| Buffer Gate
|
| ANSI Symbol
|
|
|
| Functional
|
|
|
| Truth Table
|
| Inputs |
Outputs
|
| A |
Q
|
| 0 |
0
|
| 1 |
1
|
|
|
|
|
|
A buffer, is a basic logic gate that passes its input, unchanged, to its output. It's behavior is the opposite of a NOT gate. The main purpose of a buffer is to regenerate the input, usually using a strong high and a strong low. A buffer has one input and one output; its output always equals its input. Buffers are also used to increase the propagation delay of circuits by driving the large capacitive loads.
Description
A buffer is a very basic active device that generates an output identical to its input input. In most technologies, a buffer is made of two inverter back-to-back. One of the many purposes for a buffer is to generate weak output from non-restoring logic that was used.
Design
Symbolic representation
Buffers are typically drown on schematics using one of a standard symbol. Below are three of the commonly found standard symbols.
Implementations
A buffer can be implemented in variety of of technologies.
CMOS
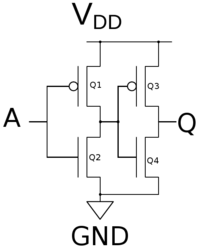
A CMOS buffer gate with one input and one output can be realized as simply two inverters back to back - built out of just 4 gates.
The table on the right shows the states of the four transistors with the various inputs of A.
| Buffer Gate by Transistor
|
| A |
Q1 |
Q2 |
Q3 |
Q4 |
Q
|
| 0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0
|
| 1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1
|
Discrete Chips
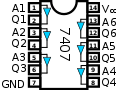
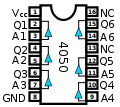
Various buffers/drivers exist chips as well for both 7400 series and 4000 series.
The 7407 is a TTL chip with 14 pins. Two pins are used for VDD and GND, the other 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. The 4050 is a CMOS Hex Buffer with 16 pins. Two pins are used for VDD and GND, 12 pins are used for the 6 independent buffers. Pins 13 and 16 are not connected. Both chips implement the expression QN = AN
4050 CMOS Hex Buffer/Driver