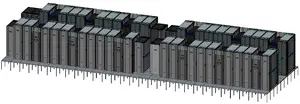
Astra is a petascale ARM supercomputer designed for Sandia National Laboratories expeced to be deployed in mid-2018. This is the first ARM-based supercomputer to exceed 1 petaFLOPS.
History
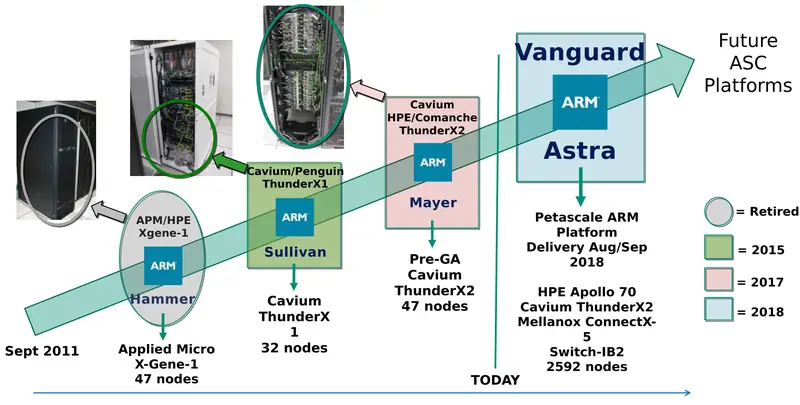
Astra is an ARM-based supercomputer expected to be deployed at Sandia National Laboratories. The computer is one of a series of prototypes commissioned by the U.S. Department of Energy as part of a program that evaluates the feasibility of emerging high-performance computing architectures as production platforms to support NNSA's mission. Specifically, Astra is designed to demonstrate the viability of ARM for DOE NNSA Supercomputing. Astra is the fourth prototype as part of the Vanguard project initiative and is by far the largest ARM-based supercomputer designed to that point.
Overview
Astra is the first ARM-based petascale supercomputer. The system consists of 5,184 Cavium ThunderX2 CN9975 processors with slightly over 1.2 MW power consumption for a peak performance of 2.322 petaFLOPS. Each ThunderX2 CN9975 has 28 cores operating at 2 GHz. Astra has close around 700 terabytes of memory and uses a 3-level fat tree interconnect.
| Components | | | Total Memory |
|---|
| Processors | 5,184
2 x 72 x 36 | | Type | DDR4 | NVMe |
|---|
| Racks | 36 | | Node | 128 GiB | ? |
|---|
| Peak FLOPS | 2.322 petaFLOPS (SP)
1.161 petaFLOPS (DP) | | Astra | 324 TiB | 403 TB |
|---|
Architecture
System
Compute Rack
Compute Node
Socket
Full-node
Bibliography