(tdp) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{title|Thermal Design Power (TDP)}} | {{title|Thermal Design Power (TDP)}} | ||
| − | '''Thermal Design Power''' ('''TDP''') is the amount of [[thermal power]] an [[integrated circuit]] | + | '''Thermal Design Power''' ('''TDP''') is the amount of [[thermal power]] an [[integrated circuit]] generates under T<sub>CASE,MAX</sub>. A TDP of an IC represents that upper point of the thermal profile and is used for determining the appropriate thermal solution design target. TDP is a measure of heat and should not be confused with [[power dissipation]] which is a measure of the rate of [[work]]. |
| + | |||
| + | == Overview == | ||
| + | As an integrated circuit operates, some of the power applied is dissipated in the form of heat. This heat must consequently be removed from the die and out of the system in order to maintain operational temperature range. The ability to remove heat depends on the power dissipation, ambient temperature, and the thermal resistance of the materials used in the construction of the package. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[[File:tdp thermal resistance.svg|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Where the total thermal resistance (ψ<sub>Junction-Ambient</sub>, ψ<sub>JA</sub>) is the thermal resistance of the Junction to Sink (ψ<sub>JS</sub> which also includes ψ<sub>TIM</sub>) and the thermal resistance of the Sink to Ambient (ψ<sub>SA</sub>). Note that this is measured in °C/W. ψ<sub>SA</sub> is a function of the heatsink material, its thermal conductivity, and its geometry. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\Psi_{\text{JA}} = \Psi_{\text{JS}} + \Psi_{\text{SA}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore the maximum allowable resistance can be calculated as | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\Psi_{\text{JA}} = \frac{T_\text{Junction} - T_A}{\text{TDP}}</math> | ||
Revision as of 20:05, 30 March 2018
Thermal Design Power (TDP) is the amount of thermal power an integrated circuit generates under TCASE,MAX. A TDP of an IC represents that upper point of the thermal profile and is used for determining the appropriate thermal solution design target. TDP is a measure of heat and should not be confused with power dissipation which is a measure of the rate of work.
Overview
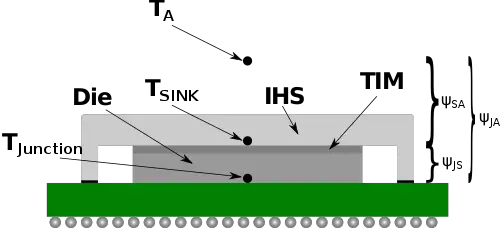
As an integrated circuit operates, some of the power applied is dissipated in the form of heat. This heat must consequently be removed from the die and out of the system in order to maintain operational temperature range. The ability to remove heat depends on the power dissipation, ambient temperature, and the thermal resistance of the materials used in the construction of the package.
Where the total thermal resistance (ψJunction-Ambient, ψJA) is the thermal resistance of the Junction to Sink (ψJS which also includes ψTIM) and the thermal resistance of the Sink to Ambient (ψSA). Note that this is measured in °C/W. ψSA is a function of the heatsink material, its thermal conductivity, and its geometry.
Therefore the maximum allowable resistance can be calculated as