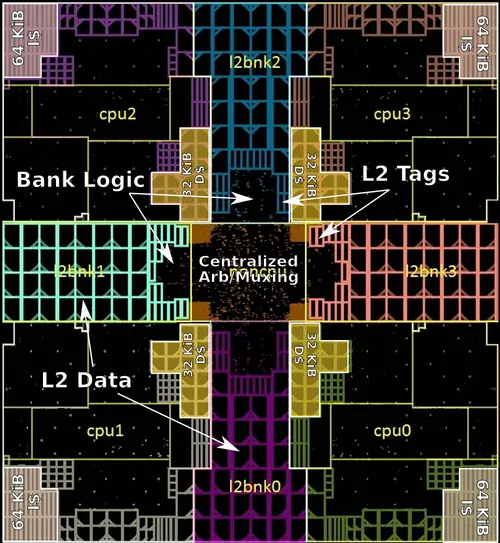
Core Cluster Overview
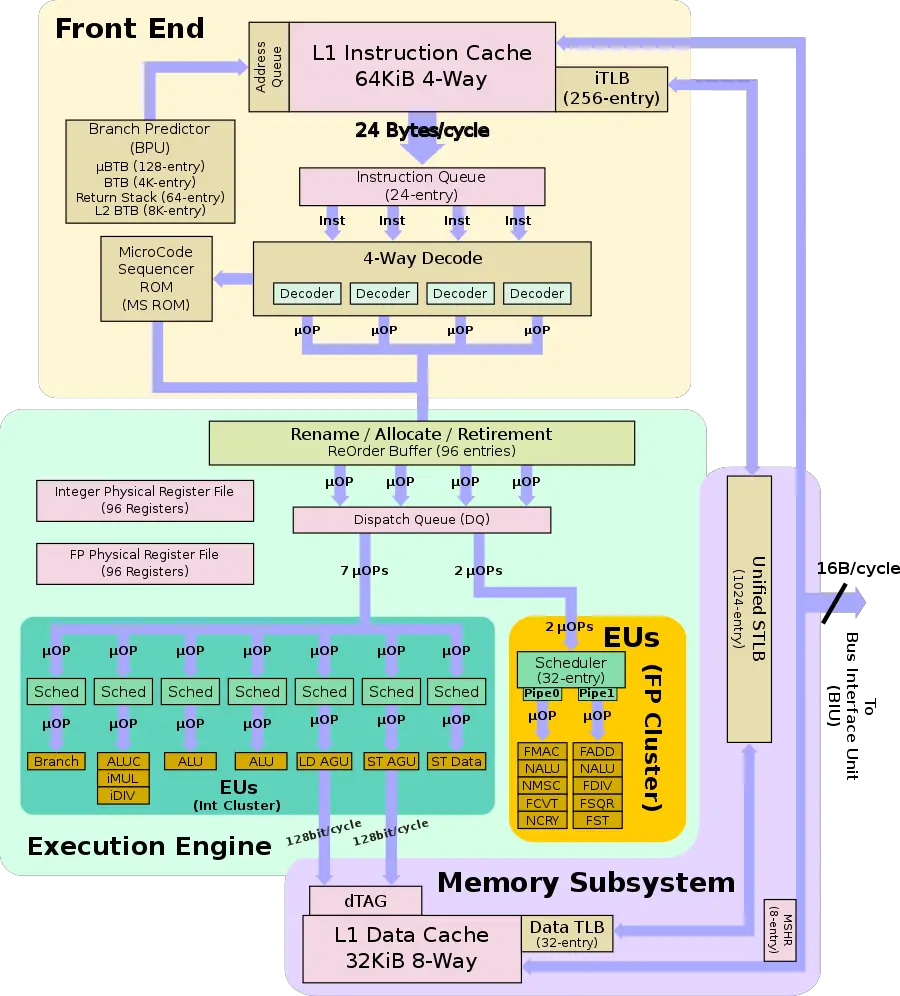
Individual Core
Memory Hierarchy
- Cache
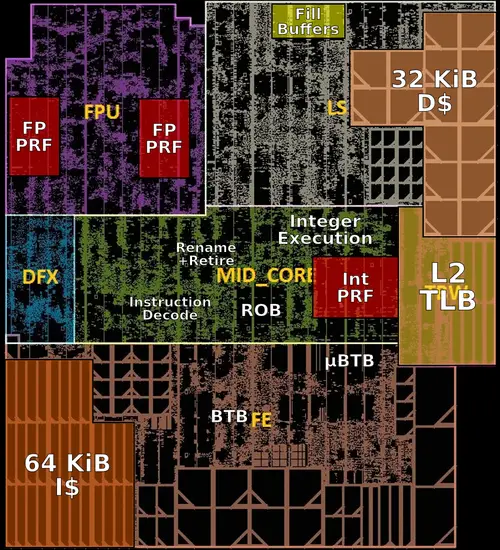
- L1I Cache
- 64 KiB, 4-way set associative
- 128 B line size
- per core
- Parity-protected
- 64 KiB, 4-way set associative
- L1D Cache
- 32 KiB, 8-way set associative
- 64 B line size
- per core
- 4 cycles for fastest load-to-use
- 16 B/cycle load bandwidth
- 16 B/cycle store bandwidth
- 32 KiB, 8-way set associative
- L2 Cache
- 2 MiB, 16-way set associative
- 4x banks (512 KiB each)
- Inclusive of L1
- 22 cycles latency
- 16 B/cycle/CPU bandwidth
- 2 MiB, 16-way set associative
- L1I Cache
Mongoose 1 TLB consists of dedicated L1 TLB for instruction cache (ITLB) and another one for data cache (DTLB). Additionally there is a unified L2 TLB (STLB).
- TLBs
- ITLB
- 256-entry
- DTLB
- 32-entry
- STLB
- 1,024-entry
- Per core
- ITLB
- BPU
- 4K-entry main BTB
- 64-entry µBTB
- 64-entry return stack
Overview
Mongoose 1 was an entirely brand new architecture from the ground up that implemented the ARMv8 ISA. The architecture supports both AArch64 and AArch32 including Thumb modes. The architecture is a quad-core design which was intended to be paired with another low-power ARM IP core.
Core
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Pipeline
Front-end
Fetch & pre-decoding
