From WikiChip
80486 - Microarchitectures - Intel
| Edit Values | |
| 80486 µarch | |
| General Info | |
| Arch Type | CPU |
| Designer | Intel |
| Manufacturer | Intel, AMD |
| Introduction | April 10, 1989 |
| Phase-out | 1995 |
| Process | 1 µm, 800 nm, 600 nm |
| Instructions | |
| ISA | x86-16, x86-32 |
| Succession | |
80486 was the microarchitecture for Intel's 80486 line of microprocessors as a successor to the 80386. Introduced in April of 89, 80486 was initially manufactured using 1 µm process (later 800 nm). For AMD, this microarchitecture was used for their Am486 and Am5x86 families. This architecture was superseded by Intel's P5 in 1992 and K5 in 1994.
History
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Process Technology
| This section is empty; you can help add the missing info by editing this page. |
Architecture
Key changes from 80386
- Testability
- JTAG interface support (Std. 1149.1-1990)
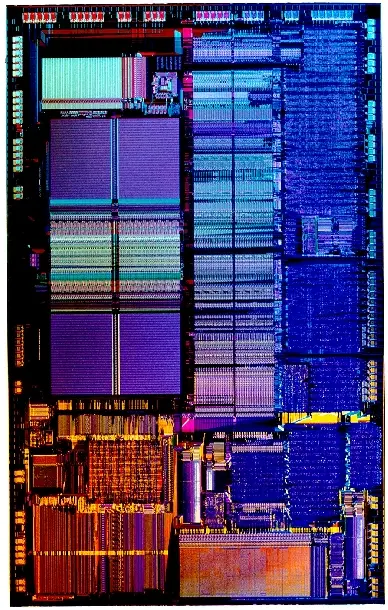
Die Shot
- 1 µm process
- 1,200,000 transistors
Facts about "80486 - Microarchitectures - Intel"
| codename | 80486 + |
| designer | Intel + |
| first launched | April 10, 1989 + |
| full page name | intel/microarchitectures/80486 + |
| instance of | microarchitecture + |
| instruction set architecture | x86-16 + and x86-32 + |
| manufacturer | Intel + and AMD + |
| microarchitecture type | CPU + |
| name | 80486 + |
| phase-out | 1995 + |
| process | 1,000 nm (1 μm, 0.001 mm) +, 800 nm (0.8 μm, 8.0e-4 mm) + and 600 nm (0.6 μm, 6.0e-4 mm) + |