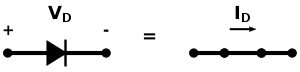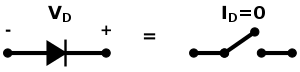(→Ideal Diode) |
(→Ideal Diode) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
:[[File:ideal diode reverse biased.svg|300px]] | :[[File:ideal diode reverse biased.svg|300px]] | ||
| + | The above can be expressed as a step function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> | ||
| + | I_D = | ||
| + | \begin{cases} | ||
| + | 0, & V_d\leq 0 \\ | ||
| + | \infty, & V_d\textgreater 0 | ||
| + | \end{cases} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:electronic components]] | [[Category:electronic components]] | ||
Revision as of 02:22, 6 August 2018
A diode is a two-terminal electronic device that permits the flow of current primarily in one direction.
Overview
A diode is a two-terminal electronic device that allows current to flow in just one direction. When flowing in the forward-biased direction, the diode acts as a wire with very low resistance, creating a short-like condition. Attempting flow in the reverse-biased direction will result in a very high resistance, prohibiting the flow of current, creating an open circuit condition.
Ideal Diode
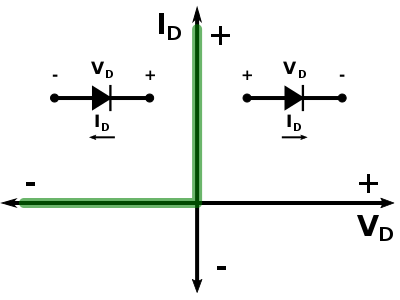
The current-voltage characteristic of an ideal diode is shown below.
The forward resistance () of the ideal diode can be obtained through Ohm's law where the forward voltage () across the diode is 0 (given from the I-V curve above) and the forward current () is any amount of current.
When conducting, an ideal diode acts as a wire with 0 Ω of resistance. In other words, in the forward-biased direction, an ideal diode is a short circuit.
For the reverse-biased resistance (), the reverse voltage () across the diode is any negative value and the reverse current () is 0.
When resisting, an ideal diode acts as a wire with ∞ Ω of resistance. In other words, in the reverse-biased direction, an ideal diode is an open circuit.
The above can be expressed as a step function.
| This article is still a stub and needs your attention. You can help improve this article by editing this page and adding the missing information. |