With the help of the branch predictor, the instructions should already be found in the level 1 instruction cache. The L1I cache is 64 KiB, 4-way set associative and has its own iTLB consisting of 256 entries. Up to 24 bytes are read from it each cycle into the instruction queue which allows them to hide very short branch bubbles. The instruction queue is a slightly more complex component than a simple buffer. The byte stream gets split up into the ARM instructions its made off, including dealing with the various mis-aligned ARM instructions such as in the case of thumb mode.
Decoding
From the instruction queue the instructions are sent to decode. Decode is a 4-way decoder which can handle both the ARM AArch64 and AArch32 instructions. Up to four µOPs are decoded and sent to the re-order buffer.
Micro-Sequencer
For some complex ARM instructions such as the ARMv7 load-store multiples instructions which result in multiple µOPs being emitted, M1 has a side micro-sequencer that will get invoked and emit the appropriate µOPs.
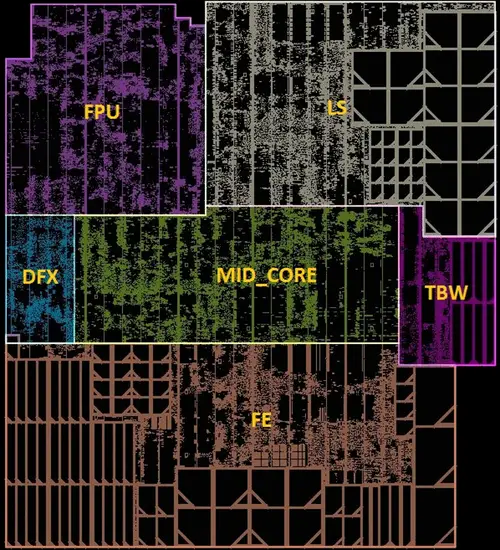
Die
Core Floorplan
Core Cluster Floorplan
References
- Burgess, Brad. "Samsung exynos M1 processor." Hot Chips 28 Symposium (HCS), 2016 IEEE. IEEE, 2016.
| codename | Mongoose 1 + |
| designer | Samsung + |
| full page name | samsung/microarchitectures/m1 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | ARMv8 + |
| manufacturer | Samsung + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | Mongoose 1 + |
| process | 14 nm (0.014 μm, 1.4e-5 mm) + |